
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
Tollens test is the chemical test for the identification of the presence of the aldehyde group in the compound.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
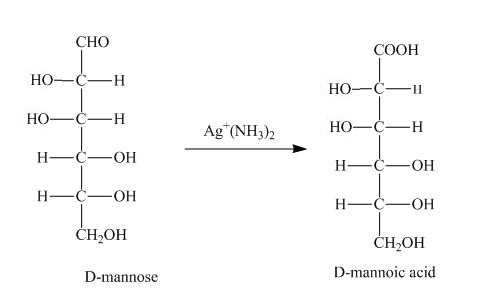
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with

Figure 1
The Tollens reagent oxidizes the aldehyde group into carboxylic acid. The D-mannose is oxidized by the
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Concept introduction:
There are two forms of sugars that is
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
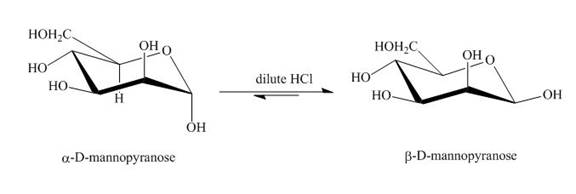
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
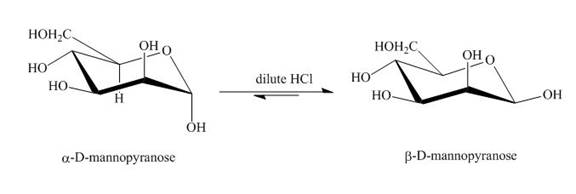
Figure 2
The conversion of both forms of sugar into each other in the presence of acid and base. That is the alpha form is converted beta and vice-versa. This change occurs until an equilibrium mixture of both compounds is obtained.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
Concept introduction:
There are two forms of sugars that is
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
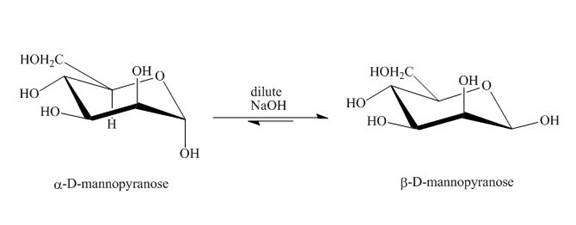
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute

Figure 3
The conversion of both forms of sugar into each other in the presence of acid or base. That is the alpha form is converted beta and vice-versa. This change occurs until an equilibrium mixture of both compounds is obtained.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with dilute
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
The aldehyde group on oxidation changes into a carboxylic acid. The oxidation of the aldehyde group present in the aldoses is done by the bromine and water into carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid of the aldoses thus formed is converted into lactones form.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
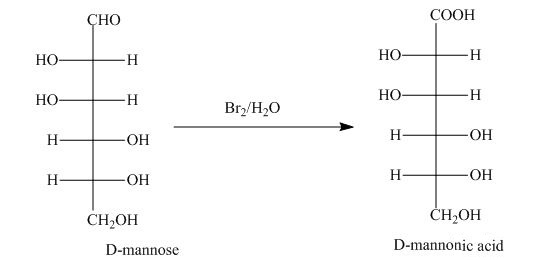
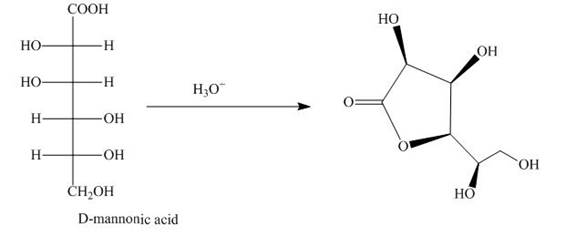
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with


Figure 4
Bromine and water oxidize the aldoses into carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid thus formed is found in the form of lactones. Lactones formed are more stable in the five-membered
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(e)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with
Concept introduction:
A monosaccharide is converted into cyclic acetals on reaction with alcohols in the presence of acidic conditions. The hydroxide group right to the oxygen atom in the pyranose ring structure is methylated and result in the formation of acetal.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
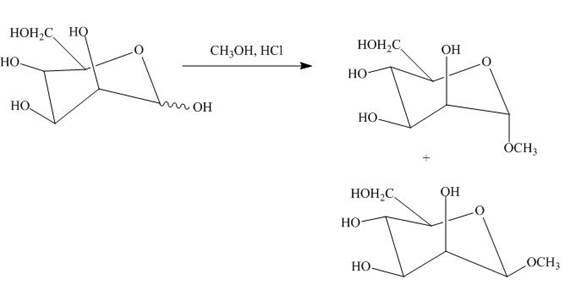
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with

Figure 5
The D-mannose on reaction with methanol and hydrochloric acid is converted into the acetal. The acetal formed is found in both forms alpha and beta regardless of the configuration of D-mannose.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with
(f)
Interpretation:
The products expected when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Esterification reaction of alcohol units of monosaccharide is also done. The esterification of the alcohol units is done in the presence of an excess of acetic anhydride and pyridine. All the alcohol units present are acylated.
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown below.
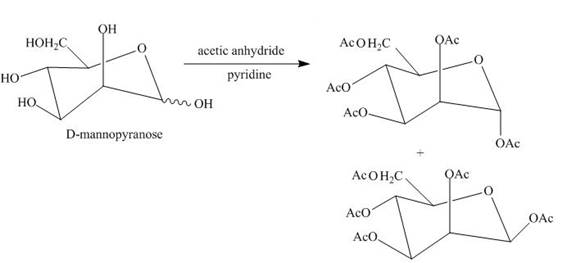
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown below.

Figure 6
Esterification of all the alcohols units present in the D-mannose is done in the presence of acetic anhydride and pyridine.
The product obtained when D-mannose is reacted with acetic anhydride/pyridine is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
Concept introduction:
Ruff’s degradation is the degradation of the sugar molecule by one carbon unit. The aldose is oxidized to the carboxylic acids using bromine water. The carboxylic acid is converted into calcium salt using the calcium hydroxide base which on further reaction with
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
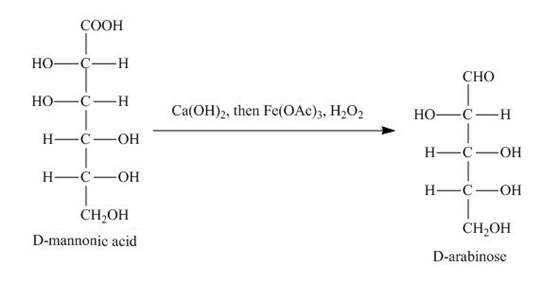
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (d) is shown below.
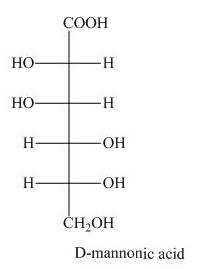
Figure 7
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with

Figure 8
The product obtained is the Ruff’s degradation product of the D-mannose. The D-mannonic acid is converted into calcium salt in the first step and then on reaction with
The product obtained when the product of part (d) is reacted with
(h)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
Concept introduction:
The alkylation of the hydroxyl group of sugars is an important reaction. The alkylation of hydroxyl groups is done with the help of alkylating agent
Answer to Problem 24.34AP
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
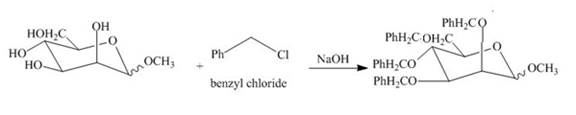
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (e) is shown below.
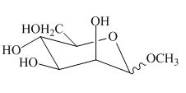
Figure 9
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with

Figure 10
The methyl D-mannopyranoside is alkylated in the strong base sodium hydroxide. The sodium hydroxide takes up the acidic proton of alcohol groups and converts them to alkoxide ion form. This alkoxide ion then substitutes the chloride group in the
The product obtained when the product of part (e) is reacted with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- Can I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forward
- I'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





