
College Physics
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134601823
Author: ETKINA, Eugenia, Planinšič, G. (gorazd), Van Heuvelen, Alan
Publisher: Pearson,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 75GP
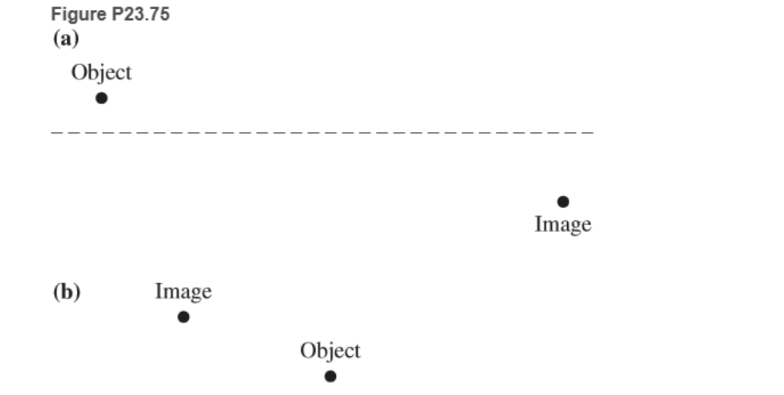
* Figure P23.75 shows three cases of the primary axis of a lens (the lens is not shown) and the location of a shining object and its image. In each case, find the location and the type of the lens (convex or concave) that could produce the image and find the focal points of the lens.

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 23 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.1 A mirror is hanging on a...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.2 You've found a concave...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.3 You place a concave mirror on...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.5 Where should you place an...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.6 If we have a mathematical...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.7 What is the main difference...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.8 If a person with normal...Ch. 23 - Review Question 23.9 Why is saying that a...Ch. 23 - Where does the image of an object in a plane...Ch. 23 - Where does the image of an object that is s meters...
Ch. 23 - 3. A plane mirror produces an image of an object...Ch. 23 - A concave mirror can produce an image that is...Ch. 23 - 5. A convex mirror can produce an image that is...Ch. 23 - 6. A virtual image is the image produced
a. on as...Ch. 23 - 7. To see an image of an object that is enlarged,...Ch. 23 - To see an image of an object that is enlarged,...Ch. 23 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 23 - 10. When drawing images of objects produced by...Ch. 23 - 11. The focal length of a glass lens is 10 cm....Ch. 23 - 12. A microbiologist uses a microscope to look at...Ch. 23 - 13. The human eye works in a similar way to which...Ch. 23 - Which of the following changes will result in a...Ch. 23 - When we draw a ray passing through the center of a...Ch. 23 - 16. You run toward a building with walls of a...Ch. 23 - 17. A tiny plane mirror can produce an image...Ch. 23 - Explain how we derived the mirror equation.Ch. 23 - 19. Explain how we derived the thin lens...Ch. 23 - Explain the difference between a real and a...Ch. 23 - You stand in front of a fun house mirror. You see...Ch. 23 - 22. A bubble of air is suspended underwater. Draw...Ch. 23 - 23. A bubble of oil is suspended in water. Draw...Ch. 23 - A typical person underwater cannot focus clearly...Ch. 23 - In a video projector, the picture that appears on...Ch. 23 - The retina has a blind spot at the place where the...Ch. 23 - You need to teach your friend how to draw rays to...Ch. 23 - Place a pencil in front of a plane mirror so that...Ch. 23 - 3.* Use geometry to prove that the virtual image...Ch. 23 - * You are 1.8 m tall. Where should you place the...Ch. 23 - 5. * Two people are standing in front of a...Ch. 23 - 6. * Test an idea Describe an experiment that you...Ch. 23 - * Describe in detail an experiment to find the...Ch. 23 - * Explain with a ray diagram how (a) a concave...Ch. 23 - 9. * Test an idea Describe an experiment to test...Ch. 23 - * Test an idea Describe an experiment to test the...Ch. 23 - 11. * Tablespoon mirror You look at yourself in...Ch. 23 - * Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to...Ch. 23 - Repeat Problem 23.12 for a convex mirror of focal...Ch. 23 - 14. Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to...Ch. 23 - 15. * Sinking ships A legend says that Archimedes...Ch. 23 - 16. * EST Fortune-teller A fortune-teller looks...Ch. 23 - * You view yourself in a large convex mirror of...Ch. 23 - * Seeing the Moon in a mirror The Moons diameter...Ch. 23 - 19. * You view your face in a +20-cm focal length...Ch. 23 - 20. * Buying a dental mirror A dentist wants to...Ch. 23 - * Using a dental mirror A dentist examines a tooth...Ch. 23 - * If you place a point-like light source on the...Ch. 23 - 24. * You have a convex lens and a candle....Ch. 23 - 25. * Explain how to draw ray diagrams to locate...Ch. 23 - * Draw ray diagrams to show how a convex lens can...Ch. 23 - 27. * Use a ruler to draw ray diagrams to locate...Ch. 23 - 28. * Repeat the procedure described in Problem...Ch. 23 - 29. * Repeat the procedure described in Problem...Ch. 23 - 30 * Repeat the procedure in Problem 23.27 for the...Ch. 23 - * Partially covering lens Your friend thinks that...Ch. 23 - * Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the...Ch. 23 - 33. *Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the...Ch. 23 - Light passes through a narrow slit, and then...Ch. 23 - * Describe two experiments that you can perform to...Ch. 23 - * Shaving/makeup mirror You wish to order a mirror...Ch. 23 - 37. Dentist lamps Dentists use special lamps that...Ch. 23 - 38. * A large concave mirror of focal length 3.0m...Ch. 23 - 39 * EST Two convex mirrors on the side of a van...Ch. 23 - Camera You are using a camera with a lens of focal...Ch. 23 - 42. * Camera A camera with an 8.0-cm focal length...Ch. 23 - Video projector An LCD video projector (LCD stands...Ch. 23 - Photo of carpenter ant You take a picture of a...Ch. 23 - * Photo of secret document A secret agent uses a...Ch. 23 - 46. * Photo of landscape To photograph a landscape...Ch. 23 - * Make a rough graph of image distance versus...Ch. 23 - * Make a rough graph of linear magnification...Ch. 23 - * Repeat Problem 23.48 for a concave lens of...Ch. 23 - BIO Eye The image distance for the lens of a...Ch. 23 - BIO Lens-retina distance Fish and amphibians...Ch. 23 - BIO Nearsighted and farsighted (a) A woman can...Ch. 23 - * BIO Prescribe glasses A man who can produce...Ch. 23 - 54. * BIO Correcting vision A woman who produces...Ch. 23 - 55. * BIO Where are the far and near points? (a) A...Ch. 23 - * BIO Age-related vision changes A 35-year-old...Ch. 23 - 5.7 Looking at an aphid You examine an aphid on a...Ch. 23 - 58. * Reading with a magnifying glass You examine...Ch. 23 - 59. * Seeing an image with a magnifying glass A...Ch. 23 - * Stamp collector A stamp collector is viewing a...Ch. 23 - * You place a +20-cm focal length convex lens at a...Ch. 23 - 62. * You place a +25-cm focal length convex lens...Ch. 23 - * EST You place a candle 10 cm in front of a...Ch. 23 - 64. * EST Repeat Problem 23.63 for an object...Ch. 23 - ** You measure the focal length of a concave lens...Ch. 23 - 66.** Telescope A telescope consists of a +4.0-cm...Ch. 23 - 67. ** Yerkes telescope The world’s largest...Ch. 23 - * Telescope A telescope consisting of a +3.0-cm...Ch. 23 - 69. *** Design a telescope You are marooned on a...Ch. 23 - * Microscope A microscope has a +0.50-cm objective...Ch. 23 - 71. ** BIO Dissecting microscope A dissecting...Ch. 23 - *** Microscope A microscope has an objective lens...Ch. 23 - 73. ** Microscope Determine the lens separation...Ch. 23 - * Figure P23.75 shows three cases of the primary...Ch. 23 - Prob. 78GPCh. 23 - ** Two-lens camera A two-lens camera (see Figure...Ch. 23 - **You have a small spherically shaped bottle made...Ch. 23 - BIO Find a farsighted person. Design an experiment...Ch. 23 - 82. BIO Find a nearsighted person. Design an...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - BIO Laser surgery for the eye LASIK...Ch. 23 - Prob. 89RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 90RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 91RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 92RPPCh. 23 - Prob. 93RPP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
The bioremediation process shown in the photograph is used to remove benzene and other hydrocarbons from soil c...
Microbiology: An Introduction
For the generic equilibrium HA(aq) ⇌ H + (aq) + A- (aq), which of these statements is true?
The equilibrium con...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
11. The electric potential at a point that is halfway between two identical charged particles is 300 V. What is...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
27. An old-fashioned single-play vinyl record rotates on a turntable at 45 rpm. What are (a) the angular veloci...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY