
Concept explainers
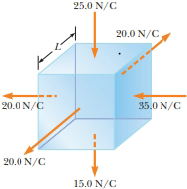
Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge L = 1.00 m in Figure P23.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric flux through the cube and (b) the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge he a single point charge?
Figure P23.32
(a)
The electric flux through the cube.
Answer to Problem 24.32P
The electric flux through the cube is
Explanation of Solution
The length of the edge of the cube is
The area vector is always out of face. The electric field going into the face of the cube makes
Write the expression for total flux through the cube
Here,
Write the area of the cube
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the electric flux through the cube is
(b)
The net charge inside the cube.
Answer to Problem 24.32P
The net charge inside the cube is
Explanation of Solution
The length of the edge of the cube is
Write the expression for flux through the cube by Gauss law
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the net charge inside the cube is
(c)
The number of charges inside the cube.
Answer to Problem 24.32P
The net charge is not a single point charge.
Explanation of Solution
The electric charge is the physical property of the matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
The net charge is not a single point charge as it does not produce a uniform field on the face of cubes. The equipotential surface of the single point charge is spherical. So the net charge is not a single point charge.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net charge is not a single point charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- A total charge Q is distributed uniformly on a metal ring of radius R. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the center of the ring at point O (Fig. P24.61)? b. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the point A lying on the axis of the ring a distance R from the center O (same length as the radius of the ring)? FIGURE P24.61arrow_forwardThe question is in the picture.arrow_forwardThe electric field everywhere on the surface of a charged sphere of radius 0.273 m has a magnitude of 520 N/C and points radially outward from the center of the sphere. (a) What is the net charge on the sphere? nC (b) What can you conclude about the nature and distribution of charge inside the sphere?arrow_forward
- The electric field on the axis of a uniformly charged ring has magnitude 400 kN/C at a point 6 cm from the ring center. The magnitude 15 cm from the center is 125 kN/C; in both cases the field points away from the ring. a. Find the rings radius b. find the rings chargearrow_forwardA particle with charge Q is located on the axis of a circle of radius R at a distance b from the plane of the circle (as shown). Show that if one-fourth of the electric flux from the charge passes through the circle, then R = √(3b).arrow_forward. A charge q located at the center of a regu- +5.80 µC is lar tetrahedron (a four-sided surface) as in Figure P15.50. Find (a) the total electric flux through the tetrahedron and (b) the electric flux through one face of the tetrahedron. Figure P15.50arrow_forward
- The electric field everywhere on the surface of a thin, spherical shell of radius 0.775 m is of magnitude 897 N/C and points radially toward the center of the sphere. (a) What is the net charge within the sphere's surface? X If the net charge inside the sphere is moved to the center of the sphere would this change the value of the electric field on the surface? nC (b) What is the distribution of the charge inside the spherical shell? O The negative charge has an asymmetric charge distribution. O The positive charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution. The negative charge has a spherically symmetric charge distribution. O The positive charge has an asymmetric charge distribution. 4arrow_forwardAn infinite sheet charge of has a charge density of +44.81 pC/m2 and covers the entire x-y plane. A second infinite sheet of charge has a charge density of −53.2 pC/m2 covers the entire y-z plane. What is the magnitude of the electric field at any point not on either surface?arrow_forward32. Assume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge1.00 m in Figure P24.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric lux through the cube and ( the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge be a single point charge? ON/C 200 N/C 200 N/C 850N/C 200N/C 5.ON/Carrow_forward
- We have a nonconducting solid sphere of radius 2.9 cm carrying a uniformly distributed positive charge of 4.3 nC. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 1 cm from the center of the sphere? b) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere? c) Now consider a conducting sphere with the same radius and total charge. In this situation, what is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere?arrow_forwardWe have a nonconducting solid sphere of radius 3.4 cm carrying a uniformly distributed positive charge of 7.6 nC. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 1.6 cm from the center of the sphere? b) What is the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4.4 cm from the center of the sphere?arrow_forwardA semicircle of radius a is in the first and Figure second quadrants, with the cen- ter of curvature at the origin. Positive charge +Q is distrib- uted uniformly around the left half of the semicircle, and nega- tive charge -Q is distributed uniformly around the right half of the semicircle (Fig. P21.86). What are the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the origin produced by this distribution of charge? +Qarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


