
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis in which ATP are formed should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, ATP's are formed in step-7 and 10.
Explanation of Solution
The
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
Two steps; 7th and 10th step are involved in the production of ATP;
- Conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate occurs with the conversion of ADP to form ATP in the presence of Phosphoglycerate kinase that transfers a phosphate group.
- Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvic acid with the conversion of ATP in the presence enzyme pyruvate kinase
(b)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which uses ATP molecules should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, ATP's are formed in step-1 and 3.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with the production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
Two steps; 1st and 3rdstep use ATP molecules.
- The first step in glycolysis, glucose converts to glucose-6-phosphate in the presence of hexokinase. It uses energy in the form of ATP and converts it to ADP molecule.
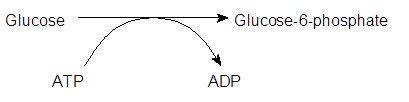
- Phosphofructokinase, with magnesium as a cofactor, changes fructose 6-phosphate into fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate.
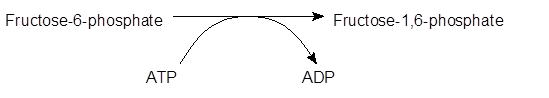
(c)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which forms a reduce coenzyme should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, step-6 forms a reduced coenzyme NADH.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions which involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with the production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
In the 6th step of glycolysis, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate converts to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. It is a dehydrogenation step that occurs in the presence of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and converts NAD+ to NADH and H+ ions.
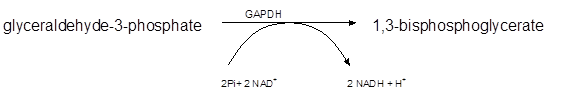
(c)
Interpretation:
The step of glycolysis which breaks a C-C bond should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Aerobic respiration occurs in two steps:
- Glycolysis
- Citric acid cycle
- Glycolysis is the first step that forms pyruvate as given below:
In the presence of oxygen means aerobic respiration, this pyruvate enters the Krebs cycle and extracts energy in the form of electrons transfer. Electrons are transferred from the pyruvate to the receptors like
Answer to Problem 31P
In glycolysis, step-4breaks a C-C bond.
Explanation of Solution
The metabolism of glucose starts from the glycolysis process. It is the first step in cellular metabolism to extract energy from glucose. It is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions which involves the conversion of glucose molecules into pyruvate with production of ATP molecules.
The overall reaction of glycolysis must be written as:
In the 4thstep of glycolysis, in the presence of enzyme Aldolase, fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate breaks into two sugar molecules. These sugar molecules are isomers of each other; dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP).
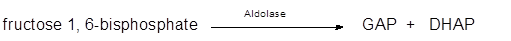
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Connect One Semester Access Card for General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- Use diagram to answer the following: 1.Is the overall rxn endo- or exothermic. Explain briefly your answer____________________2. How many steps in this mechanism?_____________3. Which is the rate determining step? Explain briefly your answer____________________4. Identify (circle and label) the reactants,the products and intermediate (Is a Cation, Anion, or a Radical?) Please explain and provide full understanding.arrow_forwardDraw the entire mechanism and add Curved Arrows to show clearly how electrons areredistributed in the process. Please explain and provide steps clearly.arrow_forward15) Create Lewis structure Br Brarrow_forward
- LIOT S How would you make 200. mL of a 0.5 M solution of CuSO4 5H2O from solid copper (II) sulfate? View Rubricarrow_forwardSteps and explantions pleasearrow_forwardMatch the denticity to the ligand. Water monodentate ✓ C₂O2 bidentate H₂NCH₂NHCH2NH2 bidentate x EDTA hexadentate Question 12 Partially correct Mark 2 out of 2 Flag question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below: Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2✔ Geometry: linear Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3 x in 12 correct out of 2 question Provide the required information for the coordination compound shown below. Na NC-Ag-CN] Number of ligands: 20 Coordination number: 2 Geometry: linear 0 Oxidation state of transition metal ion: +3Xarrow_forward
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
 Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





