
Concept explainers
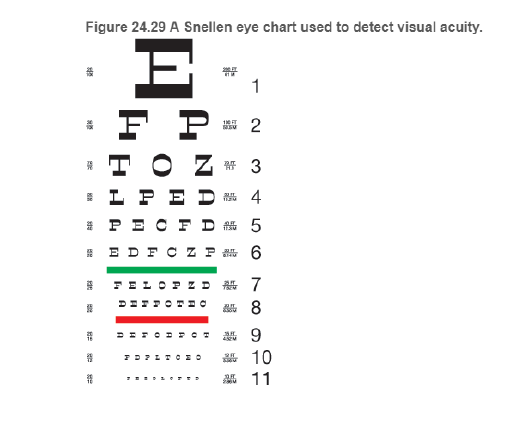
BIO What is 20/20 vision? Vision is often measured using the Snellen eye chart, devised by Dutch ophthalmologist Herman Snellen in 1862 (see Figure 24.29). With normal vision (20/20 vision), you can distinguish a letter that is 8.8 mm high from other letters of similar height at a distance of 6.1 m (20 ft) (the Snellen chart in the figure is smaller than normal size). If your vision is 20/40 the letters must be twice as high to be distinguishable. Alternatively, a person with 20/40 vision could distinguish letters from 20 ft that a person with 20/20 vision can distinguish at 40 ft. Someone with 20/60 vision could distinguish letters at 20 ft that someone with 20/20 vision could distinguish at 60 ft.
Does the Rayleigh criterion limit visual resolution? Assume that the eye's pupil is 5.0 mm in diameter for 500-nm light The Rayleigh criterion angular deflection for such light entering the eye's pupil is
If the Rayleigh criterion limited visual resolution, then from a distance of 6.1 m, you should be able to distinguish details in shapes of size
What is the visual acuity of a person with 20/20 vision mainly limited by?
a. The Rayleigh criterion
b. Chromatic aberration
c. Focal length of the eye lens
d. Diameter of the eye's pupil
e. The density of cones and rods
f. A combination of these factors
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
Pearson eText for College Physics: Explore and Apply -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- 1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device. 2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use. High Aspect Ratio Trenches Undoped Si Wafer P-doped Si 3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you use and why? 4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful. 5. You are given a composite…arrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forward
- Another worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forward
- An L−R−C series circuit has R= 280 Ω . At the frequency of the source, the inductor has reactance XLL= 905 Ω and the capacitor has reactance XC= 485 Ω . The amplitude of the voltage across the inductor is 445 V . What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor and the capacitor? What is the voltage amplitude of the source? What is the rate at which the source is delivering electrical energy to the circuit?arrow_forwardA 0.185 H inductor is connected in series with a 98.5 Ω resistor and an ac source. The voltage across the inductor is vL=−(12.5V)sin[(476rad/s)t]vL. Derive an expression for the voltage vR across the resistor. Express your answer in terms of the variables L, R, VL (amplitude of the voltage across the inductor), ω, and t. What is vR at 2.13 ms ? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA worker lifts a box under the following conditions:Horizontal distance (H): 30 cmInitial height (V): 60 cmVertical travel (D): 50 cmTorso rotation (A): 30°Frequency: 3 times/minute for 1 hourGrip: Good Question:What is the RWL for this task?What does this value mean in terms of occupational safety?arrow_forward
- Can someone helparrow_forwardCan someone help mearrow_forward3. Four identical small masses are connected in a flat perfect square. Rank the relative rotational inertias (IA, IB, IC) about the three axes of rotation shown. Axes A and B are in the plane of the square, and axis C is perpendicular to the plane, through mass m1. ΙΑ IB m2 m1 m3 Ic m4 (a) IAarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





