
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Preparation of imine:
An imine is a compound having
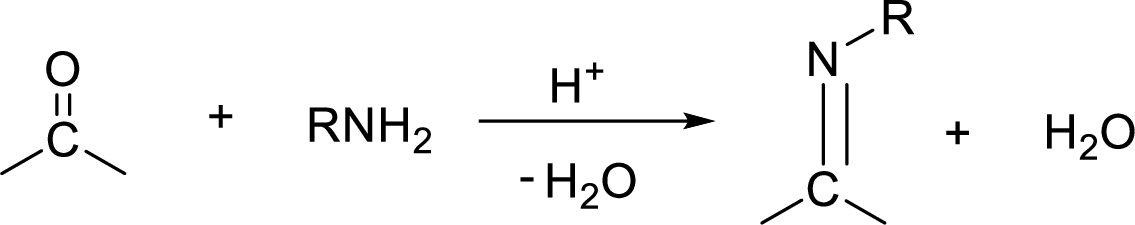
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a
(b)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Amide Hydrolysis: In presence of base, amide reacts with water to form the corresponding amine and
(c)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
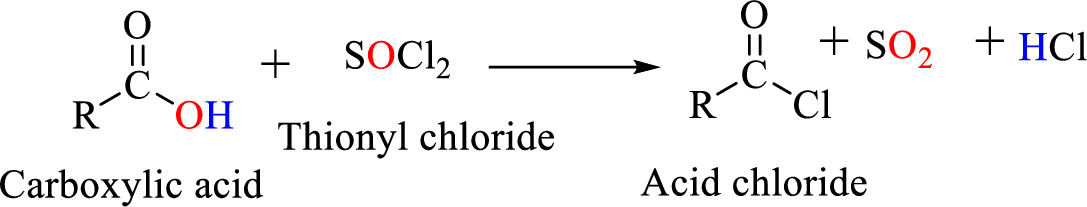
Preparation of amine: A primary amine is formed when an
Thionyl chloride:
(d)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Thionyl chloride:
(e)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Acid chlorides are most often prepared by treating a carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride.
Amide Formation: Amide is formed when an acid chloride reacts with an amine or ammonia.
Here, the chlorine atom that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom of the acid chloride is being replaced by
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction. In a reaction,
(f)
Interpretation:
Synthesis of benzylamine from the given starting material has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Preparation of amide: An amide is formed when an ester is reacted with ammonia.
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction. In a reaction,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 23 Solutions
EP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-OWL V2 ACCESS
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


