
Concept explainers
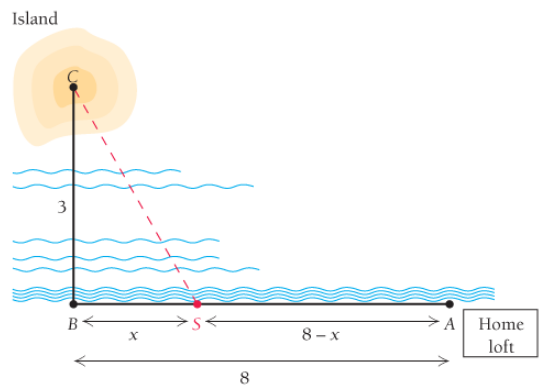
Life science: flights of homing pigeons. It is known that homing pigeons tend to avoid flying over water in the daytime, perhaps because downdrafts of air over water make flying difficult. Suppose a homing pigeon is released on an island at point C, which is 3 mi directly out in the water from a point B on shore. Point B is 8 mi downshore from the pigeon’s home loft at point A. Assume that a pigeon flying over water uses energy at a rate 1.28 times the rate over land. Toward what point S downshore from A should the pigeon fly in order to minimize the total energy required to get to the home loft at A? Assume that
S is 4.245 mi downshore from A.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Calculus and Its Applications (11th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
- 15. Please solve this and show each and every step please. PLEASE no chatgpt can I have a real person solve it please!! I am stuck. I am doing pratice problems and I do not even know where to start with this. The question is Please compute the indicated functional value.arrow_forwardUse a graph of f to estimate lim f(x) or to show that the limit does not exist. Evaluate f(x) near x = a to support your conjecture. Complete parts (a) and (b). x-a f(x)= 1 - cos (4x-4) 3(x-1)² ; a = 1 a. Use a graphing utility to graph f. Select the correct graph below.. A. W → ✓ Each graph is displayed in a [- 1,3] by [0,5] window. B. in ✓ ○ C. und ☑ Use the graphing utility to estimate lim f(x). Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. x-1 ○ A. The limit appears to be approximately ☐ . (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) B. The limit does not exist. b. Evaluate f(x) for values of x near 1 to support your conjecture. X 0.9 0.99 0.999 1.001 1.01 1.1 f(x) ○ D. + ☑ (Round to six decimal places as needed.) Does the table from the previous step support your conjecture? A. No, it does not. The function f(x) approaches a different value in the table of values than in the graph, after the approached values are rounded to the…arrow_forwardx²-19x+90 Let f(x) = . Complete parts (a) through (c) below. x-a a. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) equal a finite number? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. x→a+ ○ A. a= (Type an integer or a simplified fraction. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) B. There are no values of a for which the limit equals a finite number. b. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) = ∞o? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. x→a+ A. (Type integers or simplified fractions) C. There are no values of a that satisfy lim f(x) = ∞. + x-a c. For what values of a, if any, does lim f(x) = -∞0? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. x→a+ A. Either a (Type integers or simplified fractions) B.arrow_forwardSketch a possible graph of a function f, together with vertical asymptotes, that satisfies all of the following conditions. f(2)=0 f(4) is undefined lim f(x)=1 X-6 lim f(x) = -∞ x-0+ lim f(x) = ∞ lim f(x) = ∞ x-4 _8arrow_forwardDetermine the following limit. lim 35w² +8w+4 w→∞ √49w+w³ 3 Select the correct choice below, and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. ○ A. lim W→∞ 35w² +8w+4 49w+w3 (Simplify your answer.) B. The limit does not exist and is neither ∞ nor - ∞.arrow_forwardCalculate the limit lim X-a x-a 5 using the following factorization formula where n is a positive integer and x-➡a a is a real number. x-a = (x-a) (x1+x-2a+x lim x-a X - a x-a 5 = n- + xa an-2 + an−1)arrow_forwardThe function s(t) represents the position of an object at time t moving along a line. Suppose s(1) = 116 and s(5)=228. Find the average velocity of the object over the interval of time [1,5]. The average velocity over the interval [1,5] is Vav = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardFor the position function s(t) = - 16t² + 105t, complete the following table with the appropriate average velocities. Then make a conjecture about the value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1. Time Interval Average Velocity [1,2] Complete the following table. Time Interval Average Velocity [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] [1,2] [1, 1.5] [1, 1.1] [1, 1.01] [1, 1.001] ப (Type exact answers. Type integers or decimals.) The value of the instantaneous velocity at t = 1 is (Round to the nearest integer as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the following limit or state that it does not exist. Assume b is a fixed real number. (x-b) 40 - 3x + 3b lim x-b x-b ... Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (x-b) 40 -3x+3b A. lim x-b x-b B. The limit does not exist. (Type an exact answer.)arrow_forwardx4 -289 Consider the function f(x) = 2 X-17 Complete parts a and b below. a. Analyze lim f(x) and lim f(x), and then identify the horizontal asymptotes. x+x X--∞ lim 4 X-289 2 X∞ X-17 X - 289 lim = 2 ... X∞ X - 17 Identify the horizontal asymptotes. Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer box(es) to complete your choice. A. The function has a horizontal asymptote at y = B. The function has two horizontal asymptotes. The top asymptote is y = and the bottom asymptote is y = ☐ . C. The function has no horizontal asymptotes. b. Find the vertical asymptotes. For each vertical asymptote x = a, evaluate lim f(x) and lim f(x). Select the correct choice and, if necessary, fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. earrow_forwardExplain why lim x²-2x-35 X-7 X-7 lim (x+5), and then evaluate lim X-7 x² -2x-35 x-7 x-7 Choose the correct answer below. A. x²-2x-35 The limits lim X-7 X-7 and lim (x+5) equal the same number when evaluated using X-7 direct substitution. B. Since each limit approaches 7, it follows that the limits are equal. C. The numerator of the expression X-2x-35 X-7 simplifies to x + 5 for all x, so the limits are equal. D. Since x²-2x-35 X-7 = x + 5 whenever x 7, it follows that the two expressions evaluate to the same number as x approaches 7. Now evaluate the limit. x²-2x-35 lim X-7 X-7 = (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forwardA function f is even if f(x) = f(x) for all x in the domain of f. If f is even, with lim f(x) = 4 and x-6+ lim f(x)=-3, find the following limits. X-6 a. lim f(x) b. +9-←x lim f(x) X-6 a. lim f(x)= +9-←x (Simplify your answer.) b. lim f(x)= X→-6 (Simplify your answer.) ...arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning  Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Use of ALGEBRA in REAL LIFE; Author: Fast and Easy Maths !;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_PbWFpvkDc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYCompound Interest Formula Explained, Investment, Monthly & Continuously, Word Problems, Algebra; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P182Abv3fOk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYApplications of Algebra (Digit, Age, Work, Clock, Mixture and Rate Problems); Author: EngineerProf PH;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y8aJ_wYCS2g;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Use of ALGEBRA in REAL LIFE; Author: Fast and Easy Maths !;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9_PbWFpvkDc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYCompound Interest Formula Explained, Investment, Monthly & Continuously, Word Problems, Algebra; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P182Abv3fOk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BYApplications of Algebra (Digit, Age, Work, Clock, Mixture and Rate Problems); Author: EngineerProf PH;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y8aJ_wYCS2g;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
