
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134564234
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 24, Problem 17EAP
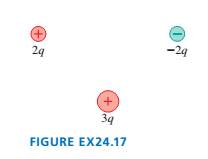
FIGURE EX24.17 shows three charges. Draw these charges on
your paper four times. Then draw two-dimensional cross sections
of three-dimensional closed surfaces through which the electric
flux is (a)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the resistance (in (2) of a 27.5 m long piece of 17 gauge copper wire having a 1.150 mm diameter?
0.445
ΧΩ
Find the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring).
d.
Ag
dFe
= 2.47
×
Find the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring).
d
Ag
= 2.51
dFe
×
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
Ch. 24 - Suppose you have the uniformly charged cube in...Ch. 24 - FIGURE Q24.2 shows cross sections of...Ch. 24 - The square and circle in FIGURE Q24.3 are in the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 4CQCh. 24 - Prob. 5CQCh. 24 - What is the electric flux through each of the...Ch. 24 - Prob. 7CQCh. 24 - The two spheres in FIGURE Q24.8 on the next page...Ch. 24 - The sphere and ellipsoid in FIGURE Q24.9 surround...Ch. 24 - A small, metal sphere hangs by an insulating...
Ch. 24 - l. FIGURE EX24.1 shows two cross sections of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.2 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.3 shows a cross section of two...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The electric field is constant over each face of...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.6 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.7 contains negative...Ch. 24 - The cube in FIGURE EX24.8 contains no net charge....Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - What is the electric flux through the surface...Ch. 24 - II The electric flux through the surface shown in...Ch. 24 - ]12. A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xy-plane....Ch. 24 - A 2.0cm3.0cm rectangle lies in the xz-plane. What...Ch. 24 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 24 - 15. A box with its edges aligned with
the...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the two...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.17 shows three charges. Draw these...Ch. 24 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE EX24.19 shows three Gaussian surfaces and...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the torus...Ch. 24 - What is the net electric flux through the cylinder...Ch. 24 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 24 - A spark occurs at the tip of a metal needle if the...Ch. 24 - The electric field strength just above one face of...Ch. 24 - The conducting box in FIGURE EX24.26 has been...Ch. 24 - FIGURE EX24.27 shows a hollow cavity within a...Ch. 24 - A thin, horizontal, 10-cm-diameter copper plate is...Ch. 24 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 24 - II A tetrahedron has an equilateral triangle base...Ch. 24 - Charges q1= —4Q and q2= +2Q are located at x = —a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 24 - A spherically symmetric charge distribution...Ch. 24 - A neutral conductor contains a hollow cavity in...Ch. 24 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 24 - 37. A 20-cm-radius ball is uniformly charged to 80...Ch. 24 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 24 - A hollow metal sphere has 6 cm and 10 cm inner and...Ch. 24 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 24 - Find the electric field inside and outside a...Ch. 24 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 24 - FIGURE P24.47 shows an infinitely wide conductor...Ch. 24 - FIGURE P24.48 shows two very large slabs of metal...Ch. 24 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 24 - A very long, uniformly charged cylinder has radius...Ch. 24 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 24 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 24 - II A long cylinder with radius b and volume charge...Ch. 24 - A spherical shell has inner radius Rin, and outer...Ch. 24 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 24 - Newton's law of gravity and Coulomb's law are both...Ch. 24 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 24 - An infinite cylinder of radius R has a linear...Ch. 24 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 24 - A sphere of radius R has total charge Q. The...Ch. 24 - II A spherical ball of charge has radius R and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- According to the provided information answer the question accorrding to grade 11 physics Jerry has decided to give up his part-time job for a new career, cat-burglar! Jerry loves the idea of dressing up like a cat all day and of course the chance of meeting Cat Woman! On Jerry's first "job" he figures out his escape plan. He travels 3.0 km south for 15 minutes and then 8.0 km west for 1.5 hours before reaching his house. Draw a sketch diagram of the path he took with all the appropriate labels.arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer all parts of the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY