
(a)
Interpretation:
For each of the given bifunctional compounds, the cyclic hemiacetal formed when treated with aqueous acid should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
- Hemiacetal are formed for the compound having both hydroxyl group and
aldehyde group in acidic condition. - The oxygen atom in the –OH group of compound attacks the carbonyl group of the same compound, thereby a ring is formed by the carbon atoms and oxygen atom of –OH group with incorporating into the ring.
To draw: the hemiacetal formed for the given molecule when treated with aqueous acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
For each of the given bifunctional compounds, the cyclic hemiacetal formed when treated with aqueous acid should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
- Hemiacetal are formed for the compound having both hydroxyl group and aldehyde group in acidic condition.
- The oxygen atom in the –OH group of compound attacks the carbonyl group of the same compound, thereby a ring is formed by the carbon atoms and oxygen atom of –OH group with incorporating into the ring.
To draw: the hemiacetal formed for the given molecule when treated with aqueous acid.
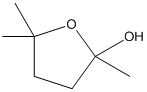
(c)
Interpretation:
For each of the given bifunctional compounds, the cyclic hemiacetal formed when treated with aqueous acid should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
- Hemiacetal are formed for the compound having both hydroxyl group and aldehyde group in acidic condition.
- The oxygen atom in the –OH group of compound attacks the carbonyl group of the same compound, thereby a ring is formed by the carbon atoms and oxygen atom of –OH group with incorporating into the ring.
To draw: the hemiacetal formed for the given molecule when treated with aqueous acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
For each of the given bifunctional compounds, the cyclic hemiacetal formed when treated with aqueous acid should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
- Hemiacetal are formed for the compound having both hydroxyl group and aldehyde group in acidic condition.
- The oxygen atom in the –OH group of compound attacks the carbonyl group of the same compound, thereby a ring is formed by the carbon atoms and oxygen atom of –OH group with incorporating into the ring.
To draw: the hemiacetal formed for the given molecule when treated with aqueous acid.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (2 SEM.)
- 2. Please consider the two all 'cis' isomers of trimethylcyclohexane drawn below. Draw the two chair conformers of each stereoisomer below (1 and 2) and calculate their torsional interaction energies in order to identify the lower energy conformer for each stereoisomer. Based on your calculations, state which of the two stereoisomers 1 and 2 is less stable and which is more stable. [1,3-diaxial CH3 CH3 = 3.7kcal/mol; 1,3-diaxial CH3 H = 0.88kcal/mol; cis-1,2 (axial:equatorial) CH3 CH3 = 0.88kcal/mol; trans-1,2-diequatorial CH3 CH3 = 0.88kcal/mol) all-cis-1,2,3- 1 all-cis-1,2,4- 2arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism by which the 1,4 product is created? Please draw it by hand with arrows and stuff.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





