Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.3, Problem 16P
Force F acts on the frame such that its component acting along member AB is 650 lb, directed from B towards A. Determine the required angle Φ(0° ≤ Φ ≤ 45°) and the component acting along member BC. Set F = 850lb and θ = 30°.
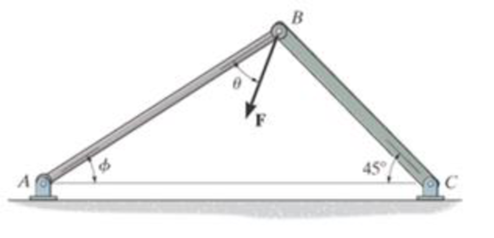
Probs. 2-15/16
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need expert handwritten solutions to this only
Two large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank
A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each
tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of
6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If,
initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt.
A
6 L/min
0.2 kg/L
x(t)
100 L
4 L/min
x(0) = 0 kg
3 L/min
B
y(t)
100 L
y(0) = 20 kg
2 L/min
1 L/min
Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks
Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t > 0:
Analytically (hand calculations)
Two springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set
in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its
equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m₂ = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and
k₂ = 2 N/m.
www.m
k₁ = 3
(y₁ = 0).
m₁ = 1
k2=2
(y₂ = 0)
|m₂ = 1
Y2
y 2
System in
static
equilibrium
(Net change in
spring length
=32-31)
System in
motion
Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system
Determine the equations of motion y₁(t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively:
Analytically (hand calculations)
Chapter 2 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 2.3 - In each case, construct the parallelogram law to...Ch. 2.3 - In each case, show how to resolve the force F into...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.3 - Two forces act on the hook. Determine the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the 30-lb force into components along the...Ch. 2.3 - The force F = 450 lb acts on the frame. Resolve...Ch. 2.3 - If force F is to have a component along the u axis...Ch. 2.3 - If = 60 and F = 450 N, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the magnitude of the resultant force is to be...
Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - The vertical force F acts downward at A on the...Ch. 2.3 - Solve with F = 350 lb. Prob. 2-4/5Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F1 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - Resolve the force F2 into components acting along...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force acting on the support is to...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.3 - The plate is subjected to the two forces at A and...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the angle for connecting member A to...Ch. 2.3 - The force acting on the gear tooth is F = 20lb....Ch. 2.3 - The component of force F acting along line aa is...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Force F acts on the frame such that its component...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) for strut AB...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the design angle (0 90) between...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.3 - Prob. 22PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 2.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 2.3 - If F1 = 30 lb and F2 = 40 lb, determine the angles...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of FA SO...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction, measured...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the magnitude of force F so that the...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is 3...Ch. 2.3 - If FB = 3 kN and = 45, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.3 - If the resultant force of the two tugboats is...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the post into its x...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 9FPCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is to...Ch. 2.4 - If the magnitude of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 34PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Resolve each force acting on the gusset plate into...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 38PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and...Ch. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 45PCh. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation of FB so...Ch. 2.4 - Determine the magnitude and orientation. measured...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 2.4 - Express F1, F2, and F3 as Cartesian vectors.Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 53PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 55PCh. 2.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 2.4 - If the resultant force acting on the bracket is...Ch. 2.4 - Prob. 58PCh. 2.4 - If F = 5 kN and = 30, determine the magnitude of...Ch. 2.6 - Sketch the following forces on the x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - In each case, establish F as a Cartesian vector,...Ch. 2.6 - Show how to resolve each force into its x, y, z...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 14FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 15FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 16FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 17FPCh. 2.6 - Prob. 18FPCh. 2.6 - The force F has a magnitude of 80 lb and acts...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 61PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 62PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 63PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 64PCh. 2.6 - The screw eye is subjected to the two forces...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 66PCh. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Specify the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 72PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 73PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 74PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 75PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 76PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 77PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 78PCh. 2.6 - Determine the coordinate direction angles of the...Ch. 2.6 - The bracket is subjected to the two forces shown....Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 81PCh. 2.6 - Prob. 82PCh. 2.6 - If the direction of the resultant force acting on...Ch. 2.6 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.6 - The pole is subjected to the force F which has...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, establish a position vector from...Ch. 2.8 - In each case, express F as a Cartesian vector....Ch. 2.8 - Express the position vector rAB in Cartesian...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 20FPCh. 2.8 - Express the force as a Cartesian vector. Prob....Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 22FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 23FPCh. 2.8 - Prob. 24FPCh. 2.8 - Determine the length of the connecting rod AB by...Ch. 2.8 - Express force F as a Cartesian vector; then...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 89PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 92PCh. 2.8 - If FB = 560 N and FC = 700 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - If FB = 700 N, and FC = 560 N, determine the...Ch. 2.8 - The plate is suspended using the three cables...Ch. 2.8 - The three supporting cables exert the forces shown...Ch. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 98PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.8 - Prob. 100PCh. 2.8 - The two mooring cables exert forces on the stern...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 102PCh. 2.8 - Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction...Ch. 2.8 - If the force in each cable tied to the bin is 70...Ch. 2.8 - If the resultant of the four forces is FR = {360k}...Ch. 2.9 - P2.8. in each case set up the dot product to find...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 9PPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 25FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the force and the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 27FPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 28FPCh. 2.9 - Find the magnitude of the projected component of...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 30FPCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of the...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 106PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 107PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 109PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 111PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the components of F =...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitudes of the projected...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 120PCh. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the two cables...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the angle between the cables AB and AC....Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projection of force...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 126PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 127PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 128PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 130PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 131PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the projected component...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 133PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 134PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 135PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 136PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 137PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 138PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 139PCh. 2.9 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR...Ch. 2.9 - Resolve F into components along the u and v axes...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 3RPCh. 2.9 - The cable at the end of the crane boom exerts a...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 5RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 6RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 7RPCh. 2.9 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f(t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forwardthis is answer to a vibrations question. in the last part it states an assumption of x2, im not sure where this assumption comes from. an answer would be greatly appreciatedarrow_forwardPlease answer with the sketches.arrow_forward
- The beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²] y 25 mm 75 mm I 25 mm 200 mm 25 mm 125 Figure Q3arrow_forwardA beam of the cross section shown in Figure Q3 is made of a steel that is assumed to be elastic- perfectectly plastic material with E = 200 GPa and σy = 240 MPa. Determine: i. The shape factor of the cross section ii. The bending moment at which the plastic zones at the top and bottom of the bar are 30 mm thick. 15 mm 30 mm 15 mm 30 mm 30 mm 30 mmarrow_forwardA torque of magnitude T = 12 kNm is applied to the end of a tank containing compressed air under a pressure of 8 MPa (Figure Q1). The tank has a 180 mm inner diameter and a 12 mm wall thickness. As a result of several tensile tests, it has been found that tensile yeild strength is σy = 250 MPa for thr grade of steel used. Determine the factor of safety with respect to yeild, using: (a) The maximum shearing stress theory (b) The maximum distortion energy theory T Figure Q1arrow_forward
- An external pressure of 12 MPa is applied to a closed-end thick cylinder of internal diameter 150 mm and external diameter 300 mm. If the maximum hoop stress on the inner surface of the cylinder is limited to 30 MPa: (a) What maximum internal pressure can be applied to the cylinder? (b) Sketch the variation of hoop and radial stresses across the cylinder wall. (c) What will be the change in the outside diameter when the above pressure is applied? [Take E = 207 GPa and v = 0.29]arrow_forwardso A 4 I need a detailed drawing with explanation し i need drawing in solution motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the か ---2-125 750 x2.01 98Parrow_forwardFigure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forward
- I need a detailed drawing with explanation so Solle 4 يكا Pax Pu + 96** motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the 55 ---20125 750 X 2.01 1989arrow_forwardAshaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNM 20,000 10,000 0 90 270 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 720arrow_forwardchanism shown in figure below, the crank OA rotates at 60 RPM counterclockwise. The velocity diagram is also drawn to scale (take dimensions from space diagram). Knowing that QCD is rigid plate, determine: a. Linear acceleration of slider at B, b. Angular acceleration of the links AC, plate CQD, and BD. D Space Diagram Scale 1:10 A ES a o,p,g b Velocity Diagram Scale 50 mm/(m/s) darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY