
Concept explainers
(a)
The electric potential of each of the three shells.
(a)
Answer to Problem 89P
The electric potential
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The inner shell is uncharged.
The middle shell has a positive charge
The outer shell has a negative charge
Formula used:
The expression for Gauss’s Law is given by,
The expression for potential is given by,
Calculation:
The required diagram is shown in Figure 1.
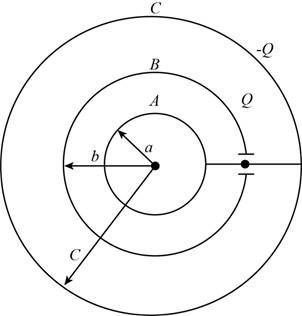
Figure 1
Applying Gauss’s law to a spherical Gaussian surface of radius
And
Applying Gauss’s law to a spherical Gaussian surface of radius
The potential between
And since
Therefore,
The inner shell too doesn’t carry charge, so the field between the points
Conclusion:
Therefore, The electric potential
(b)
The electric potential of each shell and the final charge on each shell.
(b)
Answer to Problem 89P
The electric potential of the shell
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Given:
The inner shell is uncharged.
The middle shell has a positive charge
The outer shell has a negative charge
Formula used:
The expression for Gauss’s Law is given by,
The expression for potential is given by,
Calculation:
When the inner and outer shells are connected their potentials become equal as a consequence of the distribution of charge.
The charges on the surface
The value of
The potential of shells a and c is given by,
The electric field between the points
The enclosed charge for
The potential difference between b and ciscalculated as,
Solve further,
Equate equation (2) and (3).
Substitute
The potential across
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric potential of the shell
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Vol. 1
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





