
Concept explainers
EXPANDED STATEMENT OF
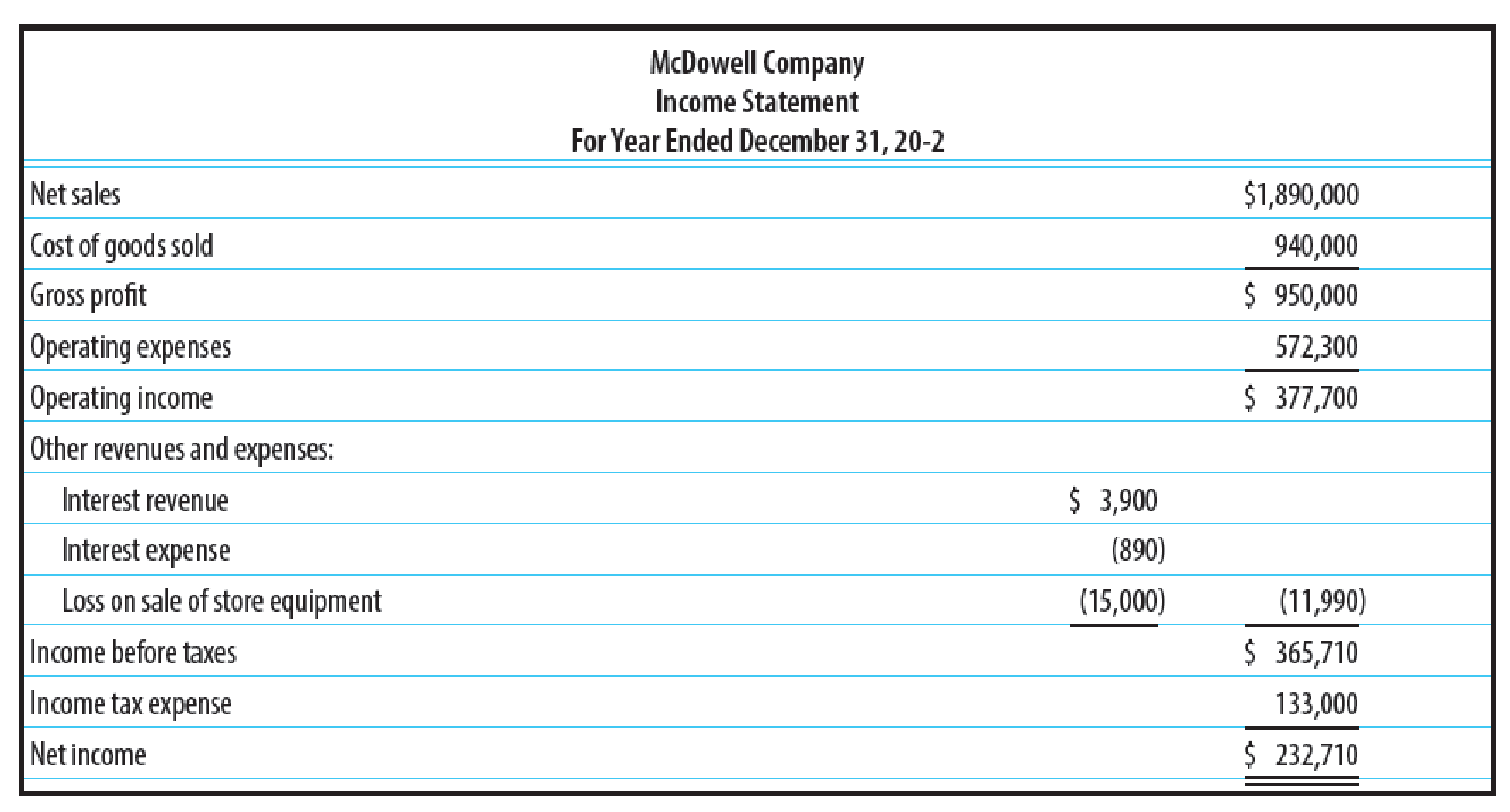

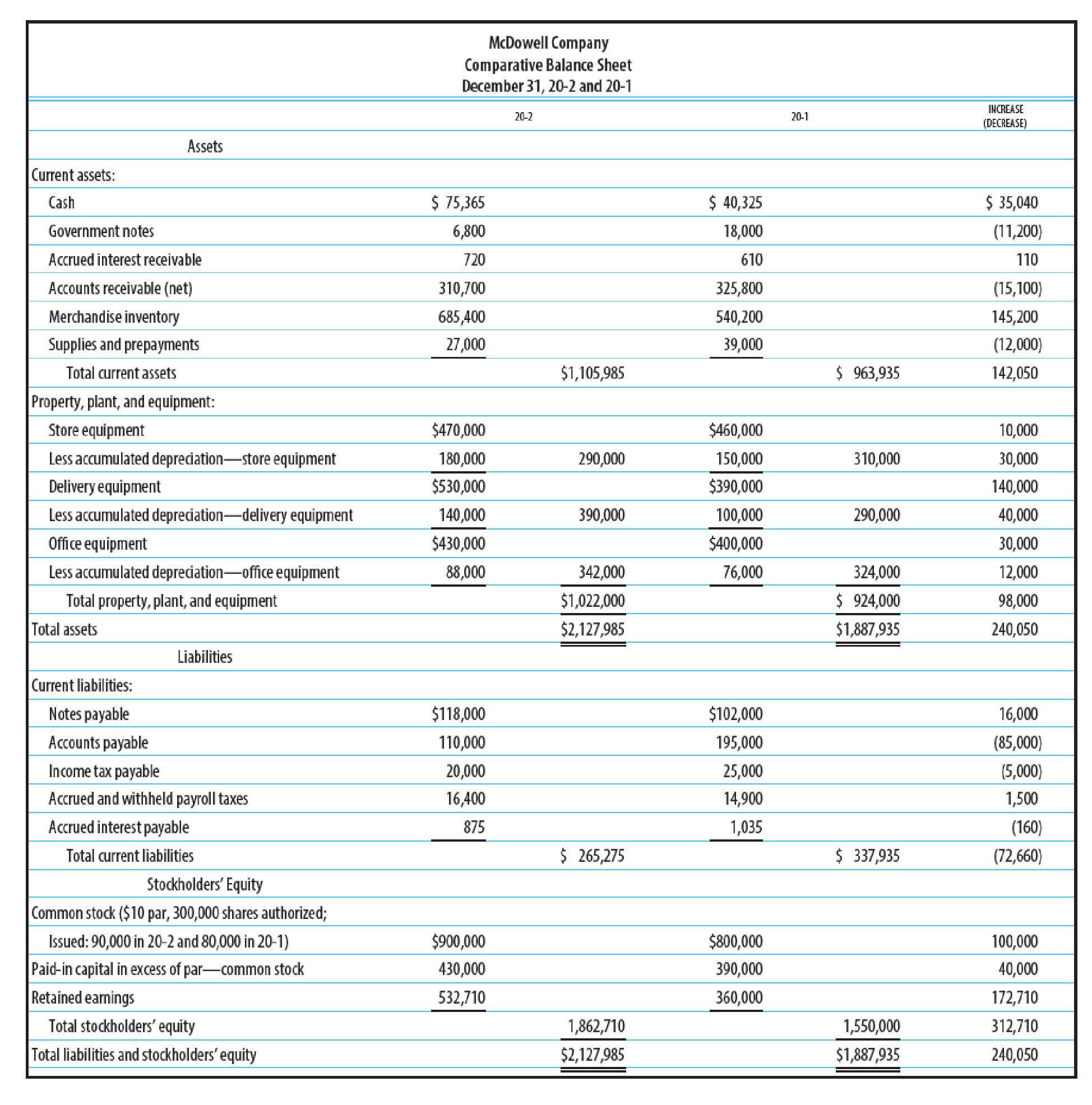
Additional information:
1. Store equipment was sold in 20-2 for $35,000. Additional information on the store equipment sold is provided below.
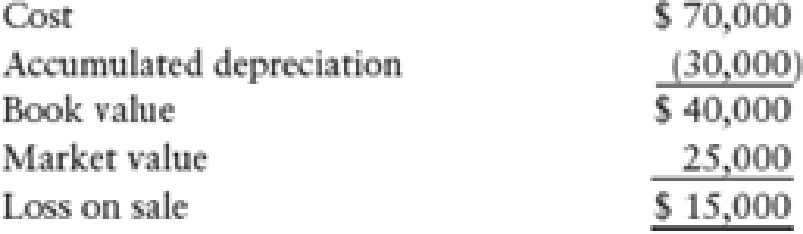
2.
3. The following purchases were made for cash:

4. Declared and paid cash dividends of $60,000.
5. Issued 10,000 shares of $10 par common stock for $142 per share.
6. Acquired additional office equipment by issuing a note payable for $ 16,000.
REQUIRED
Prepare a statement of cash flows explaining the change in cash and cash equivalents for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
SCHEDULE FOR CALCULATION OF CASH GENERATED FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES Using the information provided in Problem 23-12A for McDowell Company, prepare the following:
1. A schedule for the calculation of cash generated from operating activities for McDowellCompany for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
2. A partial statement of cash flows for McDowell Company reporting cash from operating activities under the direct method for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
1.
Prepare a schedule for the calculation of cash generated from operating activities for M Company for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
Explanation of Solution
Direct method: Under direct method, cash receipts from customers (cash inflows) and cash payments to suppliers (cash outflows) are reported under the operating activities.
Operating activities: Operating activities include cash inflows and outflows from business operations.
Prepare a schedule for the calculation of cash generated from operating activities for M Company for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
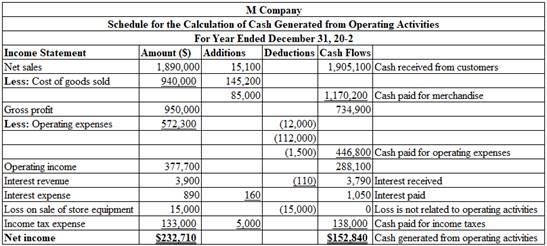
Table (1)
2.
Prepare a statement of cash flows for M Company under the direct method for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
Direct method: Under direct method, cash receipts from customers (cash inflows) and cash payments to suppliers (cash outflows) are reported under the operating activities.
Operating activities: Operating activities include cash inflows and outflows from business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from operating activities using direct method:
| Cash flows from operating activities (Direct method) |
| Add: Cash receipts. |
| Cash receipt from customer |
| Dividend received |
| Interest received |
| Less: Cash payments: |
| To supplier for acquisition of inventory |
| To employees |
| For interest on loans |
| Income tax expenses and other operating expenses |
| Net cash provided from or used by operating activities |
Table (2)
Cash flows from investing activities: Investing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company for acquisition of long term assets. It includes the purchase or sale of equipment or land, or marketable securities, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from investing activities:
| Cash flows from investing activities |
| Add: Proceeds from collection of loan made to borrowers |
| Sale of marketable securities / investments |
| Sale of property, plant and equipment |
| Proceeds from discounting notes receivables |
| Deduct: Purchase of fixed assets/long-lived assets |
| Loan made by the company to others |
| Purchase of marketable securities |
| Net cash provided from or used by investing activities |
Table (3)
Cash flows from financing activities: Financing activities refer to the activities carried out by a company to mobilize funds to carry out the business activities. It includes raising cash from long-term debt or payment of long-term debt, which is used for business operations.
The below table shows the way of calculation of cash flows from financing activities:
| Cash flows from financing activities |
| Add: Issuance of common stock |
| Proceeds from borrowings by signing of a mortgage |
| Proceeds from sale of treasury stock |
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
| Deduct: Payment of dividend |
| Repayment of debt |
| Interest paid |
| Redemption of debt |
| Purchase of treasury stock |
| Net cash provided from or used by financing activities |
Table (4)
Prepare a statement of cash flows for M Company under the direct method for the year ended December 31, 20-2.
| M Company | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method (Partial) | ||
| For the Year Ended December 20-2 | ||
| Details | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||
| Cash receipts: | ||
| Cash received from customers | 1,905,100 | |
| Interest received | 3,790 | |
| Total cash receipts | 1,908,890 | |
| Cash payments: | ||
| Cash paid for merchandise | (1,170,200) | |
| Cash paid for operating expenses | (446,800) | |
| Cash paid for interest | (1,050) | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | (138,000) | |
| Total cash payments | (1,756,050) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $152,840 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||
| Sold store equipment | $25,000 | |
| Purchased store equipment | (64,000) | |
| Purchased delivery equipment | (140,000) | |
| Purchased office equipment | (30,000) | |
| Net cash used by investing activities | (209,000) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||
| Issued common stock | $140,000 | |
| Paid cash dividends | (60,000) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 80,000 | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $23,840 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, January 1, 20-2 | 58,325 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, December 31, 20-2 | $82,165 | |
| Schedule of Noncash Investing and Financing Activities: | ||
| Acquired store equipment by issuing a note payable | $16,000 | |
Table (5)
Working notes:
Prepare the schedule in the changes of current assets and liabilities.
| Schedule in the Change of Assets and Liabilities | ||||
| Details | Amount ($) | Adjustment in Operating Activities | ||
| Accounts | 20-2 | 20-1 | Increase/ (Decrease) | |
| Accounts receivable | 310,700 | 325,800 | (15,100) | Add |
| Merchandised inventory | 685,400 | 540,200 | 145,200 | Less |
| Accounts payable | 110,000 | 195,000 | (85,000) | Less |
| Income tax payable | 20,000 | 25,000 | (5,000) | Less |
| Supplies and prepayments | 27,000 | 39,000 | (12,000) | Add |
| Accrued and withheld payroll taxes | 16,400 | 14,900 | 1,500 | Add |
| Accrued interest receivable | 720 | 610 | 110 | Less |
| Accrued interest payable | 875 | 1,035 | (160) | Less |
Table (4)
Calculate the amount of cash received from customers.
Calculate the amount of cash received for interest.
Calculate the amount of cash paid for merchandise in 20-2.
Compute the amount of cash received from customers in 20-2.
Compute the amount of cash paid for interest in 20-2.
Compute the amount of cash paid for income taxes in 20-2.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23A Solutions
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
- Direct materials price variancearrow_forward$ 36,000 204,000 The Drysdale, Koufax, and Marichal partnership has the following balance sheet immediately prior to liquidation: Cash Noncash assets Liabilities Drysdale, loan $ 50,000 10,000 Total assets $ 240,000 Drysdale, capital (50%) Koufax, capital (30%) Marichal, capital (20%) Total liabilities and capital 70,000 60,000 50,000 $ 240,000 Required: a-1. Determine the maximum loss that can be absorbed in Step 1. Then, assuming that this loss has been incurred, determine the next maximum loss that can be absorbed in Step 2. a-2. Liquidation expenses are estimated to be $15,000. Prepare a predistribution schedule to guide the distribution of cash. b. Assume that assets costing $74,000 are sold for $60,000. How is the available cash to be divided? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.arrow_forwardCalculate GP ratio round answers to decimal placearrow_forward
- What is the gross profit percentage for this periodarrow_forwardThe company's gross margin percentage is ?arrow_forwardProblem 19-13 (Algo) Shoney Video Concepts produces a line of video streaming servers that are linked to personal computers for storing movies. These devices have very fast access and large storage capacity. Shoney is trying to determine a production plan for the next 12 months. The main criterion for this plan is that the employment level is to be held constant over the period. Shoney is continuing in its R&D efforts to develop new applications and prefers not to cause any adverse feelings with the local workforce. For the same reason, all employees should put in full workweeks, even if that is not the lowest-cost alternative. The forecast for the next 12 months is MONTH FORECAST DEMAND January February March April 530 730 830 530 May June 330 230 July 130 August 130 September 230 October 630 730 800 November December Manufacturing cost is $210 per server, equally divided between materials and labor. Inventory storage cost is $4 per unit per month and is assigned based on the ending…arrow_forward
- Compute 007s gross profit percentage and rate of inventory turnover for 2016arrow_forwardHeadland Company pays its office employee payroll weekly. Below is a partial list of employees and their payroll data for August. Because August is their vacation period, vacation pay is also listed. Earnings to Weekly Vacation Pay to Be Employee July 31 Pay Received in August Mark Hamill $5,180 $280 Karen Robbins 4,480 230 $460 Brent Kirk 3,680 190 380 Alec Guinness 8,380 330 Ken Sprouse 8,980 410 820 Assume that the federal income tax withheld is 10% of wages. Union dues withheld are 2% of wages. Vacations are taken the second and third weeks of August by Robbins, Kirk, and Sprouse. The state unemployment tax rate is 2.5% and the federal is 0.8%, both on a $7,000 maximum. The FICA rate is 7.65% on employee and employer on a maximum of $142,800 per employee. In addition, a 1.45% rate is charged both employer and employee for an employee's wages in excess of $142,800. Make the journal entries necessary for each of the four August payrolls. The entries for the payroll and for the…arrow_forwardThe direct materials variance is computed when the materials are purchasedarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





