
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of Isobutyl amine has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
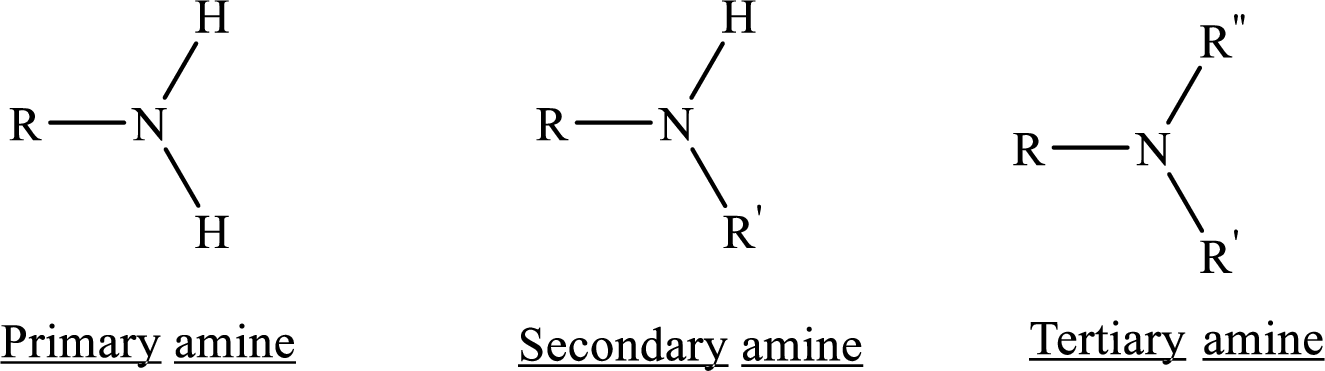
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of triphenylamine has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
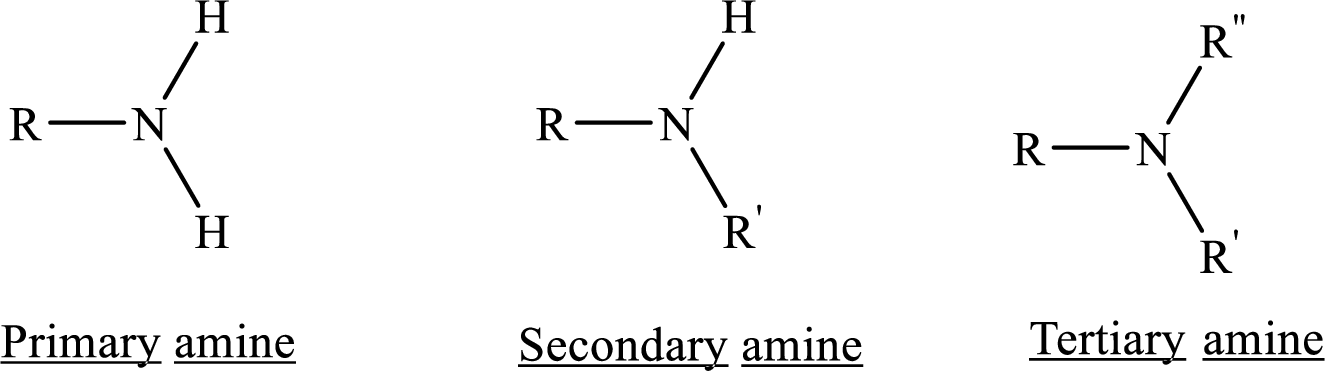
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula of diisopropylamine has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry Structure is the arrangement of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule, specifically which atoms are chemically bonded to what other atoms with what kind of chemical bond.
Amines are the derivatives of ammonia
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the amide, different types of amides can form.
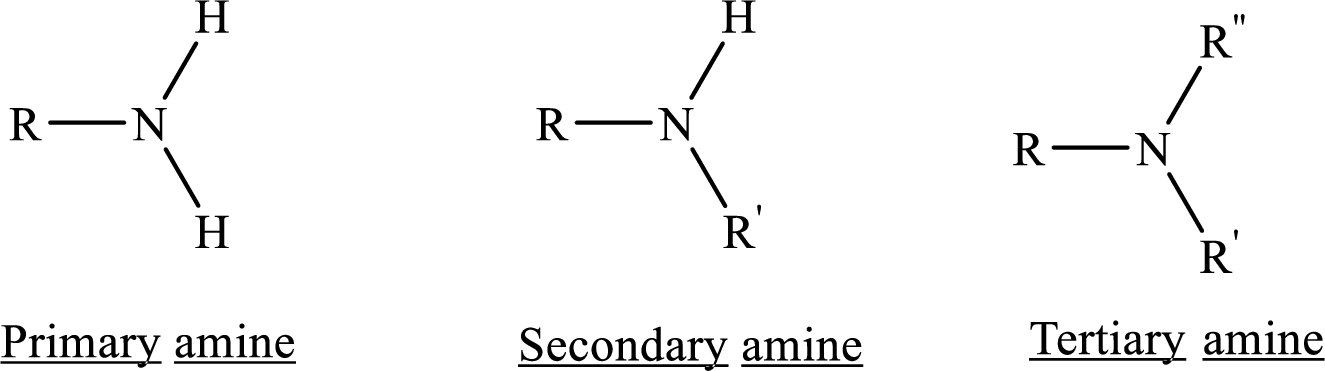
From the name of the compound its structure can be determined.
Primary amines can be named in the IUPAC system in several ways,
For simple amines the suffix – amine is added to the name of the alkyl substituent.
The suffix-amine can be used in place of the final –e in the name of the parent compound.
For a secondary amine an N prefixes the compound giving the shorter carbon chain and its chain prefix name.
For a tertiary amine an N, N prefixes the compound giving the two shorter carbon chains and their side chain prefix names.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

