
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780135245033
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 47EAP
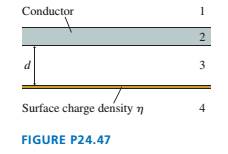
FIGURE P24.47 shows an infinitely wide conductor parallel
to and distance d from an infinitely wide plane of charge with
surface charge density
regions 1 to 4?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls
4.4 A man is dragging a trunk up the
loading ramp of a mover's truck. The
ramp has a slope angle of 20.0°, and
the man pulls upward with a force F
whose direction makes an angle of 30.0°
75.0°
with the ramp (Fig. E4.4). (a) How large a force F is necessary for the
component Fx parallel to the ramp to be 90.0 N? (b) How large will the
component Fy perpendicular to the ramp be then?
Figure E4.4
30.0
20.0°
1.
*
A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle e, with an initial velocity
magnitude v., from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile lands on the tabletop
a horizontal distance R (the "range") away from where it left the launcher. Set this
up as a formal problem, and solve for vo (i.e., determine an expression for Vo in
terms of only R, 0., and g). Your final equation will be called Equation 1.
Chapter 24 Solutions
MASTERPHYS:KNIGHT'S PHYSICS ACCESS+WKB
Ch. 24 - Suppose you have the uniformly charged cube in...Ch. 24 - FIGURE Q24.2 shows cross sections of...Ch. 24 - The square and circle in FIGURE Q24.3 are in the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 4CQCh. 24 - Prob. 5CQCh. 24 - What is the electric flux through each of the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 7CQCh. 24 - The two spheres in FIGURE Q24.8 on the next page...Ch. 24 - The sphere and ellipsoid in FIGURE Q24.9 surround...Ch. 24 - A small, metal sphere hangs by an insulating...
Ch. 24 - l. FIGURE EX24.1 shows two cross sections of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.2 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.3 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.6 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.7 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.8 contains no net charge....Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - II The electric flux through the surface shown in...Ch. 24 - ]12. A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xy-plane....Ch. 24 - A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xz-plane. What...Ch. 24 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 24 - 15. A box with its edges aligned with
the...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.17 shows three charges. Draw these...Ch. 24 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE EX24.19 shows three Gaussian surfaces and...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the torus...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the cylinder...Ch. 24 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 24 - A spark occurs at the tip of a metal needle if the...Ch. 24 - The electric field strength just above one face of...Ch. 24 - The conducting box in FIGURE EX24.26 has been...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.27 shows a hollow cavity within a...Ch. 24 - A thin, horizontal, 10-cm-diameter copper plate is...Ch. 24 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 24 - II A tetrahedron has an equilateral triangle base...Ch. 24 - Charges q1= —4Q and q2= +2Q are located at x = —a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 24 - A spherically symmetric charge distribution...Ch. 24 - A neutral conductor contains a hollow cavity in...Ch. 24 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 24 - 37. A 20-cm-radius ball is uniformly charged to 80...Ch. 24 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has 6 cm and 10 cm inner and...Ch. 24 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 24 - Find the electric field inside and outside a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE P24.47 shows an infinitely wide conductor...Ch. 24 - FIGURE P24.48 shows two very large slabs of metal...Ch. 24 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 24 - A very long, uniformly charged cylinder has radius...Ch. 24 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 24 - II A long cylinder with radius b and volume charge...Ch. 24 - A spherical shell has inner radius Rin, and outer...Ch. 24 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 24 - Newton's law of gravity and Coulomb's law are both...Ch. 24 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 24 - An infinite cylinder of radius R has a linear...Ch. 24 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 24 - A sphere of radius R has total charge Q. The...Ch. 24 - II A spherical ball of charge has radius R and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, o,y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0., y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forward4.56 ... CALC An object of mass m is at rest in equilibrium at the origin. At t = 0 a new force F(t) is applied that has components Fx(t) = k₁ + k₂y Fy(t) = k3t where k₁, k2, and k3 are constants. Calculate the position (1) and veloc- ity (t) vectors as functions of time.arrow_forward4.14 ⚫ A 2.75 kg cat moves in a straight line (the x-axis). Figure E4.14 shows a graph of the x- component of this cat's velocity as a function of time. (a) Find the maximum net force on this cat. When does this force occur? (b) When is the net force on the cat equal to zero? (c) What is the net force at time 8.5 s? Figure E4.14 V₁ (m/s) 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0 t(s) 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0arrow_forward
- 4.36 ... CP An advertisement claims that a particular automobile can "stop on a dime." What net force would be necessary to stop a 850 kg automobile traveling initially at 45.0 km/h in a distance equal to the di- ameter of a dime, 1.8 cm?arrow_forward4.46 The two blocks in Fig. P4.46 are connected by a heavy uniform rope with a mass of 4.00 kg. An up- ward force of 200 N is applied as shown. (a) Draw three free-body diagrams: one for the 6.00 kg block, one for B the 4.00 kg rope, and another one for the 5.00 kg block. For each force, indicate what object exerts that force. (b) What is the acceleration of the system? (c) What is the tension at the top of the heavy rope? (d) What is the tension at the midpoint of the rope? Figure P4.46 F= 200 N 4.00 kg 6.00 kg 5.00 kgarrow_forward4.35 ⚫ Two adults and a child want to push a wheeled cart in the direc- tion marked x in Fig. P4.35 (next page). The two adults push with hori- zontal forces F and F as shown. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the smallest force that the child should exert. Ignore the effects of friction. (b) If the child exerts the minimum force found in part (a), the cart ac- celerates at 2.0 m/s² in the +x-direction. What is the weight of the cart? Figure P4.35 F₁ = 100 N 60° 30° F2 = 140 Narrow_forward
- 4.21 ⚫ BIO World-class sprinters can accelerate out of the starting blocks with an acceleration that is nearly horizontal and has magnitude 15 m/s². How much horizontal force must a 55 kg sprinter exert on the starting blocks to produce this acceleration? Which object exerts the force that propels the sprinter: the blocks or the sprinter herself?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forward
- The kinetic energy of a pendulum is greatest Question 20Select one: a. at the top of its swing. b. when its potential energy is greatest. c. at the bottom of its swing. d. when its total energy is greatest.arrow_forwardPart a-D plarrow_forwardThe figure (Figure 1) shows representations of six thermodynamic states of the same ideal gas sample. Figure 1 of 1 Part A ■Review | Constants Rank the states on the basis of the pressure of the gas sample at each state. Rank pressure from highest to lowest. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. ▸ View Available Hint(s) highest 0 ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ Reset Help B F A D E The correct ranking cannot be determined. Submit Previous Answers × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Provide Feedback lowest Next >arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY