
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
The compounds,
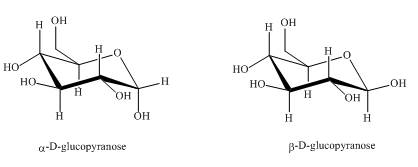
Explanation of Solution
The compounds,
They are diastereomers also as they are not mirror images of each other. The structure of both the compounds is shown below.

Figure 1
These two compounds are anomers as well as diastereomers as shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism between molecules. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
The compounds,
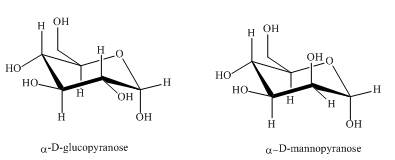
Explanation of Solution
Both the above structures of

Figure 2
The compounds
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism between molecules. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
The compounds,
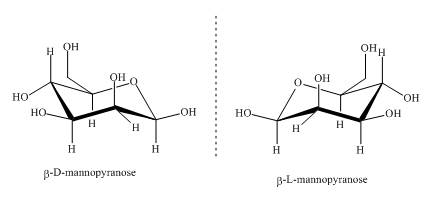
Explanation of Solution
Sugars can be divided into two groups based on the symmetry of carbon atoms. If the molecule has asymmetric carbon atom it will have a non superimposable mirror image. The non superimposable mirror images are known as enantiomers. As the given compounds are non super imposable mirror images of each other they are enantiomers. This can be well explained by the illustrations shown below.

Figure 3
These two compounds
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism between molecules. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
The compounds,
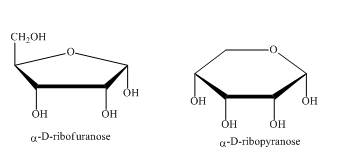
Explanation of Solution
As the isomers are the compounds, having similar chemical formula but different structures. These two compounds have same chemical formula. The chemical structure is of these two compounds is quite different as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4
In the above shown compounds, one is a pentose sugar furanose while the other is a hexose sugar pyranose.
These two compounds,
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism between molecules. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
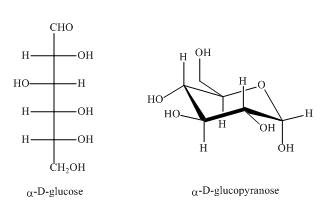
Explanation of Solution
As the isomers are the compounds, having similar chemical formula but different structures. Both the above structures are constitutional isomers as shown below in the Figure.

Figure 5
In the above shown compounds, one is a ring structure having keto group while the other is open ring structure having aldehyde as the
The given compounds
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether the compounds,
Concept introduction:
Sugars show different types of isomerism between molecules. They may be enantiomers, epimers, anomers, or diastereomers depending upon chirality and plane of symmetry in molecules. It also depends on stereochemistry of different carbons. The naming of the same compound can be done in different manners.
Answer to Problem 24.39AP
The compounds,
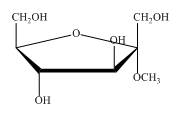
Explanation of Solution
The structure of

Figure 6
So, the compound is same, they are identical. In first name it is taken as methyl derivative of
The compound shown in Figure 6 can be named as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE AND S
- Can I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph, if you could show exactly where it needs to pass through please.arrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 1,3-dihydroxy-2-pentanone. Explanation Check Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. Х C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of use +arrow_forward0.500 moles of NOCl are placed into a 1.00 L vessesl at 700K and after the system comes to equilibrium, the consentration of NOCl is 0.440 M. Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction: 2NOCL (g) --> 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g)arrow_forwardWhat is the hydronium ion concentration in a solution of water that has a hydroxide ion concentrationof 1.0 x 10-2 M?arrow_forward
- Identify conjugate acid-base pairs in the following reactions:HBr (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + Br- (aq) - OH (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H2O (l) + CH3COO- (aq)arrow_forward4:45 PM Tue Apr 1 K 77% Problem 9 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting structure, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Then draw any missing organic intermediates or products for this reaction. Include all lone pairs in the structures. Ignore inorganic byproducts, counterions, and solvents. :0: H Select to Add Arrows HI CH3OH H+ ·HO CH3OH, H+ 0:0 H H Select to Add Arrows tion Versirate CH3OH, H* Select to Draw Productarrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph? If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forward
- G 1. PPh3, THF 2. 3. LiH, THF ' THF H Harrow_forwardPlease EnCircle or Fill-In your Choice CLEARLY: 21. Please Sketch the intermediates for each step below. Draw the Product which would result from the following series of reactions. Name each Type of Rx: 1. Br2, FeBr3 2. Mg, ether 3. ethylene oxide 4. H₂O+ 5. PBr3 6. Mg, ether 7. 8. H3O+, heat (-H₂O 9. HF ?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this question. All required information should be in data table.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


