
Concept explainers
a) CH3CHNH2 or CH3CH2 CONH2
Interpretation:
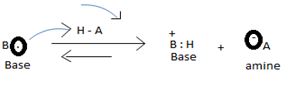
The levis concept (due to GN levis) which is the most general concept of a base defines a base as any species which is sufficient electron rich and contains at last one or more unshared electron pains available for donation, which subsequent electronic interaction or an apparent band formation with an acid, an electron deficient species.
Answer:
Ethylamine CH3CH2NH2 is more basic the amide (ethylamide) CH3CH2CoNH2.
Explanation:
Thus basicity is an attribute defecting the extent of overlapping of this done electron pain donation. Quantitative it is measured by this extent; and also, any structural or chemical environmental factor that tends to increase or active increase the extent of available of donation of this electron pain(s) to a nembutal acid is acid to enhance the basicity of a levis base.
On the basis of the above, we examine what structure or other factor in the two given molecules amide and amine lead then to the bases at all in the fast; and what facter causes them to be which laser copying strengths.
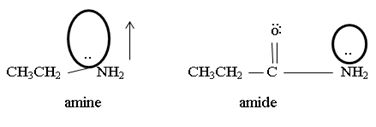
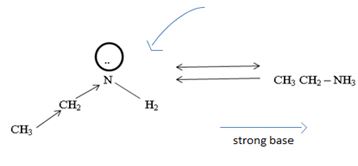
1) Fact I, Both are nitrogenous bases ie the basicity is due, intermediate to the problem of an unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom of the –NH2-amine group. Thus more available then electron pair of on incident acid, the stronger is the base. Closely, the base strength all the diminished of any factor causes this electron pair to the less available for be genetics within appropriate acid.
2) Fact II, → considered ethylamine and ethanamide.
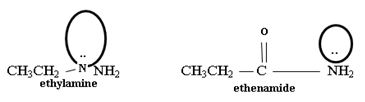
Ethanamide is much stronger base because of the electron releasing positive inductive +g effect of the ethyl (alkyl) group makes the N lone pair more available to any incident proton H+.
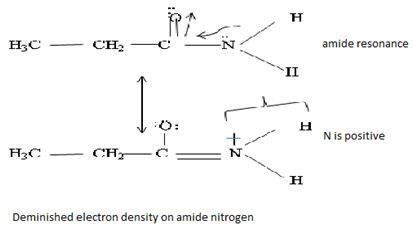
Havens is ethanamide, true is an incident stability caused by delocalization of the nitrogen line-pair electron through orbital overall with the carbonyl group. In resonance terms, amides are more states, and also then reactive than amides because this are hybrids of two resonance forms this amide resonance stabilization is lost when the nitrogen atom is protonated. So petroleum is disfavored. The following structural resonance form and electron density diagrams shown a significants reduced electron density on the amide nitrogen.
Oxygen – pauling electrons acids = 3.44
Nitrogen – pauling electrons acids = 3.04
Further the very electrons acid values of N is O, specifies the electron delocalization form N to O in amides, and consolidate the structure resonance forms.
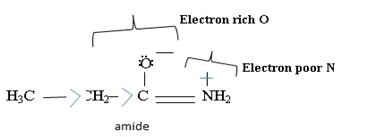
Thus, the very factor that lands amides then reactive also causes their reduced basicity than
Conclusion:
Form the above teach of relative basicity, it comes urtherit saying that population bile basics acids are governed by structural features in substances and chemical environments.
b) NCOH or CH3NH2
Interpretation:
As the outset, let it be said that acidity and basicity are measures of equilibrium (
Sodium hyduxide is a potentates much stronger base than methylamine.
Explanation:
The stronger this officials the more is the ease of proton uptake, and more is the hold on this proton; thus the stronger the species as a base.
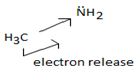
Organic bases are potencies much stronger bases than organic bases, v3 amines. Thus NCOH is a much stronger base then CH3NH2 an methylamine CH3NH2, the basicity is attributed to the presence of the unshared electron paid on the nitrogen of the amino group. The extent of available of this electron pair is increased by the inductive release of electron dentist by the methyl group. This miles methylamine strong organic base, but ten, then NAOH, the inorganic base.
Conclusion:
Sodium hyduxide is a potentates much stronger base than methylamine.
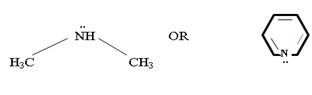
c) CH3NHCH3 or pyridine
Interpretation:
In organic bases, the basics is exhibited to the extent of available of a lone pair(s) of electron an nitrogen atom of the amino group, the more available then electron pair for uptake of a proton, the stronger the base.
Explanation:
In dimethyl amine, inductive release of electrons by the two methyl groups increase the electron density on the nitrogen atom to an appropriate degree. The compound is thus a very strong base, convenes, in the heterocyclic amine pyridine, the line electron pair on nitrogen is lost by amides delocalization into the benzene ring and nitrogen causes c positive change. Thus it is a very week base.
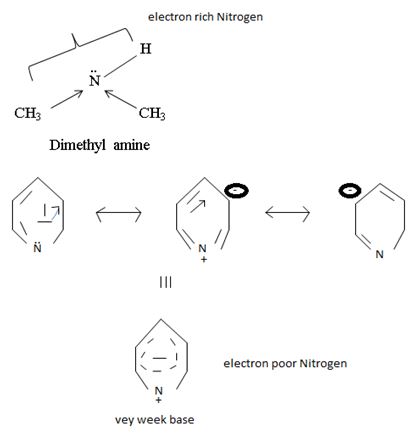
Conclusion:
Basicity in organic amines thus is a measure of the extent of availability of an unshared electron pair on the amines stronger amines than both
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- Problem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forwardPredict the organic product of Y that is formed in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic product. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPlease choose the best reagents to complete the following reactionarrow_forward
- Problem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forwardProblem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic side productarrow_forward
- predict the product formed by the reaction of one mole each of cyclohex-2-en-1-one and lithium diethylcuprate. Assume a hydrolysis step follows the additionarrow_forwardPlease handwriting for questions 1 and 3arrow_forwardIs (CH3)3NHBr an acidic or basic salt? What happens when dissolved in aqueous solution? Doesn't it lose a Br-? Does it interact with the water? Please advise.arrow_forward
