
a) N, N-Dimethylaniline
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name N, N-Dimethylaniline.
Answer to Problem 48AP
The IUPAC names given for the
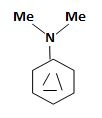
Explanation of Solution
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
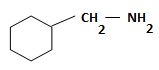
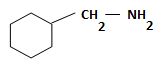
b) (Cyclohexylmethyl) amine.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (Cyclohexylmethyl) amine.
Answer to Problem 48AP
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Explanation of Solution
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
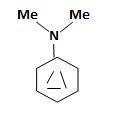
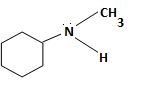
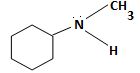
c) N-Methylcyclohexylamine
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name N-Methylcyclohexylamine.
Answer:
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Explanation:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
Conclusion:
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Answer to Problem 48AP
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.

Explanation of Solution
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.

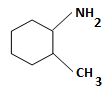
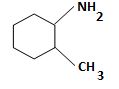
d) (2-Methylcyclohexyl) amine.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (2-Methylcyclohexyl) amine.
Answer to Problem 48AP
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Explanation of Solution
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
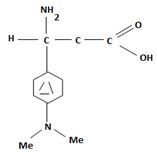
e) 3-(N, N-Dimethylamino)propanoic acid.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 3-(N, N-Dimethylamino)propanoic acid.
Answer to Problem 48AP
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Explanation of Solution
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound – the alkene name ends with the suffix –ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
The IUPAC names given for the amines have the following structures.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- 7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forwardIndicate the compound formula: dimethyl iodide (propyl) sulfonium.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
