
(a)
Interpretation:
The other products obtained from the highly stereo and regioselective reaction of O-alkylation during the formation of Gilvarin M. has to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
Regioselectivity:
Regioselectivity is the preference of one direction of
Stereoselectivity:
Stereoselectivity is the property of a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
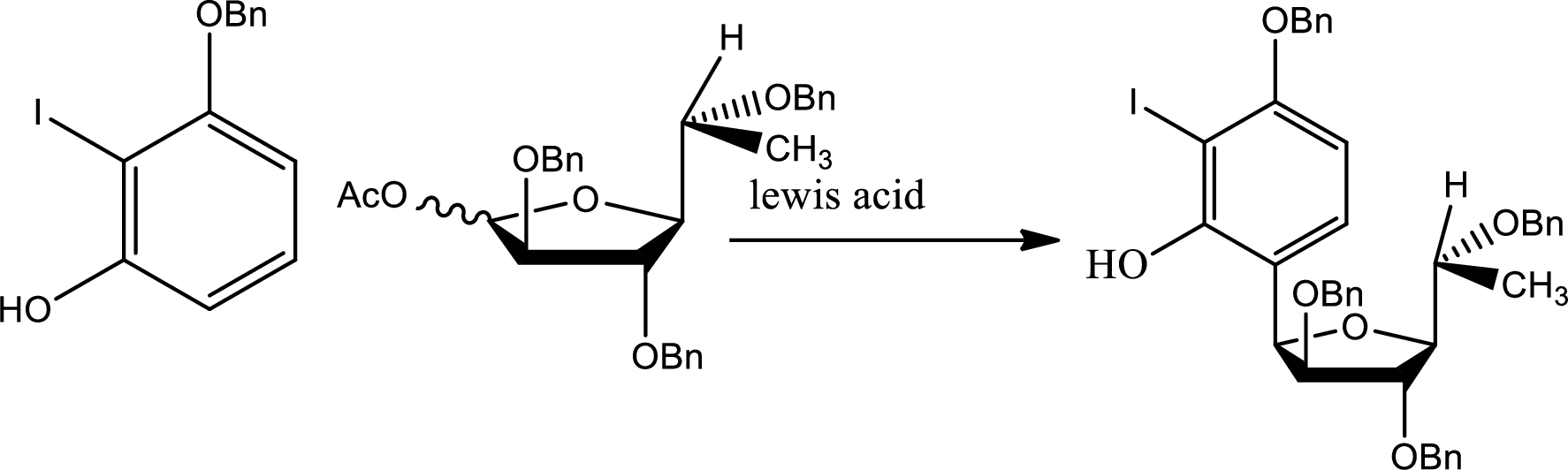
The other possibility is,
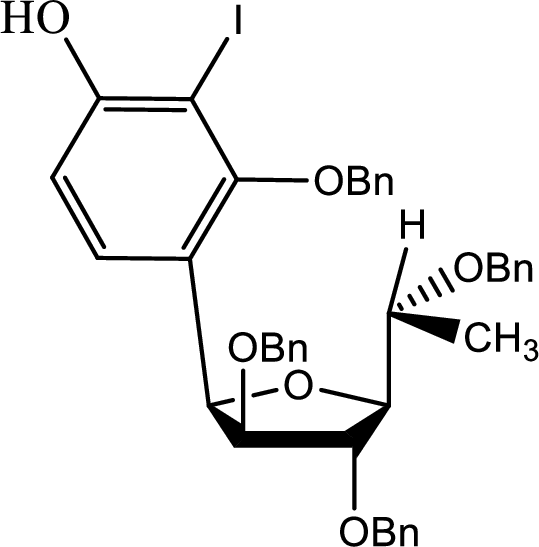
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the compound C has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acid-base reaction:
The species that donates proton or accepts lone pair of electrons are called acids and those who accepts proton or donates lone pair of electrons are called base.
The
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The pathway of formation of C is,
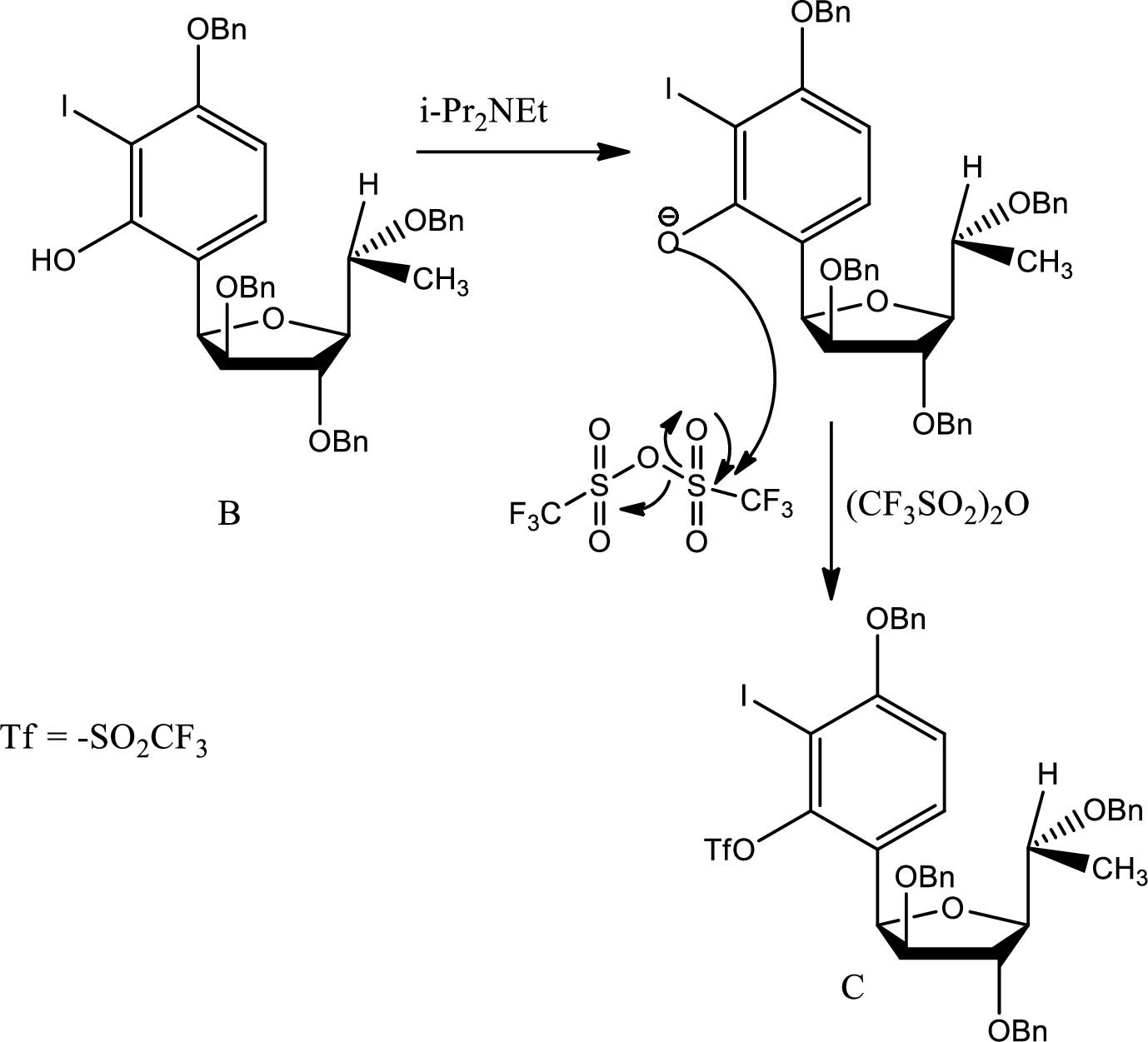
Here the
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of compound D has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Lithium halogen exchange:
Organolithium reagents are characterised by the presence of
The reaction of lithium metal at low temperature with an
The same reaction happens with the haloarenes also,
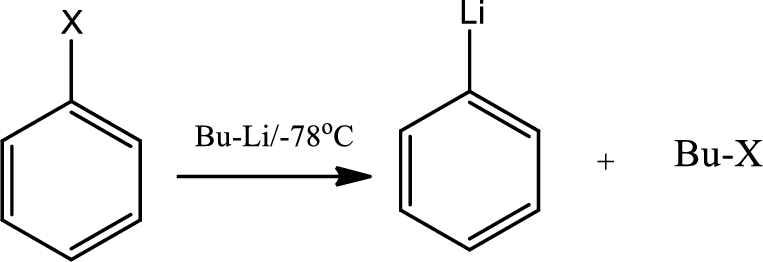
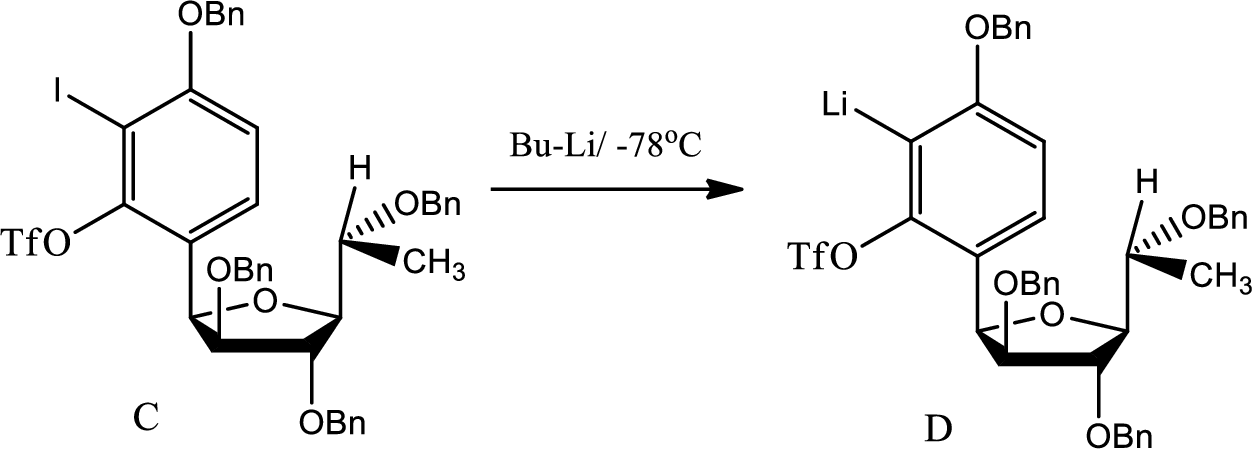
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction for the formation of D is as follows,
(d)
Interpretation:
Structure of E has to be given along with the mechanism of formation of E from D.
Concept introduction:
Benzyne formation:
Benzynes are highly reactive intermediate species that are made from
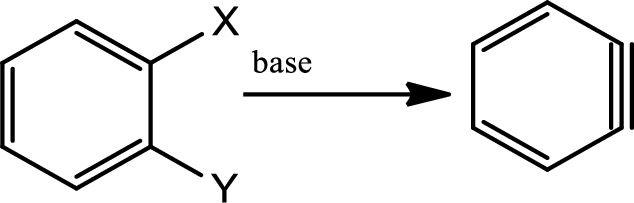
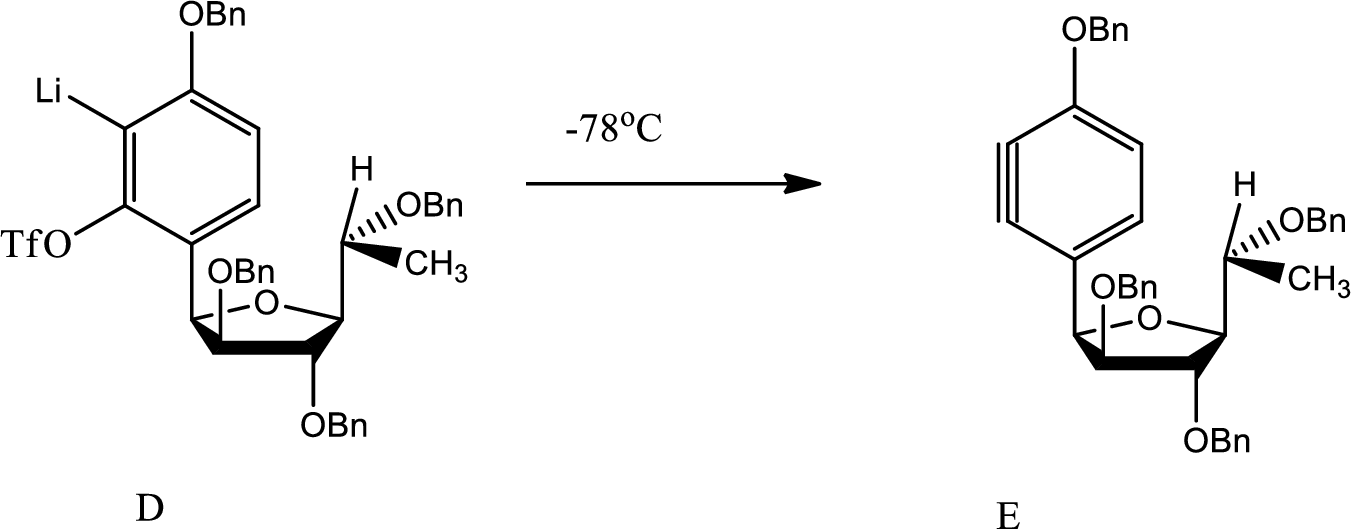
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Here benzyne formation occurs due to removal of
(e)
Interpretation:
A mechanism for formation of F from E has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Diels Alder reaction:
The Diels-Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted
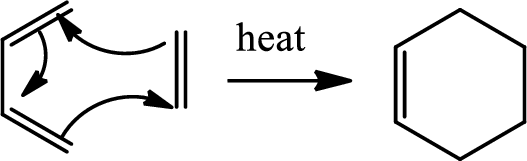
(e)
Explanation of Solution
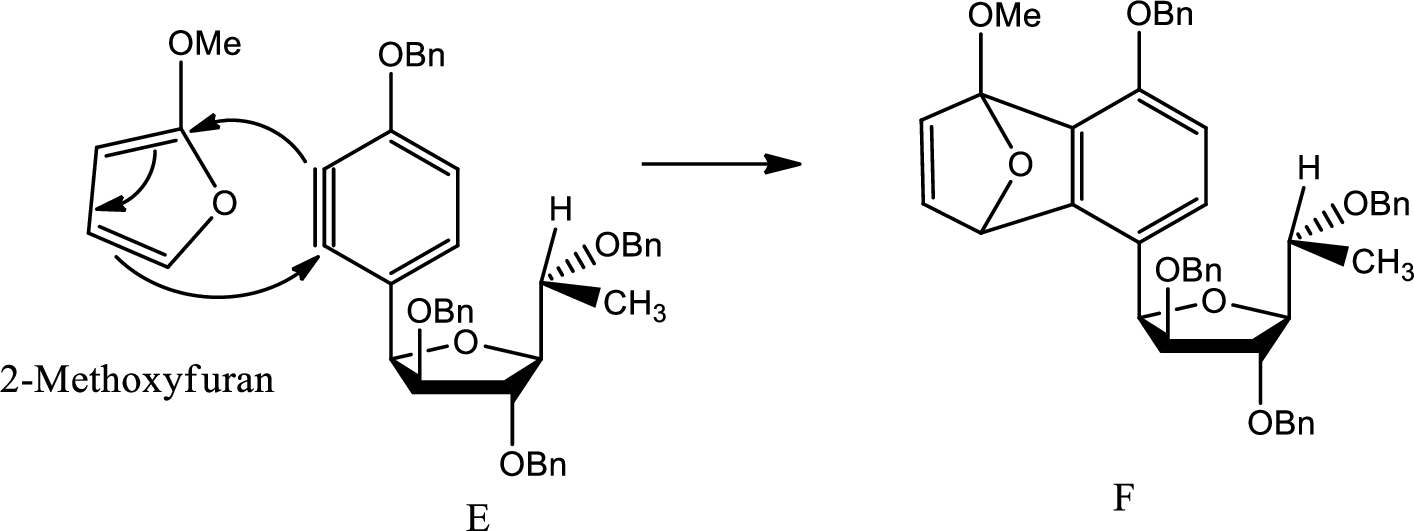
Here Diels Alder reaction occurs between furan and benzyne. A new ring is formed.
(f)
Interpretation:
Mechanism from F to G has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Hydrolysis:
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a water molecule ruptures one or more chemical bonds. This is mainly used for substitution, elimination and fragmentation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Hydrolysis is reverse of condensation reaction because in this process water is added to beak down.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Here aqueous work up leads to breaking of the bridging oxygen bond by protonating the oxygen. Thus the angle strain increases as positive charge on electronegative oxygen is tough. Thus the bond breaks and the charge formed is stabilised by electron donating effect of
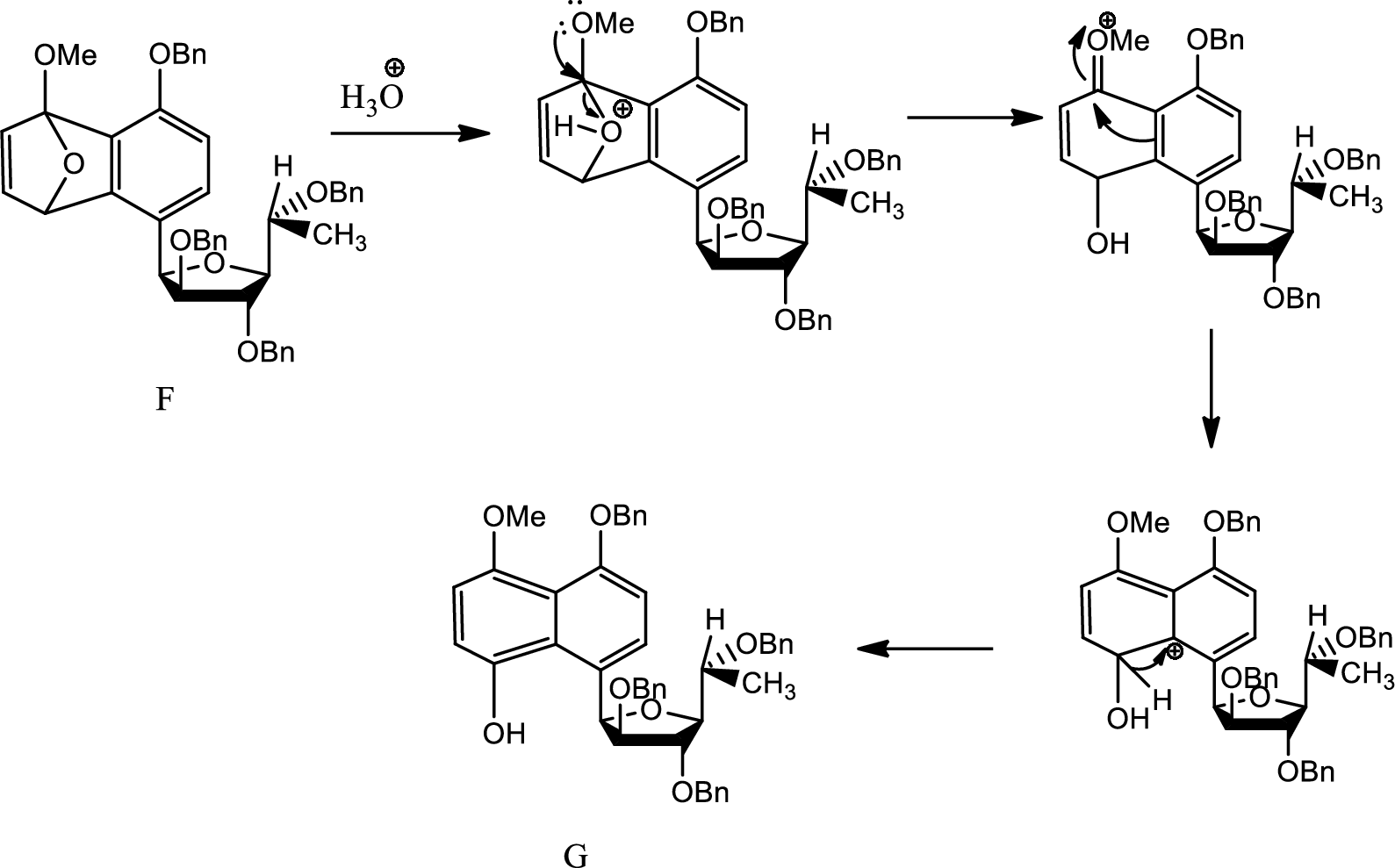
Thus G is formed from F.
(g)
Interpretation:
The reagents and condition from G to H has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Acid-base reaction:
The species that donates proton or accepts lone pair of electrons are called acids and those who accepts proton or donates lone pair of electrons are called base.
The
(g)
Explanation of Solution
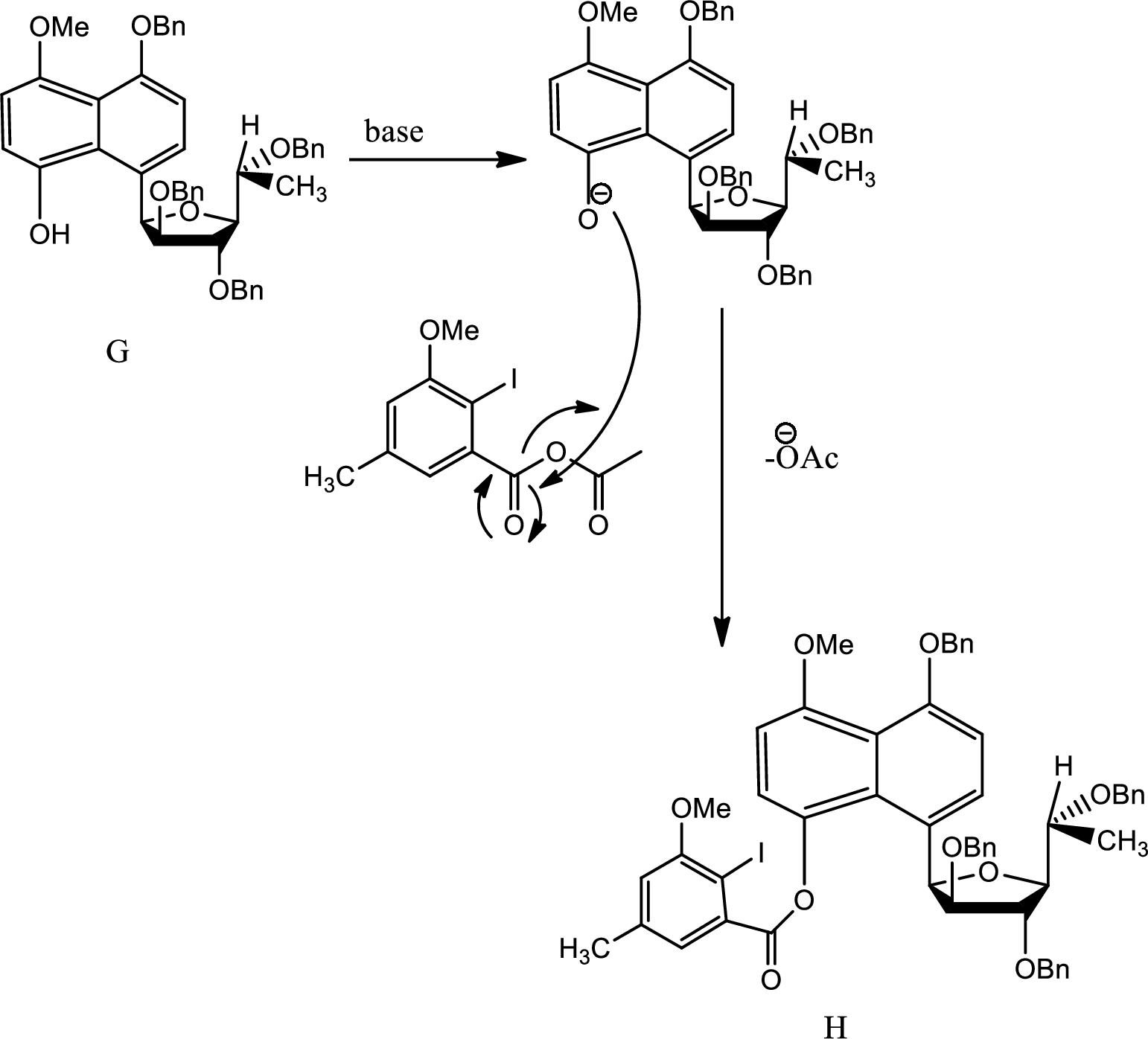
Here on giving base the acidic hydrogen from phenol is removed and the new carbanion formed undergoes
Thus H is formed from G.
(h)
Interpretation:
Reagents and condition for conversion of H to I has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Cross coupling:
A cross coupling reaction is defined as a reaction that creates a
In the case of palladium catalysed cross-coupling reactions the other metal or metalloids are commonly
Suzuki coupling:
The Suzuki coupling uses a boron compound and an alkenyl, aryl or alkyl halide or triflate as the carbon sources with a palladium salt as a catalyst. The reaction is mainly used to form biaryls. The mechanism of the reaction starts with an oxidative addition followed by transmetallation in which the substituent on the borane replaces the ligand on the palladium concluding with the reductive elimination of the palladium to form the new carbon-carbon bond. The base may serve as a new labile ligand to palladium or it may activate the borane by coordination.
Generalized reaction,
Oxidative addition and ligand exchange,
Borane activation
Reaction,
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
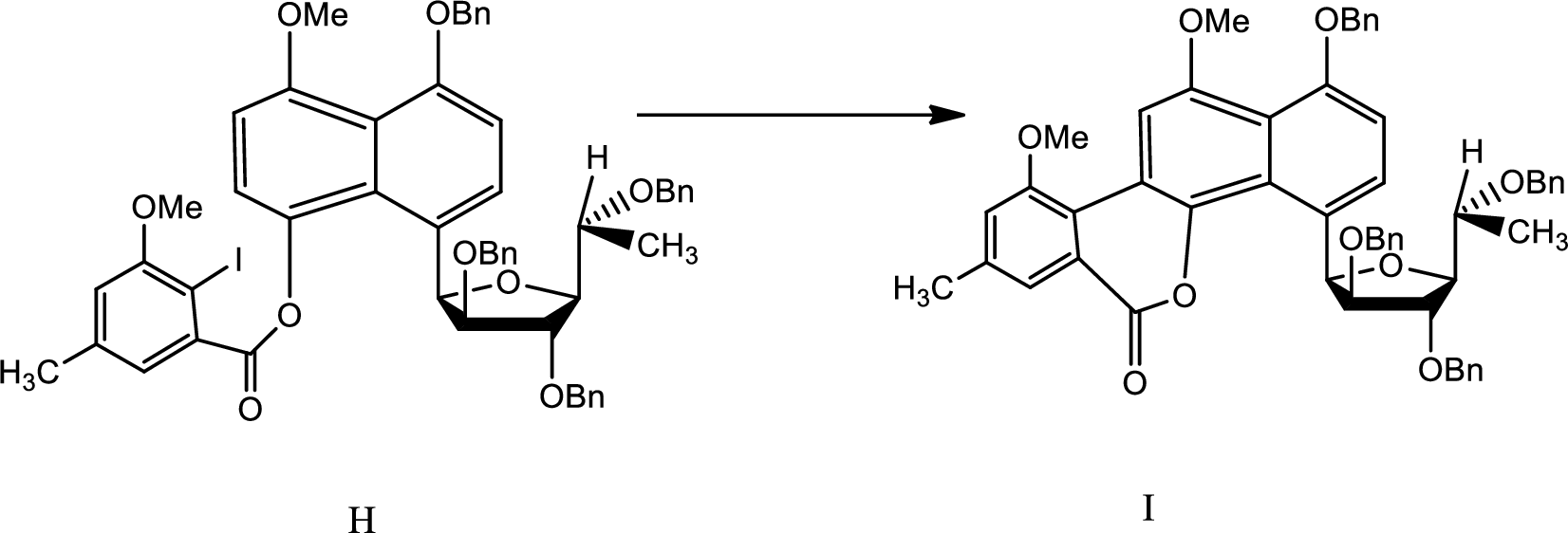
The reaction proceeds as follows,
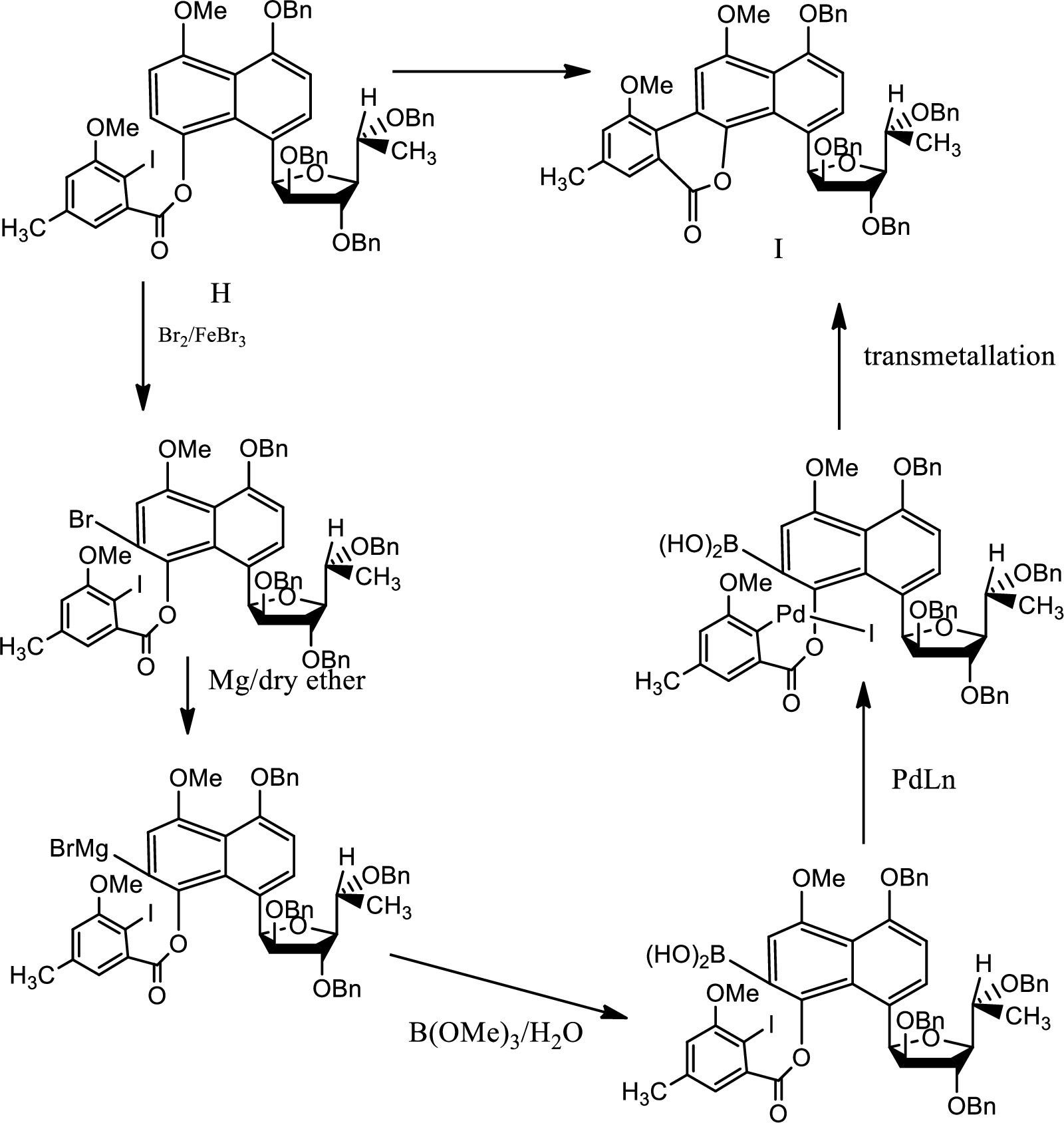
1st boron has to be added so that via transmetallation by intramolecular Suzuki coupling the product can be formed.
(i)
Interpretation:
Reagent needed to form Gilvocarcin M. from I has to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
Protection-deprotection:
A protecting group is introduced to a molecule by chemical modification of a
Hydrogenolysis:
Hydrogenolysis is a chemical reaction whereby a carbon carbon bond or carbon heteroatom single bond is cleaved by hydrogen gas catalytically.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is given as,
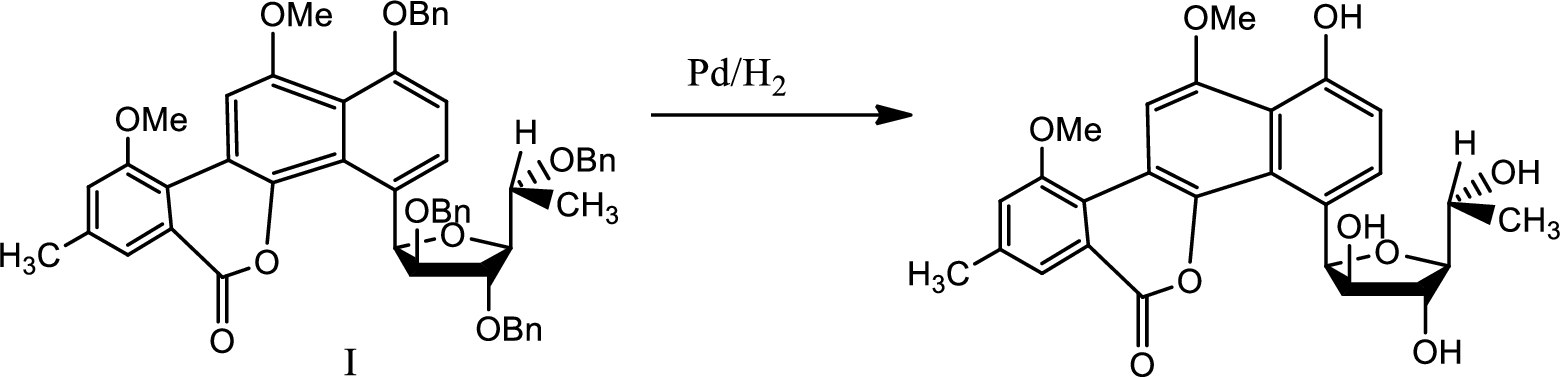
Here deprotection is done by hydrogenolysis with the help of palladium and catalytic amount of hydrogen.
(j)
Interpretation:
Probable source of chiral centres has to be found.
Concept introduction:
Chiral centre:
Chiral centre is defined as an atom bonded to four different chemical species. It is a stereo centre that holds the atom in such way that the structure may not be superimposable to its mirror image. They give optical isomerism.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The source of the chiral centre is only the five membered carbohydrate ring attached to the benzene ring as shown below,
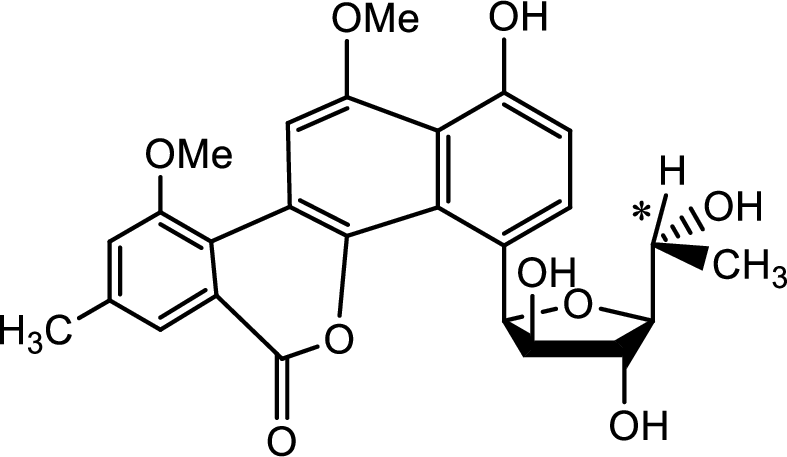
The chiral centre is marked with the asterisk.
(k)
Interpretation:
The need of protection of hydroxyl group has to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Protection-deprotection:
A protecting group is introduced to a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction specially in multistep organic synthesis.
(k)
Explanation of Solution
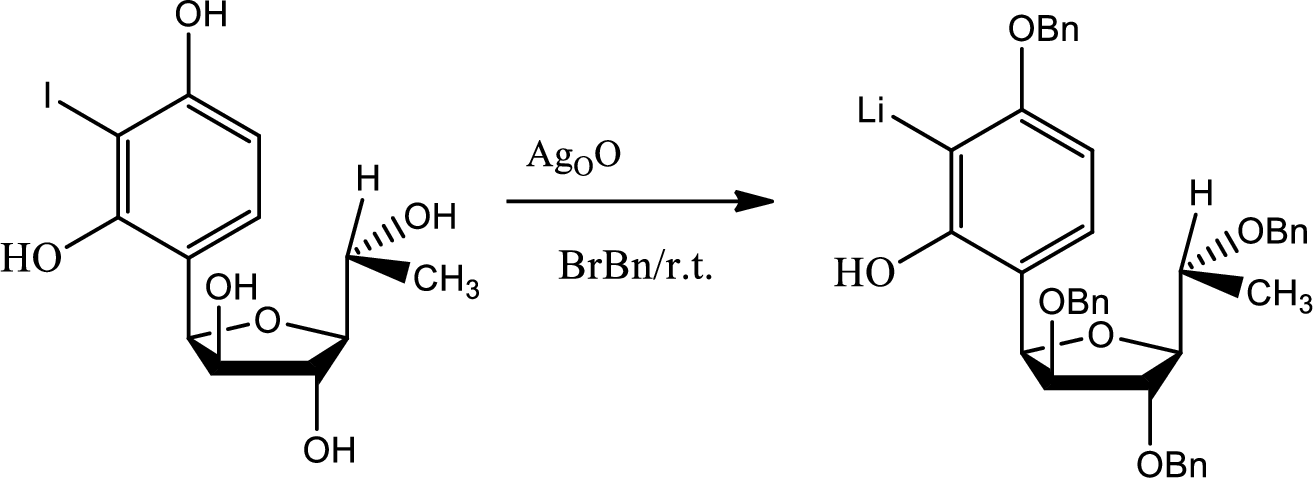
If protection has not been done to the hydroxyl groups then there were possibilities of getting so many unwanted products.
During the acid base reaction all the hydroxyl groups could have lost the proton and thus all the substitution could have taken place in different places. The benzyne formation could have hampered and the stereochemistry could have changed.
The process of protection to the hydroxyl group is given by,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify and provide a concise explanation of the concept of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the context of chemical analysis. Provide specific examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide a concise explanation of a specific analytical instrument capable of detecting and quantifying trace compounds in food samples. Emphasise the instrumental capabilities relevant to trace compound analysis in the nominated food. Include the specific application name (eg: identification and quantification of mercury in salmon), outline a brief description of sample preparation procedures, and provide a summary of the obtained results from the analytical process.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of what 'Seperation Science' is. Also describe its importance with the respect to the chemical analysis of food. Provide specific examples.arrow_forward
- 5. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn. H3C CH3arrow_forwardState the name and condensed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardState the name and condensed formula of the isothiazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and thiosemicarbazide.arrow_forward
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


