
Concept explainers
To label: The parts of the conjunctive in Figure 24.1 (a).
Introduction: The eye of a human is a specialized organ. It has the ability to process and receive visual details. The light is detected by the eye and converted into
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
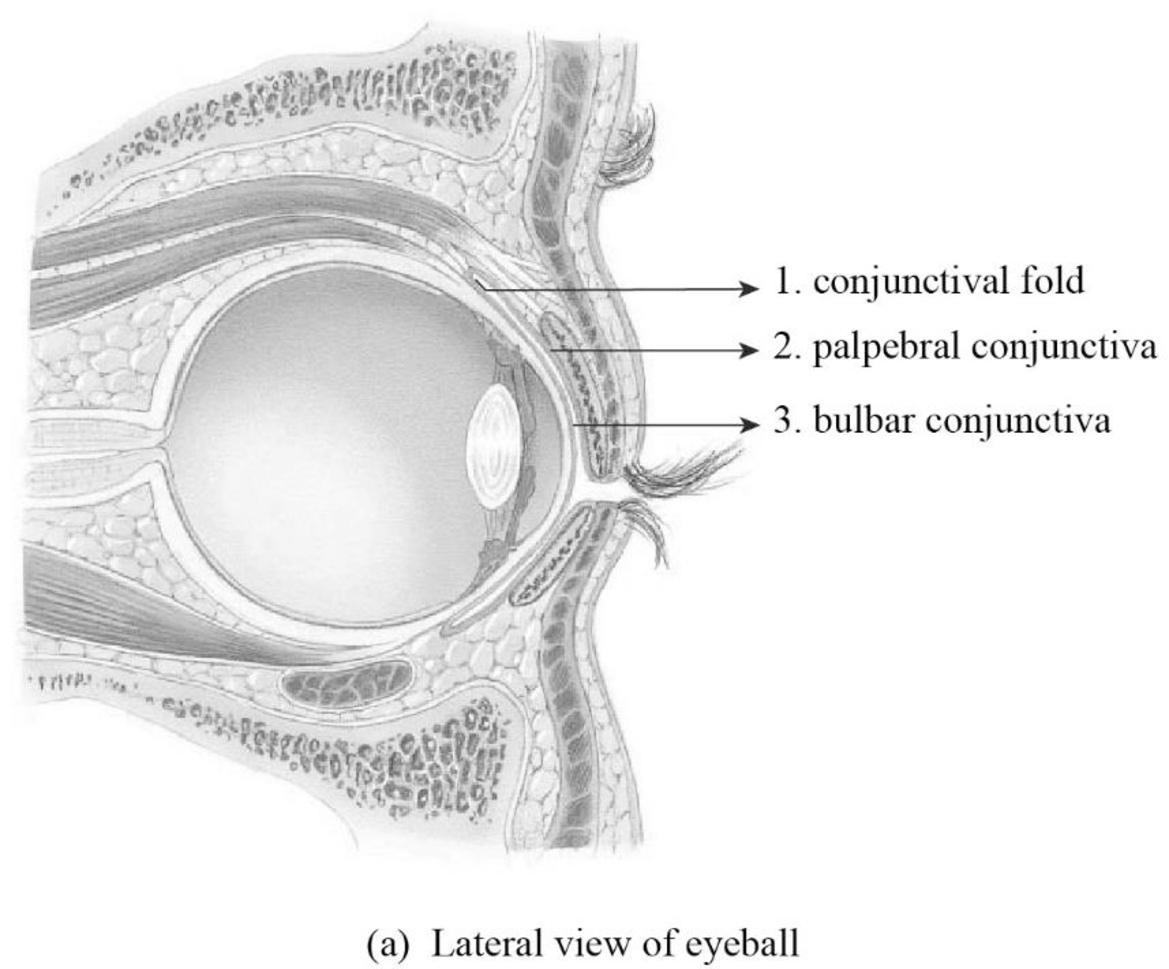
Fig1: The parts of conjunctiva
Explanation of Solution
1. Conjunctival fold: The conjunctiva is the mucous membrane. The eyelids’ inner surface and eyeballs’ exposed surface are lined by the conjunctiva. The pocket is formed by the conjunctival fold that possesses contacts from moving toward the eyeball’s posterior part.
2. Palpebral conjunctiva: The palpebral conjunctiva is the portion of the conjunctiva. The interior of the eyelid is covered by the palpebral conjunctiva.
3. Bulbar conjunctiva: The bulbar conjunctiva is otherwise referred to as ocular conjunctiva and it is a portion of the conjunctiva. The bulbar conjunctiva does not cover the cornea. It covers the anterior portion of the white of the eye.
To label: The structures of the lacrimal apparatus in Figure 24.1 (b).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
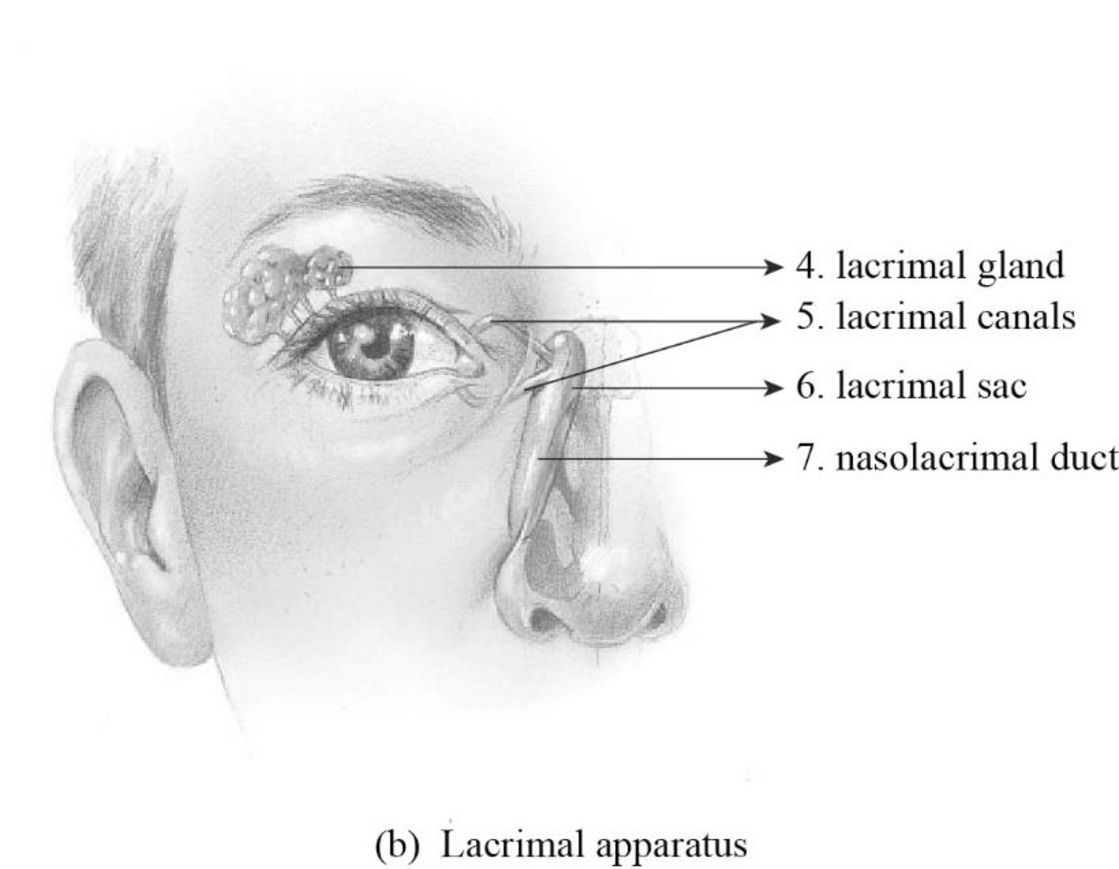
Fig1: The structures of the lacrimal apparatus
Explanation of Solution
A group of structure involved in draining and generating tears is referred to as the lacrimal apparatus.
4. Lacrimal gland: The lacrimal gland secretes and generates tears onto the surface of the eye. The fluid is released continuously by the lacrimal gland, which protects and cleanses the surface of the eyes.
5. Lacrimal canals: They are small channels found in every eyelid and it is also called as lacrimal canaliculi. The tear is drained into the enlarged lacrimal sac from the eyes by the lacrimal canals.
6. Lacrimal sac: The dilated oval upper end of the nasolacrimal duct is lacrimal sac. The lacrimal sac is also referred to as lachrymal sac.
7. Nasolacrimal duct: The nasolacrimal duct is otherwise known as the tear duct. The tear is received by the enlarged nasolacrimal duct from the lacrimal sac and the tears are drained into the nasal cavity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
EBK LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ANATOMY AND P
- 22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forwardCan you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forward
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- Describe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





