
Concept explainers
(a)
The electric potential of each of the three shells.
(a)
Answer to Problem 89P
The electric potential
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The inner shell is uncharged.
The middle shell has a positive charge
The outer shell has a negative charge
Formula used:
The expression for Gauss’s Law is given by,
The expression for potential is given by,
Calculation:
The required diagram is shown in Figure 1.
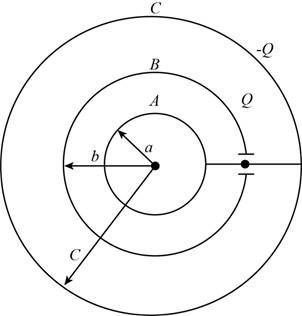
Figure 1
Applying Gauss’s law to a spherical Gaussian surface of radius
And
Applying Gauss’s law to a spherical Gaussian surface of radius
The potential between
And since
Therefore,
The inner shell too doesn’t carry charge, so the field between the points
Conclusion:
Therefore, The electric potential
(b)
The electric potential of each shell and the final charge on each shell.
(b)
Answer to Problem 89P
The electric potential of the shell
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Given:
The inner shell is uncharged.
The middle shell has a positive charge
The outer shell has a negative charge
Formula used:
The expression for Gauss’s Law is given by,
The expression for potential is given by,
Calculation:
When the inner and outer shells are connected their potentials become equal as a consequence of the distribution of charge.
The charges on the surface
The value of
The potential of shells a and c is given by,
The electric field between the points
The enclosed charge for
The potential difference between b and ciscalculated as,
Solve further,
Equate equation (2) and (3).
Substitute
The potential across
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric potential of the shell
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- A coat hanger of mass m = 0.255 kg oscillates on a peg as a physical pendulum as shown in the figure below. The distance from the pivot to the center of mass of the coat hanger is d = 18.0 cm and the period of the motion is T = 1.37 s. Find the moment of inertia of the coat hanger about the pivot.arrow_forwardReview Conceptual Example 3 and the drawing as an aid in solving this problem. A conducting rod slides down between two frictionless vertical copper tracks at a constant speed of 3.9 m/s perpendicular to a 0.49-T magnetic field. The resistance of th rod and tracks is negligible. The rod maintains electrical contact with the tracks at all times and has a length of 1.4 m. A 1.1-Q resistor is attached between the tops of the tracks. (a) What is the mass of the rod? (b) Find the change in the gravitational potentia energy that occurs in a time of 0.26 s. (c) Find the electrical energy dissipated in the resistor in 0.26 s.arrow_forwardA camera lens used for taking close-up photographs has a focal length of 21.5 mm. The farthest it can be placed from the film is 34.0 mm. (a) What is the closest object (in mm) that can be photographed? 58.5 mm (b) What is the magnification of this closest object? 0.581 × ×arrow_forward
- Given two particles with Q = 4.40-µC charges as shown in the figure below and a particle with charge q = 1.40 ✕ 10−18 C at the origin. (Note: Assume a reference level of potential V = 0 at r = ∞.) Three positively charged particles lie along the x-axis of the x y coordinate plane.Charge q is at the origin.Charge Q is at (0.800 m, 0).Another charge Q is at (−0.800 m, 0).(a)What is the net force (in N) exerted by the two 4.40-µC charges on the charge q? (Enter the magnitude.) N(b)What is the electric field (in N/C) at the origin due to the two 4.40-µC particles? (Enter the magnitude.) N/C(c)What is the electrical potential (in kV) at the origin due to the two 4.40-µC particles? kV(d)What If? What would be the change in electric potential energy (in J) of the system if the charge q were moved a distance d = 0.400 m closer to either of the 4.40-µC particles?arrow_forward(a) Where does an object need to be placed relative to a microscope in cm from the objective lens for its 0.500 cm focal length objective to produce a magnification of -25? (Give your answer to at least three decimal places.) 0.42 × cm (b) Where should the 5.00 cm focal length eyepiece be placed in cm behind the objective lens to produce a further fourfold (4.00) magnification? 15 × cmarrow_forwardIn a LASIK vision correction, the power of a patient's eye is increased by 3.10 D. Assuming this produces normal close vision, what was the patient's near point in m before the procedure? (The power for normal close vision is 54.0 D, and the lens-to-retina distance is 2.00 cm.) 0.98 x marrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardA shopper standing 2.00 m from a convex security mirror sees his image with a magnification of 0.200. (Explicitly show on paper how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for mirrors found on page 1020. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (a) Where is his image (in m)? (Use the correct sign.) -0.4 m in front of the mirror ▾ (b) What is the focal length (in m) of the mirror? -0.5 m (c) What is its radius of curvature (in m)? -1.0 marrow_forwardAn amoeba is 0.309 cm away from the 0.304 cm focal length objective lens of a microscope.arrow_forward
- Two resistors of resistances R1 and R2, with R2>R1, are connected to a voltage source with voltage V0. When the resistors are connected in series, the current is Is. When the resistors are connected in parallel, the current Ip from the source is equal to 10Is. Let r be the ratio R1/R2. Find r. I know you have to find the equations for V for both situations and relate them, I'm just struggling to do so. Please explain all steps, thank you.arrow_forwardBheem and Ram, jump off either side of a bridge while holding opposite ends of a rope and swing back and forth under the bridge to save a child while avoiding a fire. Looking at the swing of just Bheem, we can approximate him as a simple pendulum with a period of motion of 5.59 s. How long is the pendulum ? When Bheem swings, he goes a full distance, from side to side, of 10.2 m. What is his maximum velocity? What is his maximum acceleration?arrow_forwardThe position of a 0.300 kg object attached to a spring is described by x=0.271 m ⋅ cos(0.512π⋅rad/s ⋅t) (Assume t is in seconds.) Find the amplitude of the motion. Find the spring constant. Find the position of the object at t = 0.324 s. Find the object's velocity at t = 0.324 s.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





