
Concept explainers
(a)
Construct ray diagrams to locate the images and estimate the image height in each of the following cases.
A 10-cm-tan object located 5 cm in front of a spherical convex mirror with a radius of curvature of 20 cm.
Answer to Problem 56QAP
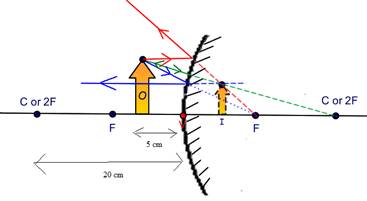
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculations:
Conclusion:
(b)
Construct ray diagrams to locate the images and estimate the image height in each of the following cases.
A 10-cm-tall object located 10 cm in front of a spherical convex mirror with a radius of curvature of 20 cm.
Answer to Problem 56QAP
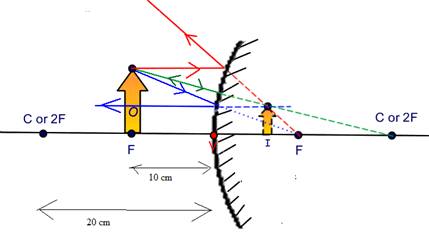
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculations:
Conclusion:
(c)
Construct ray diagrams to locate the images and estimate the image height in each of the following cases.
A 10-cm-tall object located 20 cm in front of a spherical convex minor with a radius of curvature of 20 cm.
Answer to Problem 56QAP
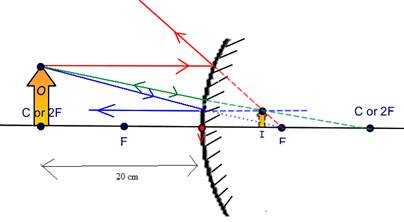
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Calculations:
Conclusion:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Sketch a sign wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardSketch a sine wave depicting 3 seconds of wave activity for a 5 Hz tone.arrow_forwardThe drawing shows two long, straight wires that are suspended from the ceiling. The mass per unit length of each wire is 0.050 kg/m. Each of the four strings suspending the wires has a length of 1.2 m. When the wires carry identical currents in opposite directions, the angle between the strings holding the two wires is 20°. (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing the forces that act on the right wire with respect to the x axis. Account for each of the strings separately. (b) What is the current in each wire? 1.2 m 20° I -20° 1.2 marrow_forward
- 2). How much energy is stored in the 50-μF capacitor when Va - V₁ = 22V? 25 µF b 25 µF 50 µFarrow_forward9). A series RC circuit has a time constant of 1.0 s. The battery has a voltage of 50 V and the maximum current just after closing the switch is 500 mA. The capacitor is initially uncharged. What is the charge on the capacitor 2.0 s after the switch is closed? R 50 V a. 0.43 C b. 0 66 C c. 0.86 C d. 0.99 C Carrow_forward1). Determine the equivalent capacitance of the combination shown when C = 12 pF. +11/20 2C C Carrow_forward
- 3). When a capacitor has a charge of magnitude 80 μC on each plate the potential difference across the plates is 16 V. How much energy is stored in this capacitor when the potential difference across its plates is 42 V? a. 1.0 mJ b. 4.4 mJ c. 3.2 mJ d. 1.4 mJ e. 1.7 mJarrow_forward5). A conductor of radius r, length & and resistivity p has resistance R. It is melted down and formed into a new conductor, also cylindrical, with one fourth the length of the original conductor. The resistance of the new conductor is a. 1 R 161 b. 1 R C. R d. 4R e. 16Rarrow_forward8). Determine the magnitude and sense (direction) of the current in the 10-Q2 resistor when I = 1.8 A. 30 V L 50 V 10 Ω 20 Ω a. 1.6 A right to left b. 1.6 A left to right C. 1.2 A right to left d. 1.2 A left to right e. 1.8 A left to right R PGarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





