
Concept explainers
(a)
The electric potential at the point on
(a)
Answer to Problem 27P
The electric potential at the point on
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The charge on each particle is
Formula used:
The expression for the potential at the point whose coordinates is
Calculation:
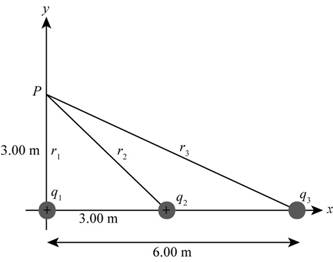
Figure (1)
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The potential at the point is calculated as,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric potential at the point on
(b)
The electric potential at the point on
(b)
Answer to Problem 27P
The electric potential at the point on
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The charge on first and second particle is
The charge on third particle is
Formula used:
The expression for the potential at the point whose coordinates is
Calculation:
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The potential at the point is calculated as,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric potential at the point on
(c)
The electric potential at the point on
(c)
Answer to Problem 27P
The electric potential at the point on
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The charge on first and third particle is
The charge on second particle is
Formula used:
The expression for the potential at the point whose coordinates is
Calculation:
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The distance to the point
The potential at the point is calculated as,
Conclusion:
Therefore, The electric potential at the point on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Can you help me to solve this two questions can you teach me step by step how to solve it.arrow_forwardGiven: ruler 11.56 g, small washer 1.85 g each, large washer 24.30g each Use the data in Data Tables 4 and 5 to experimentally determine the mass of your ruler. Use one of your 2 trials with 1 small washer at 0 cm, one of your 2 trials with 2 small washers at 0 cm, and one of your 2 trials with 3 small washers at 0 cm to find three experimental values for the mass of the ruler. How do you experimentalls determine the mass?arrow_forwardCompare the 3 experimental masses of your ruler to the measured mass of your ruler (Data Table 1) by calculating the percent error for each experimental value. Which trial provided the best data for determining the mass of the ruler? Please help, I am not sure how to calculate this. Thanks!arrow_forward
- Please help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Please graph unsing centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line. Thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardBased on your graph, explain how centripetal force is affected when the hanging mass changes. Does your graph verify the relationship in the equation r = x^i + y^j = r cos ωt I + r sin ωt^j?arrow_forward
- Did your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. My data shows that they are not equal to each other. So what does this mean? Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease help, everytime I try to input the data only one point shows on the graph. Graph of centripetal force, Fc, versus V E2 from Activity 1. Include a line of best fit and record the equation of the line.arrow_forwardExplain how your experiment met the condition for equilibrium in Equation 4: ΣFvertical = ΣFy = 0.arrow_forward
- Can i get answer and solution for this question and can you teach me What we use to get the answer.arrow_forwardCan i get answer and solution and can you teach me how to get it.arrow_forwardConsider a image that is located 30 cm in front of a lens. It forms an upright image 7.5 cm from the lens. Theillumination is so bright that that a faint inverted image, due to reflection off the front of the lens, is observedat 6.0 cm on the incident side of the lens. The lens is then turned around. Then it is observed that the faint,inverted image is now 10 cm on the incident side of the lens.What is the index of refraction of the lens?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





