Concepts of Genetics Plus Mastering Genetics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (12th Edition) (What's New in Genetics)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134811390
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino, Darrell Killian
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 29ESP
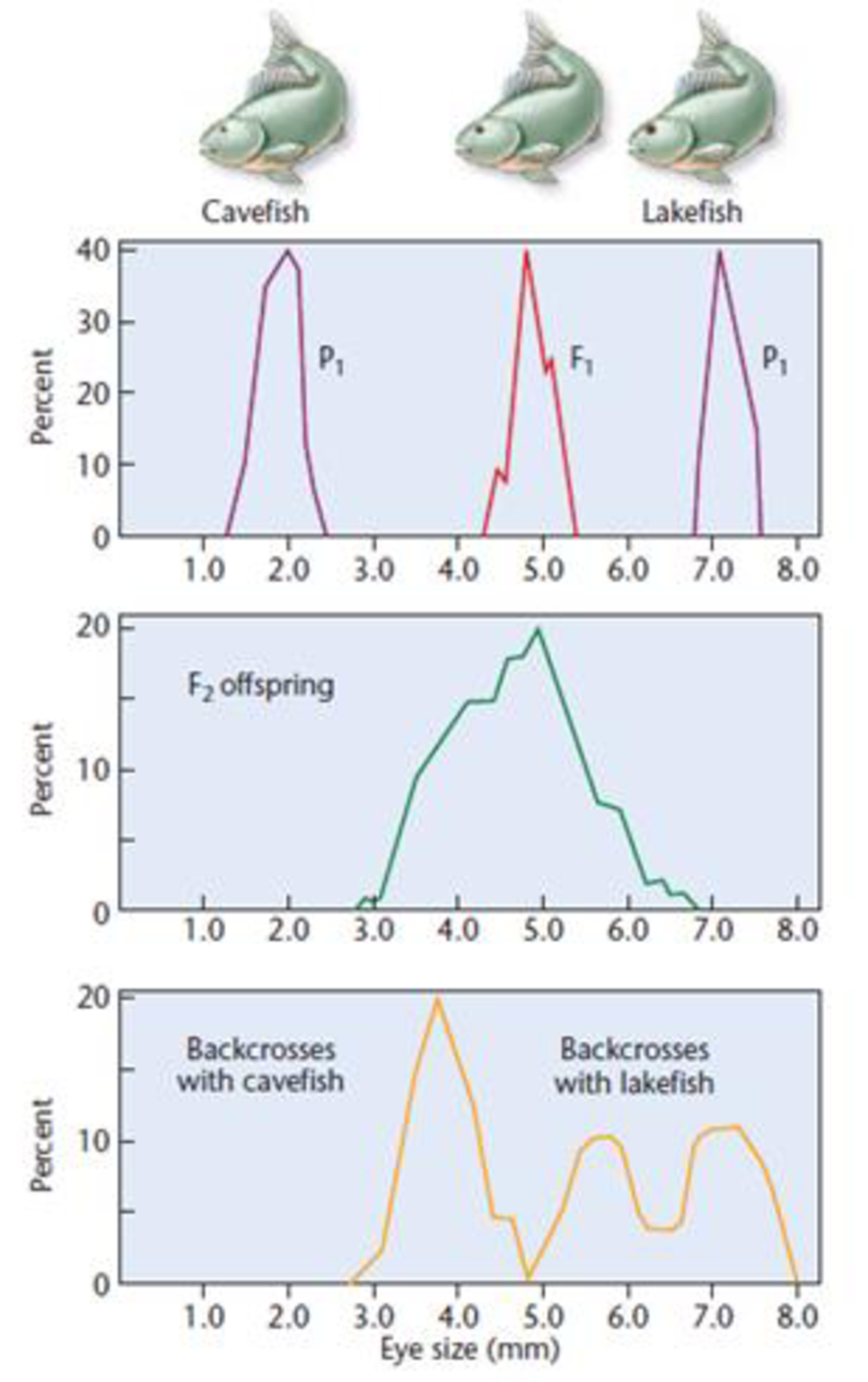
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F1 hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F1 × F1 cross and those from backcrosses (F1 × cavefish and F1 × lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens’s results and respond to the following questions:
- (a) Based strictly on the F1 and F2 results of Wilkens’s initial crosses, what possible explanation concerning the inheritance of eye size seems most feasible?
- (b) Based on the results of the F1 backcross with cavefish, is your explanation supported? Explain.
- (c) Based on the results of the F1 backcross with lakefish, is your explanation supported? Explain.
- (d) Wilkens examined about 1000 F2 progeny and estimated that 6–7 genes are involved in determining eye size. Is the
sample size adequate to justify this conclusion? Propose an experimental protocol to test the hypothesis. - (e) A comparison of the embryonic eye in cavefish and lakefish revealed that both reach approximately 4 mm in diameter. However, lakefish eyes continue to grow, while cavefish eye size is greatly reduced. Speculate on the role of the genes involved in this problem.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
would this be considered a novel protein and if not how can I fix it so it is and can you draw the corrections please
In as much detail as possible, hand draw a
schematic diagram of the hypothalamic-pituitary-
gonad (HPG) axis in the human male. Be sure to
include all the relevant structures and hormones.
You must define all abbreviations the first time
you use them. Please include (and explain) the
feedback loops.
A negligence action was brought by a mother against a hospital on behalf of her minor daughter. It alleged that when the mother was 13 years of age, the hospital negligently transfused her with Rh-positive blood. The mother's Rh-negative blood was incompatible with and sensitized by the Rh-positive blood. The mother discovered her condition 8 years later during a routine blood screening ordered by her healthcare provider in the course of prenatal care. The resulting sensitization of the mother's blood allegedly caused damage to the fetus, resulting in physical defects and premature birth.
Did a patient relationship with the transfusing hospital exist?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics Plus Mastering Genetics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (12th Edition) (What's New in Genetics)
Ch. 25 - A homozygous plant with 20-cm-diameter flowers is...Ch. 25 - The following table shows measurements for fiber...Ch. 25 - The following cable gives the percentage of twin...Ch. 25 - At an interview with a genetic counselor, a couple...Ch. 25 - Prob. 2CSCh. 25 - At an interview with a genetic counselor, a couple...Ch. 25 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on a...Ch. 25 - CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list...Ch. 25 - Define the following: (a) polygenic, (b) additive...Ch. 25 - A dark-red strain and a white strain of wheat are...
Ch. 25 - Height in humans depends on the additive action of...Ch. 25 - An inbred strain of plants has a mean height of 24...Ch. 25 - Erma and Harvey were a compatible barnyard pair,...Ch. 25 - In the following table, average differences of...Ch. 25 - What kind of heritability estimates (broad sense...Ch. 25 - List as many human traits as you can that are...Ch. 25 - Corn plants from a test plot are measured, and the...Ch. 25 - The following variances were calculated for two...Ch. 25 - The mean and variance of plant height of two...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14PDQCh. 25 - Prob. 15PDQCh. 25 - In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies...Ch. 25 - Prob. 17PDQCh. 25 - Prob. 18PDQCh. 25 - In a population of 100 inbred, genotypically...Ch. 25 - Many traits of economic or medical significance...Ch. 25 - A 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant,...Ch. 25 - In a cross between a strain of large guinea pigs...Ch. 25 - Type A1B brachydactyly (short middle phalanges) is...Ch. 25 - In a series of crosses between two true-breeding...Ch. 25 - Students in a genetics laboratory began an...Ch. 25 - Prob. 26ESPCh. 25 - Canine hip dysplasia is a quantitative trait that...Ch. 25 - Floral traits in plants often play key roles in...Ch. 25 - In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forwardState the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.arrow_forwardDiagram of check cell under low power and high powerarrow_forward
- a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?arrow_forwardWhat is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Where did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How do Plants Handle Stress?; Author: Alex Dainis;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TYsnveEHqec;License: Standard Youtube License