
Concept explainers
(a)
To explain: The way through which nondisjunction of the synthetic chromosome would give rise to a colony that is half red and half white.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) clone large pieces of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
In the given experiment, Heiter and colleagues constructed synthetic chromosomes to find out the components of yeast chromosomes. They constructed plasmids with different parts of chromosomes. They observed proper segregation of synthetic chromosomes during mitosis. According to the assay, wild-type yeast colonies are white and mutated copies of adenine-requiring yeast colonies are red.
During non-disjunction of synthetic chromosomes, one daughter cell and its entire descendants obtain two copies of the synthetic chromosome and give rise to colonies that are white. On the other hand, other daughter cell and all of its descendants obtain no copies of the synthetic chromosome and give rise to colonies that are red. This leads the formation of half-white, half-red colony.
(b)
To explain: The way through which loss of the synthetic chromosome would give rise to a colony that is half red and half pink.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) clone large pieces of DNA in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of DNA replication machinery and causes the movement of replication fork.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
If synthetic chromosome loss, one daughter cell and all of its descendants obtain one copy of the synthetic chromosome that give rise to form pink colony. The other daughter cell and all of its descendants obtain no copies of the synthetic chromosome and give rise to form red colony. Thus, a colony formed that is half-pink and half-red.
(c)
To determine: The size of the centromere necessary for normal mitotic segregation along with the reason.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are necessary to clone large pieces of DNA in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of DNA replication machinery and causes the movement of replication fork.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Heiter and colleagues estimated that the frequency of aberrant mitotic procedures with different types of synthetic chromosomes by counting the frequency of different colony types. They constructed synthetic chromosomes with DNA fragments of various sizes having a known centromere.
Based on the given data, it can be concluded that the centromere size needed for normal mitotic segregation should be less than 0.63 kbp. This is because all the fragments of DNA of 0.63 kbp size contain mitotic stability and cannot show loss of chromosomes.
Thus, the minimum functional centromere should be less than 0.63 kbp, because all fragments of this size or larger determine relative mitotic stability.
Thus, the centromere size required for normal mitotic segregation should be smaller than 0.63 kbp.
(d)
To explain: The way through which the synthetic chromosomes can be replicated more-or-less properly.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are required to clone large pieces of DNA in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of DNA replication machinery and causes the movement of replication fork.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Telomeres are ribonucleic proteins that are the “protective ends” of “linear chromosomes”. Telomeres generally shorten throughout the lifetime of a person. The synthetic chromosomes are constructed to determine the components of yeast chromosomes.
Telomeres are not required to replicate circular chromosomes beacuse telomeres are important to completely replicate linear DNA. Since, synthetic chromosomes are circular; hence, telomeres are not required for their replication
(e)
To explain: The chromosome size required for normal mitotic segregation and the reasons for it.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are required to clone large pieces of DNA in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of DNA replication machinery and causes the movement of replication fork.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
According to given data, if chromosome size is larger, then there will be less chances of total error rate. Larger is the chromosome, the more closely it is segregated. According to the given data, neither a lesser size below, neither which the synthetic chromosome is fully unstable, nor does a greater size above, which stability wills no longer change.
(f)
To determine: Whether the centeromeric and telomeric sequences used in this experiment explain the mitotic stability of normal yeast chromosomes or must other elements be involved.
Introduction:
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are required to clone large pieces of DNA in yeast cells. It can generate unlimited number of DNA copies. Cloning genomic DNA into YAC is useful to analyze very long DNA sequence such as human genes.
The three types of DNA sequence that are necessary to ensure proper propagation and replication of a YAC in a yeast cell are as follows:
1) Centromere for the attachment of mitotic spindle fibers. It attracts one copy of each replicated chromosome into each new daughter cell.
2) Telomere is found at each end of a chromosome. It prevents the linear DNA from degradation.
3) Autonomous replicating sequence (origin of replication) allows assembly of DNA replication machinery and causes the movement of replication fork.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Graphical representation:
Fig.1 represents the graphical representation of the length of DNA and total percentage of the error rate.
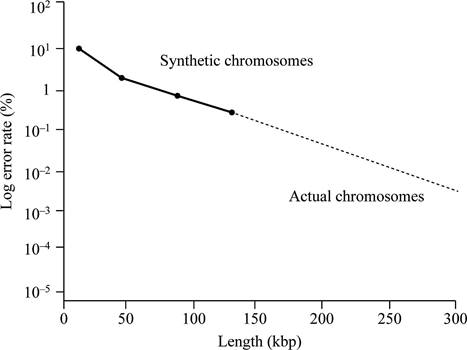
Fig.1: The length of DNA and total percentage of the error rate.
Normal yeast chromosomes are linear in structure and ranges from 250 kbp to 2,000 kbp. They have a mitotic error frequency of 10-5 per cell division. Based on the given data, a graph can be plotted. This graph is plotted against the length of DNA and total percentage of the error rate.
Hence, it can be concluded that the replication will not be stable even if the synthetic chromosomes are longer in size like normal yeast chromosomes. It is due to the requirement of some additional elements (other, as yet undiscovered, elements) are required for stability that occur in normal chromosomes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTR
- 7. A solution of aniline in diethyl ether is added to a separatory funnel. Which ONE of the following aqueous solutions will remove aniline from the ether layer (and transfer it to the aqueous layer) if it is added to the separatory funnel and the funnel is shaken? A) aqueous NH3 B) aqueous Na2CO3 C) aqueous HCl D) aqueous NaOH E) aqueous CH3COONa (sodium acetate)arrow_forward11. Which of the following choices is the best reagent to use to perform the following conversion? A) 1. LiAlH4 2. H₂O B) HCI, H₂O D) NaOH, H₂O E) Na№3 ? 'N' 'N' C) 1. CH3MgBr 2. HCI, H₂Oarrow_forwardNH2 ΝΗΣ NH₂ NH2 NH2 A OCH3 NO₂ B C D E 1. Which one of the five compounds above is the strongest base? 2. Which one of the five compounds above is the second-strongest base? (That is, which one is next-to-strongest base?) 3. Which one of the five compounds above is the weakest base? 4. Which one of the five compounds above is the second-weakest base? (That is, which one is next-to-weakest base?) NO2arrow_forward
- Draw a diagram to demonstrate 3' to 5' exonuclease activity?arrow_forward1. Write the piece of mRNA that would code for the amino acid sequence NH3 - met - tyr - cys- his- CO2. Label the 5' and 3' ends. (diagram attached) 2.arrow_forwardYou were tasked with purifying an untagged transcription factor (molecular weight 65,000Da, isoelectric point unknown) from a contaminant Protein A (molecular weight 50,000 Da, isoelectric point 5.0). You were also instructed to use the protein for crystallization studies after purification.i) In the initial purification step, which type of chromatography should you attempt? Explain your choice and specify the requirements of the buffer solution you should use. ii) Analyzing the proteins recovered from step i) using SDS-PAGE, you still observed a faint band of Protein A in addition to the transcription factor band. Given the limited time available for further purification, you must choose ONE appropriate chromatography method to maximize the chances of separating the two proteins as well as your crystallization studies. Provide a detailed explanation of your selection and the techniques/strategies you would employ to achieve this.arrow_forward
- You were given a mixture of two proteins with different isoelectric points and molecular weights:• Protein X: pI 4.2, MW 42,000• Protein Y: pI 9.8, MW 90,000Using a Tris-glycine discontinuous native gel (pH8.3) electrophoresis system with a running gel of 12%, only a single band was observed upon protein staining after electrophoresis. Explain the observed result and discuss possible factors affecting protein migration in this system.arrow_forwardThe standard cost of Product B manufactured by Oriole Company includes 3.5 units of direct materials at $5.40 per unit. During June, 27,300 units of direct materials are purchased at a cost of $5.15 per unit, and 27,300 units of direct materials are used to produce 7,600 units of Product B. (a) Compute the total materials variance and the price and quantity variances. Total materials variance Materials price variance Materials quantity variance $ (b) Compute the total materials variance and the price and quantity variances, assuming the purchase price is $6.35 and the quantity purchased and used is 26,300 units. Total materials variance Materials price variance Materials quantity variance $arrow_forwardThe pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to form acetyl CoA. E₁, E2, and E3 are abbreviations for the enzymes of the complex. Classify the enzyme names, prosthetic groups, and reactions as E1, E2, or E3. E₁ E2 Answer Bank E3 transfer of electrons to FAD and then to NAD+ transfer of acetyl group to coenzyme A formation of hydroxyethyl-TPP hydroxyethyl group transferred to lipoamide thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) FAD lipoamide dihydrolipoyl transacetylase pyruvate dehydrogenase dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenasearrow_forward
- Patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency show high levels of lactic acid in the blood. However, in some cases, treatment with dichloroacetate (DCA), which inhibits the kinase associated with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, lowers lactic acid levels. How does DCA act to stimulate pyruvate dehydrogenase activity? DCA activates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. DCA increases phosphorylation levels of pyruvate dehydrogenase. DCA inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. ODCA activates pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase. What does this suggest about pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in patients who respond to DCA? The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is active only when phosphorylated by the kinase. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is active only in the presence of the kinase. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is completely inactive. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex displays some residual activity.arrow_forwardThe reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron-transport chain. The energy from the electron-transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation. Which compounds donate electrons to the electron- transport chain? H₂O NADH பப NAD+ ATP ADP FADH₂ FAD Which compounds are the final products of the electron-transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation? H₂O NADH NAD+ ΠΑΤΡ Π ADP FADH₂ FAD Which compound is the final electron acceptor in the electron-transport chain? Оно NADH NAD+ ATP ADP FADH₂ FADarrow_forwardHexokinase in red blood cells has a Michaelis constant (KM) of approximately 50 μM. Because life is hard enough as it is, let's assume that hexokinase displays Michaelis-Menten kinetics. What concentration of blood glucose yields an initial velocity (V) equal to 90% of the maximal velocity (Vmax)? [glucose] = What does the calculated substrate concentration at 90% Vmax tell you if normal blood glucose levels range between approximately 3.6 and 6.1 mM? Hexokinase operates near Vmax only when glucose levels are low. Hexokinase normally operates far below Vmax. Hexokinase operates near Vmax only when glucose levels are high. Hexokinase normally operates near Vmax mMarrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





