Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.4, Problem 46P
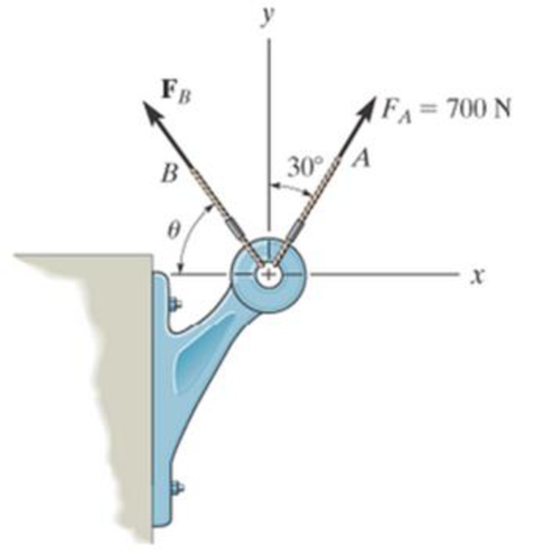
Determine the magnitude and orientation θ of FB so that the resultant force is directed along the positive y axis and has a magnitude of 1500 N.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I don't want an AI solution please.
I don't want an AI solution please.
I don't want an AI solution please.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 2.3 - In each case, construct the parallelogram law to...Ch. 2.3 - In each case, show how to resolve the force F into...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Two forces act on the hook. Determine the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - The force F = 450 lb acts on the frame. Resolve...Ch. 2.3 - If force F is to have a component along the u axis...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - The vertical force F acts downward at A on the...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - The plate is subjected to the two forces at A and...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the angle for connecting member A to...Ch. 2.3 - The force acting on the gear tooth is F = 20lb....Ch. 2.3 - The component of force F acting along line aa is...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) for strut AB...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) between...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 22PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA SO...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction, measured...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of force F so that the...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is 3...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is to...Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 38PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation. measured...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 53PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 58PCh. 2.4 - If F = 5 kN and = 30, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.6 - Sketch the following forces on the x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Show how to resolve each force into its x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 14FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 15FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 16FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 17FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 18FPCh. 2.6 - The force F has a magnitude of 80 lb and acts...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 61PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 62PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 63PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 64PCh. 2.6 - The screw eye is subjected to the two forces...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - The bracket is subjected to the two forces shown....Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 81PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 82PCh. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - The pole is subjected to the force F which has...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 20FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 22FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 23FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 24FPCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 89PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 92PCh. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - The plate is suspended using the three cables...Ch. 2.8 - The three supporting cables exert the forces shown...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 98PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 100PCh. 2.8 - The two mooring cables exert forces on the stern...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 102PCh. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - If the resultant of the four forces is FR = {360k}...Ch. 2.9 - P2.8. in each case set up the dot product to find...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 9PPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 25FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 27FPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 28FPCh. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 30FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 106PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 107PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 109PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 111PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 120PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 126PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 127PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 136PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.9 - Resolve F into components along the u and v axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 3RPCh. 2.9 - The cable at the end of the crane boom exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 5RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 6RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 7RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1.7 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.23 using two beam elements. A. E. I constant M₂ T + FIGURE 1.23 A fixed-pinned beam subjected to a momentarrow_forward42 PART 1 Introduction A. E. I constant FIGURE 1.22 A fixed-pinned beam. 1.6 Find the stress distribution in the beam shown in Fig. 1.22 using two beam elements.arrow_forward1.4 Using a one-beam element idealization, find the stress distribution under a load of P for the uniform cantilever beam shown in Fig. 1.20. A, E, I constant L FIGURE 1.20 A uniform cantilever beamarrow_forward
- Mechanical engineering,FBD required.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardPlease Please use MATLAB with codes and graph. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure is attached below.arrow_forward
- Please only step 6 (last time I asked it was cut off at that point)arrow_forwardPlease Please use a MATLAB with codes and grap. Recreate the following four Figures of the textbook using MATLAB and the appropriate parameters. Comment on your observations for each Figure. List all of the parameters that you have used. The figure attached below.arrow_forwardI REPEAT!!!!! I NEED HANDDRAWING!!!!! NOT A USELESS EXPLANATION!!!! I REPEAT SUBMIT A HANDDRAWING IF YOU CANNOT UNDERSTAND THIS SKIP IT ! I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forward
- I need the real handdrawing complete it by adding these : Pneumatic Valves Each linear actuator must be controlled by a directional control valve (DCV) (e.g., 5/2 or 4/2 valve). The bi-directional motor requires a reversible valve to change rotation direction. Pressure Regulators & Air Supply Include two pressure regulators as per the assignment requirement. Show the main compressed air supply line connecting all components. Limit Switches & Safety Features Attach limit switches to each actuator to detect positions. Implement a two-handed push-button safety system to control actuator movement. Connections Between Components Draw air supply lines linking the compressor, valves, and actuators. Clearly label all inputs and outputs for better understanding.arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forwardAn elastic bar of the length L and cross section area A is rigidly attached to the ceiling of a room, and it supports a mass M. Due to the acceleration of gravity g the rod deforms vertically. The deformation of the rod is measured by the vertical displacement u(x) governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + b(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = Edx du Hooke's law (1) b(x) = gp= body force per unit volume where E is the constant Young's modulus, p is the density, and σ(x) the axial stress in the rod. g * I u(x) L 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License