
Concept explainers
(a)
The shape of the equipotential surfaces in the region around the charge.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The supplementary and inherent essential property of some subatomic particles such as electron due to which they interact with each other is known as electric charge. The standard unit of electric charge is Coulomb which is symbolized as
The appearance of the equipotential surfaces in the region around the charge is concentric with the middle wire as the geometry of the Geiger tube is cylindrical. An equipotential surface is a surface that is either real or imaginary around a point charge. The electric potential on the equipotential surface is equivalent at each point, and these equipotential surfaces are formed at some distance from the point charge.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the shape of the equipotential surfaces in the region around the charge is concentric with the central or middle wire.
(b)
The radii of the five surfaces that have potentials equals to
(b)
Answer to Problem 64P
The radii of the five surfaces that have potentials equals to
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The potential of first surface is
The potential of second surface is
The potential of third surface is
The potential of fourth surface is
The potential of fifth surface is
Formula used:
The expression for the relationship between electric potential due to point charge and the electric field of the point charge is given by,
Calculation:
Suppose the potential to be zero at
The radius for
The radius for
The radius for
The radius for
The radius for
The sketch is shown below.
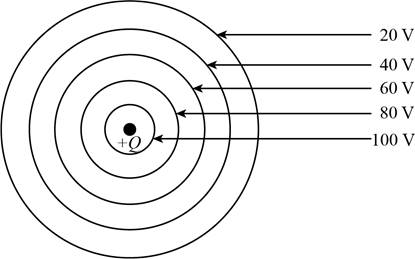
Figure 1
Conclusion:
Therefore, the radii of the five surfaces that have potentials equals to
(c)
The spacing between the equipotential surfaces.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The surface where the magnitude of gravitational potential is the same at all points is known as equipotential, and it coincides with the directions of the gravitational force. A liquid surface is in equilibrium is the best example to understand the concept of the equipotential surface.
The spacing between the equipotential surfaces is closest together but are not equally spaced, it means the electric field becomes stronger. If the field is not performing any work on the particle as it travels from one position to another then the direction of the field’s force must be normal to the direction of the movement of the particle.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the spacing between the equipotential surfaces is closest together
(d)
The electric field strength between
(d)
Answer to Problem 64P
The electric field strength between
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The potential of equipotential surface has
Formula used:
The expression for the average value of the magnitude of the electric field is given as,
The expression for the exact value of the electric field strength is given as,
Calculation:
The average value of the magnitude of the electric field is calculated as,
The exact value of the electric field strength is calculated as,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field strength between
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Vol. 1
- 3. If the force of gravity stopped acting on the planets in our solar system, what would happen? a) They would spiral slowly towards the sun. b) They would continue in straight lines tangent to their orbits. c) They would continue to orbit the sun. d) They would fly straight away from the sun. e) They would spiral slowly away from the sun. 4. 1 The free-body diagram of a wagon being pulled along a horizontal surface is best represented by A F N B C 0 Ꭰ FN E a) A b) B c) C app app The app 10 app d) e) ס ח D E 10 apparrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardThe acceleration of an object sliding along a frictionless ramp is inclined at an angle 0 is 9. a) g tano b) g cose c) g sino 10. d) g e) zero A 1.5 kg cart is pulled with a force of 7.3 N at an angle of 40° above the horizontal. If a kinetic friction force of 3.2 N acts against the motion, the cart's acceleration along the horizontal surface will be a) 5.0 m/s² b) 1.6 m/s² c) 2.4 m/s² 11. d) 1.0 m/s² e) 2.7 m/s² What is the net force acting on an object with a mass of 10 kg moving at a constant velocity of 10 m/s [North]? a) 100 N [North] b) 100 N [South] 10 N [North} d) 10 N [South] e) None of these.arrow_forwardModified True/False - indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If the statement is false, correct the statement to make it true. 12. An object in uniform circular motion has a constant velocity while experiencing centripetal acceleration. 13. An object travelling in uniform circular motion experiences an outward centrifugal force that tends to pull the object out of the circular path. 14. An object with less inertia can resist changes in motion more than an object with more inertia. 15. For an object sliding on a horizontal surface with a horizontal applied force, the frictional force will always increase as the applied force increases.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





