
Concept explainers
Introduction:
Contribution Margin:
Contribution Margin is the profit earned from the sale of per unit and is the sum of turnover of the company less their direct sales costs. The margin is computed to measure the company’s ability to pay the fixed costs with the generated revenue after the payment of direct sales costs.
The Company always prefer a product with high contribution margins as they can easily cover the cost of manufacturing a product and generate a profit.
Requirement-1:
To determine:
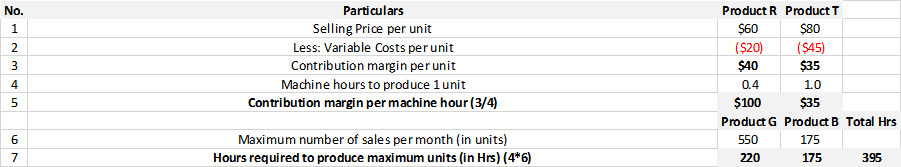
The contribution margin per machine hour of Sung Company that is generated by each product.
Answer to Problem 5BPSB
Solution:
Below table shows the contribution of per machine hour for Project R and Project T.
Explanation of Solution
The contribution margin per machine hour is calculated by using the formula:
Therefore the Contribution Margin per machine hour for the Products R and T are calculated as follows:
Product R:
Given,
Contribution Margin per unit= $40
Machine hours to produce 1 unit= 0.4
Contribution Margin per Unit= $40/0.4=$100
Product T:
Given,
Contribution Margin per unit= $35
Machine hours to produce 1 unit= 1
Contribution Margin per Unit= $35/1=$35
Hence the contribution margin per machine hour for Product R is $100 and Product T is $35.
Requirement-2:
To determine:
The number of units of Products R and Products T produced by the company and total contribution margin , if the company continues to operate with only one shift.
Answer to Problem 5BPSB
Solution:
Below table shows the calculation of units produced for the most profitable sales mix and total contribution margin if the company continues with single shift.
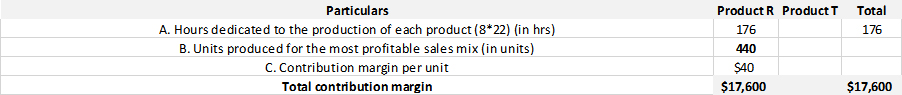
Explanation of Solution
Step-1:
The hours dedicated to the production of each product in single shift = 8 Hours * 22 Working Days
The hours dedicated to the production of each product in single shift = 176 hours
Step-2:
Calculation of Units produced for most profitable sales mix when the company continues
with single shift.
Units Produced for the most profitable sales mix is calculated by using the formula:
Therefore the units produced for the most profitable sales mix=176/0.4=440 units
Step-3:
Calculation of contribution margin:
The contribution margin is computed by using the formula below:
Therefore the contribution margin of the product mix =440 units*$40=$17,600.
Hence the total units produced will be 440 units if the company operates in single shift of 8 hours for 22 working days and its total contribution margin is $17,600.
Requirement-3a:
To determine:
The number of units of Product R and T produced by the company and total contribution margin if the company adds another shift in addition to 8 hours.
Answer to Problem 5BPSB
Solution:
Below table shows the number of units produced by the company when it adds additional shift, total contribution margin in respect to change of shift.

Explanation of Solution
Step-1:
Hours dedicated for the production of products is done based on the ratio of maximum sales unit and machine hours to produce each unit.
Hours dedicated for the production of Product R= 550*0.4=220 hours
Total hours available after adding additional shift=22*16=352 hours
Hours dedicated for the production of Product T= Total hours available-Hours dedicated for the production of Product R
Hours dedicated for the production of Product T=352-220=132 hours
Step-2:
Calculation of Units produced for most profitable sales mix when the company adds additional shift:
Product R:
Units produced for most profitable sales mix =220/0.4=550 Units
Product T:
Units produced for most profitable sales mix =132/1=132 Units
Step-3:
Calculation of Total Contribution Margin:
The contribution margin is computed by using the formula below:
Units produced for the most profitable sales mix*Contribution margin per unit
Contribution Margin for Product R:
Units produced for the most profitable sales mix: 550 Units
Contribution margin per unit: $40
Therefore the contribution margin of Product R is 550 units*$40=$22,000.
Contribution Margin for Product T:
Units produced for the most profitable sales mix: 132 Units
Contribution margin per unit: $35
Therefore the contribution of Product T is 132 units*$35=$4,620.
Therefore the total contribution margin will be $22,000+$4,620=$26,620.
Requirement-3b:
To discuss:
The company whether to prefer adding new shift in addition to existing single shift of 8 hours.
Answer to Problem 5BPSB
Solution:
Yes, the company should add the new shift in addition to the existing shift of 8 hours.
Explanation of Solution
Increase in additional shift of 8 hours per day promotes the increase in productivity of the Sung Company to 682 Units compared to productivity of 440 units when it operates in single shift.
Requirement-4:
To discuss:
The company whether to pursue the marketing strategy by spending $4,500 additional costs to increase the maximum sales to 675 units of Product R by doubling the shift.
Answer to Problem 5BPSB
Solution:
No, the company should not pursue this marketing strategy with additional costs as this leads to the operating loss of the company.
Explanation of Solution
Below table shows the calculation for products by doubling the shifts and increasing the marketing costs by $4,500 to increase the maximum sales of Product R to 675 units.
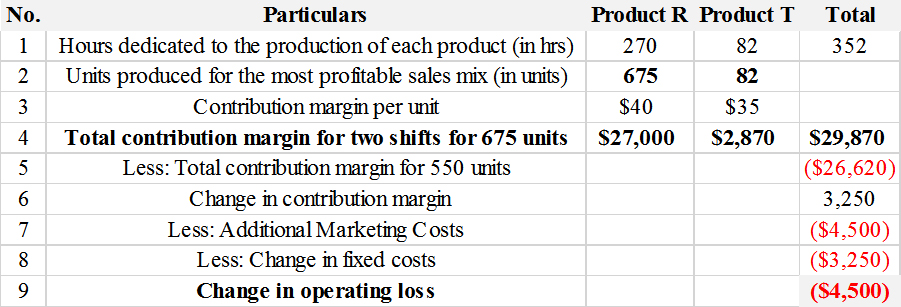
Hours dedicated for the production of Product R= 675*0.4=270 hours
Total hours available after adding additional shift=22*16=352 hours
Hours dedicated for the production of Product T= Total hours available-Hours dedicated for the production of Product R
Hours dedicated for the production of Product T=352-270=82 hours
There is an operating loss of sales mix for the company of $4,500 and hence the idea of doubling the shift and spending additional costs for marketing to increase sales is not advisable to the management to proceed with.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Fundamental Accounting Principles -Hardcover
- Nonearrow_forwardAtwater Chemicals produces an engine additive for machinery. The additive is produced by adding various ingredients to a petroleum-based lubricant. Atwater purchases the lubricant from two suppliers, Woodlawn Petroleum and Spokane Chemicals. The quality of the final product depends directly on the quality of the lubricant. If the lubricant is "off," Atwater has to dispose of the entire batch. Because all lubricant can be "off," Atwater uses a measure it calls the “yield,” which is computed as Yield = Good output ÷ Input where the output and input are both measured in barrels. As a benchmark, Atwater expects to get 12 barrels of good output for every 16 barrels of lubricant purchased for a yield of 75 percent (= 12 barrels of output ÷ 16 barrels of lubricant). Data on the two suppliers for the past year follow: Woodlawn Petroleum Spokane Chemicals Total Total inputs purchased (barrels) 5,760 3,600 9,360 Good output (barrels) 3,744 3,096 6,840 Average price (per barrel) $ 121.00 $…arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- Watko Entertainment Systems (WES) buys audio and video components for assembling home entertainment systems from two suppliers, Bacon Electronics and Hessel Audio and Video. The components are delivered in cartons. If the cartons are delivered late, the installation for the customer is delayed. Delayed installations lead to contractual penalties that call for WES to reimburse a portion of the purchase price to the customer. During the past quarter, the purchasing and delivery data for the two suppliers showed the following: Bacon Hessel Total Total purchases (cartons) 5,000 3,000 8,000 Average purchase price (per carton) $ 168 $ 184 $ 174 Number of deliveries 40 20 60 Percentage of cartons delivered late. 30% 15% 25% The Accounting Department recorded $241,800 as the cost of late deliveries to customers. Required: Assume that the average quality, measured by the percentage of late deliveries, and prices from the two companies will continue as in the past. Also…arrow_forwardWhat is the amount of cash elmont would receive from the sale?arrow_forwardWhat is its net income or loss ?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





