
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134564234
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 24, Problem 20EAP
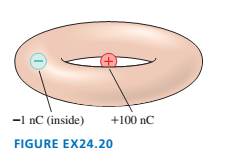
What is the net electric flux through the torus (i.e., doughnut
shape) of FIGURE EX24.20?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
A
30
PLEASE help with the experimental setup for this theory because i am so confused.
Part 2 - Geometry and Trigonometry
1. Line B touches the circle at a single point. Line A extends radially through the center of
the circle.
A
B
(a) Which line is tangential to the circumference of the circle?
(b) What is the angle between lines A and B.
2. In the figure below what is the angle C?
30
45
3. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
30°
4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
A
30°
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
Ch. 24 - Suppose you have the uniformly charged cube in...Ch. 24 - FIGURE Q24.2 shows cross sections of...Ch. 24 - The square and circle in FIGURE Q24.3 are in the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 4CQCh. 24 - Prob. 5CQCh. 24 - What is the electric flux through each of the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 7CQCh. 24 - The two spheres in FIGURE Q24.8 on the next page...Ch. 24 - The sphere and ellipsoid in FIGURE Q24.9 surround...Ch. 24 - A small, metal sphere hangs by an insulating...
Ch. 24 - l. FIGURE EX24.1 shows two cross sections of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.2 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.3 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.6 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.7 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.8 contains no net charge....Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - II The electric flux through the surface shown in...Ch. 24 - ]12. A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xy-plane....Ch. 24 - A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xz-plane. What...Ch. 24 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 24 - 15. A box with its edges aligned with
the...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.17 shows three charges. Draw these...Ch. 24 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE EX24.19 shows three Gaussian surfaces and...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the torus...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the cylinder...Ch. 24 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 24 - A spark occurs at the tip of a metal needle if the...Ch. 24 - The electric field strength just above one face of...Ch. 24 - The conducting box in FIGURE EX24.26 has been...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.27 shows a hollow cavity within a...Ch. 24 - A thin, horizontal, 10-cm-diameter copper plate is...Ch. 24 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 24 - II A tetrahedron has an equilateral triangle base...Ch. 24 - Charges q1= —4Q and q2= +2Q are located at x = —a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 24 - A spherically symmetric charge distribution...Ch. 24 - A neutral conductor contains a hollow cavity in...Ch. 24 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 24 - 37. A 20-cm-radius ball is uniformly charged to 80...Ch. 24 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has 6 cm and 10 cm inner and...Ch. 24 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 24 - Find the electric field inside and outside a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE P24.47 shows an infinitely wide conductor...Ch. 24 - FIGURE P24.48 shows two very large slabs of metal...Ch. 24 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 24 - A very long, uniformly charged cylinder has radius...Ch. 24 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 24 - II A long cylinder with radius b and volume charge...Ch. 24 - A spherical shell has inner radius Rin, and outer...Ch. 24 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 24 - Newton's law of gravity and Coulomb's law are both...Ch. 24 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 24 - An infinite cylinder of radius R has a linear...Ch. 24 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 24 - A sphere of radius R has total charge Q. The...Ch. 24 - II A spherical ball of charge has radius R and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Details solution No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forwardWill you please walk me through the calculations in more detail for solving this problem? I am a bit rusty on calculus and confused about the specific steps of the derivation: https://www.bartleby.com/solution-answer/chapter-3-problem-15e-modern-physics-2nd-edition/9780805303087/7cf8c31d-9476-46d5-a5a9-b897b16fe6fcarrow_forward
- please help with the abstract. Abstract - This document outlines the format of the lab report and describes the Excel assignment. The abstract should be a short paragraph that very briefly includes the experiment objective, method, result and conclusion. After skimming the abstract, the reader should be able to decide whether they want to keep reading your work. Both the format of the report and the error analysis are to be followed. Note that abstract is not just the introduction and conclusion combined, but rather the whole experiment in short including the results. I have attacted the theory.arrow_forwardUsing the Experimental Acceleration due to Gravity values from each data table, Data Tables 1, 2, and 3; determine the Standard Deviation, σ, mean, μ, variance, σ2 and the 95% Margin of Error (Confidence Level) Data: Ex. Acc. 1: 12.29 m/s^2. Ex. Acc. 2: 10.86 m/s^2, Ex. Acc. 3: 9.05 m/s^2arrow_forwardIn the Super Smash Bros. games the character Yoshi’s has a “ground pound” down special move where he launches himself downward to attack an enemy beneath him. A) If Yoshi flings himself downwards at 9.76 miles per hour to hit an enemy 10.5 m below him, how fast is Yoshi traveling when he hits the enemy? 1 mile = 1609 m B) How much time does it take Yoshi to hit the enemy beneath him?arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forwardPlz no chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY