
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
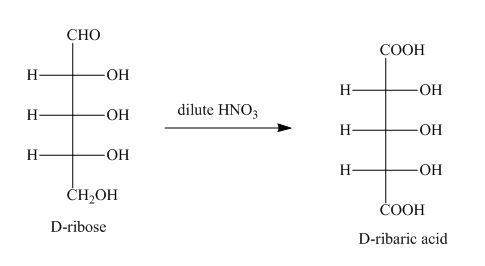
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.

Figure 1
The oxidation of D-ribose into D-ribaric acid occurs in the presence of dilute nitric acid.
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with dilute ![]() is shown in Figure 1.
is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Kiliani-Fischer process is is the reaction pathway by which an aldose is extended by one carbon unit. The first step of this reaction is the attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group resulting in the formation of the cyanohydrins. The cyanohydrins thus formed is reduced to imine with catalytic hydrogenation. The imine thus formed can easily be hydrolyzed by into aldose and ammonium ion.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
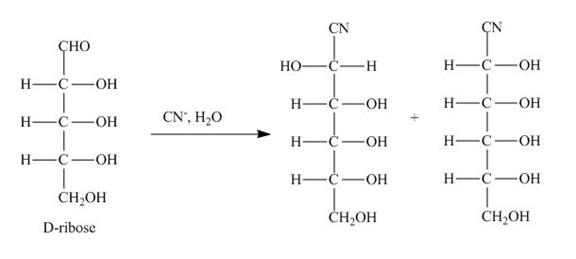
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.

Figure 2
The D-ribose is converted into cyanohydrins by the nucleophilic attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group.
The products obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() are shown in Figure 2.
are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Kiliani-Fischer process is is the reaction pathway by which an aldose is extended by one carbon unit. The first step of this reaction is the attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde group resulting in the formation of the cyanohydrins. The cyanohydrins thus formed is reduced to imine with catalytic hydrogenation. The imine thus formed can easily be hydrolyzed by into aldose and ammonium ion.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.
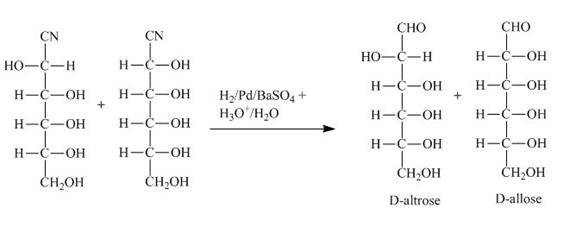
Explanation of Solution
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown below.
are shown below.

Figure 3
The product of part (b) is the cyanohydrin of D-ribose which is then converted into the extended aldose, altrose and allose. The catalytic hydrogenation of cyanohydrin into imine is done by ![]() . The imine then formed is hydrolyzed into the altrose and allose by
. The imine then formed is hydrolyzed into the altrose and allose by ![]() .
.
The products obtained when the product of part (b) is reacted with ![]() and
and ![]() are shown in Figure 3.
are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
A monosaccharide is converted into cyclic acetals on reaction with alcohols in the presence of acidic conditions. The hydroxide group right to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring structure is methylated and result in the formation of acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
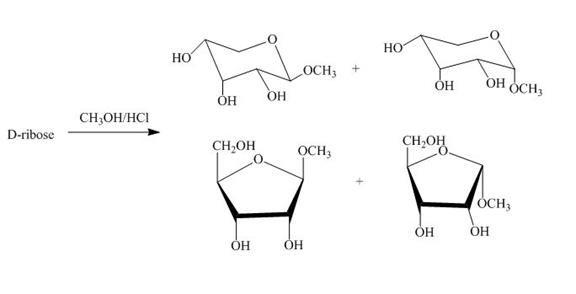
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
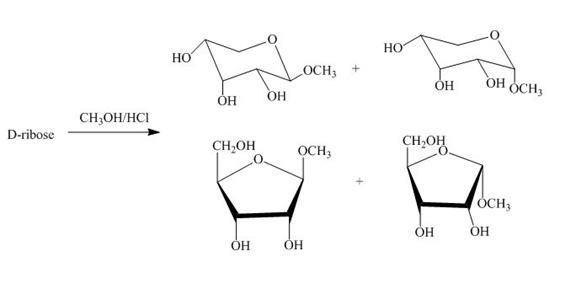
Figure 4
The D-ribose on reaction with methanol and hydrochloric acid is converted into the acetal. The acetal formed is found in both forms alpha and beta regardless of the configuration of D-ribose.
The product obtained when D-ribose is reacted with ![]() is shown in Figure 4.
is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is to be stated.
is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The methylation of the hydroxyl group of sugars is an important reaction. The methylation of hydroxyl groups is done with the help of methylating agent dimethyl sulfate in the presence of strong base sodium hydroxide.
Answer to Problem 24.35AP
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown below.
is shown below.

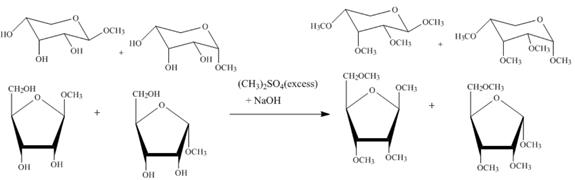
Figure 5
The four products of part (d) are alkylated in the strong base sodium hydroxide. The sodium hydroxide takes up the acidic proton of alcohol groups and converts them to alkoxide ion form. This alkoxide ion then attacks on the dimethyl sulfate (also a methylating agent) and take up the methyl group simultaneously eliminating the methyl sulfate group.
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with ![]() (excess) and
(excess) and ![]() is shown in Figure 5.
is shown in Figure 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- Draw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forward
- Can you help me understand the CBC method on metal bridging by looking at this problem?arrow_forwardA partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


