
Concept explainers
Problem 23-3B
Flexible budget preparation; computation of materials, labor, and
P1P2P3
Suncoast Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product.
Direct materials (6 lbs. @ $5 per lb.) …………………. $ 27
Direct labor (2 hrs. @ $17 per hr.) ……………………... 18
Overhead (2 hrs. @ $ 18.50 per hr.) ……………………. 24
Total
The predetermined overhead rate ($ 16.00 per direct labor hour) is based on an expected volume of 75% of the factory’s capacity of 20,000 units per month. Following are the company’s budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75% capacity level.
Overhead Budget (75% Capacity)
Variable overhead costs
Indirect materials ……………………………………… $ 22,000
Indirect labor …………………………………………… 90,000
Power …………………………………………………… 22,500
Repairs and maintenance ……………………………….. 45,000
Total variable overhead costs …………………………… $180,000
Fixed overhead costs
Depreciation- Machinery ………………………………… 72,000
Taxes and insurance ……………………………………… 18,000
Supervision ………………………………………………... 66,000
Total fixed overhead costs …………………………………180,000
Total overhead costs ………………………………………………$ 360,000
The company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity in October.
Direct materials (91,000 lbs. @ $5.10 per lb) …………………… $ 420,900
Direct labor (30,500 hrs. @ $ 17.25 per hr.) ……………………… 280,440
Overhead costs
Indirect materials …………………………………………. $ 21,600
Indirect labor ………………………………………………. 82,260
Power ………………………………………………………. 23,100
Repairs and maintenance …………………………………… 46,800
Depreciation-Building ……………………………………… 24,000
Depreciation-Machinery …………………………………….. 75,000
Taxes and insurance …………………………………………. 16,500
Supervision …………………………………………………… 66,000
355,260
Total costs ……………………………………………………………_____
$1,056,600 _______
Required
- Examine the monthly overhead budget to (a) determine the costs per unit for each variable overhead item and its total per unit costs and (b) identity the total fixed costs per month.
- Prepare flexible overhead budgets (as in Exhibit 23.12) for October showing the amounts of each variable and fixed cost at the 65%, 75%, and 85% capacity levels.
- Compute the direct materials cost variance, including its price and quantity variances.
- Compute the direct labor cost variance, including its rate and efficiency variances.
- Prepare a detailed overhead variance report (as in Exhibit 23.16) that shows the variances for individual items of overhead.
EXHIBIT 23.12 Flexible Overhead Budgets
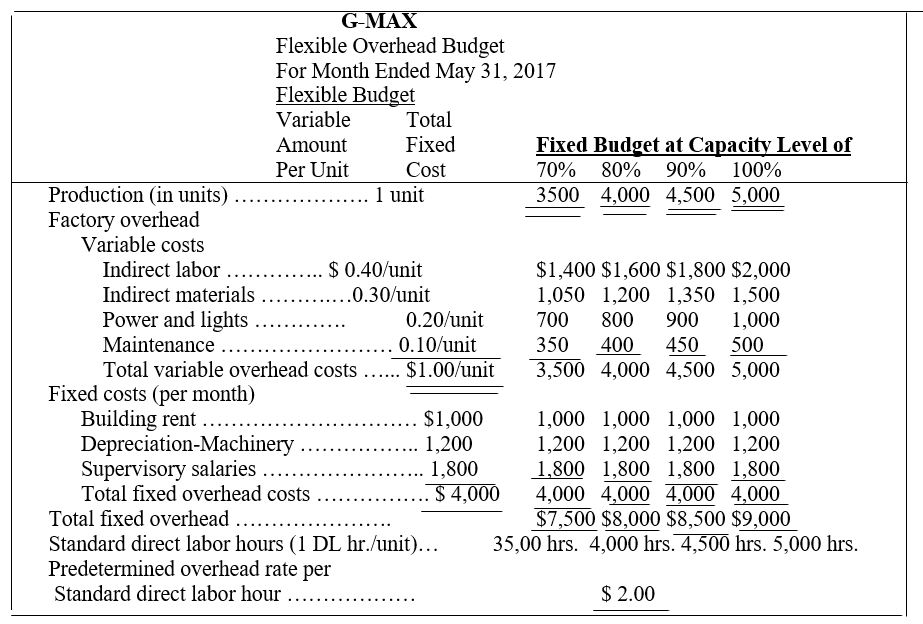
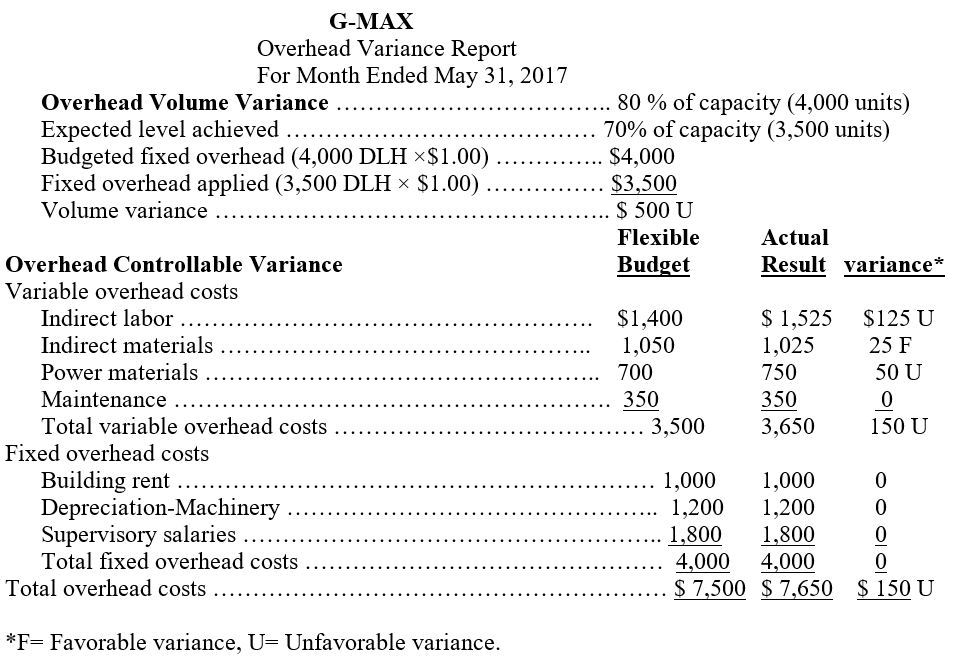
EXHIBIT 23.16 Overhead Variance Report
Flexible Budget:
A flexible budget is prepared for more than one level of production and it is flexible in nature. Flexible budget can vary according to the actual level of production. It eliminates the volume variance between the budgeted values and actual result of production.
Material Price Variance:
At the actual quantity, the difference between the actual cost and standard cost is known as material price variance.
Material Quantity Variance:
The material quantity variance measures the efficiency of a production in terms of material utilization. It is computed by determining the difference between the standard quantity to used and actual quantity of material used in the production at the standard rate.
Labor Rate Variance:
At the actual direct labor hours, the variance between the actual direct labor cost based on actual rate incurred and the budgeted direct labor cost based on standard rate is called direct labor cost variance.
Direct Labor Efficiency Variance:
Direct labor efficiency variance measures the efficiency in utilization of direct labor costs by determining the difference between the actual labor hours and the direct labor hours allowed at the standard rate.
To determine:
1. Determine the cost per unit of each variable overhead item and its total per unit costs and identify the total fixed costs per month.
2. Preparing flexible budgets showing the amounts of each variable and fixed cost at the 65%, 75% and 85% capacity levels.
3. Computation of direct materials cost variance, showing price and quantity variances.
4. Computation of direct labor cost variance, showing rate and efficiency variances.
5. Preparation of overhead variance report that shows the variances for individual items of overhead.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
1. The total per unit costs is $12 and the total fixed cost per month is $180,000.
2. The total overhead cost at 65%, 75%, and 85% is $336,000, $360,000, and $384,000 respectively.
3. The direct material cost variance is $15,900 (U) with unfavorable price variance of $6,900 and quantity variance of $9,000.
4. Direct labor cost variance is $10,440 (U) with unfavorable rate variance of $6,840 and efficiency variance of $3,600.
5. Suncoast Company has favorable overhead volume variance of $48,000 and unfavorable controllable variance of $4,740.
1.
| Overhead items | Variable cost per unit | Fixed cost per month |
| Variable overhead costs | ||
| Indirect materials | $1.50 | |
| Indirect labor | $6.00 | |
| Power | $1.50 | |
| Repairs and maintenance | $3.00 | |
| Total variable overhead costs | $12.00 | |
| Fixed overhead costs | ||
| Depreciation – Building | $24,000 | |
| Depreciation – Machinery | $72,000 | |
| Taxes and insurance | $18,000 | |
| Supervision | $66,000 | |
| Total fixed overhead costs | $180,000 |
2.
| SUNCOAST COMPANY Flexible Overhead Budgets For the Month Ended December 31. |
|||||
| Flexible Budget | Flexible Budget at Capacity Level of | ||||
| Variable cost per unit | Fixed cost per month | 65% | 75% | 85% | |
| Production (in units) | 1 unit | 13,000 | 15,000 | 17,000 | |
| Variable overhead costs | |||||
| Indirect materials | $1.50 | $19,500 | $22,500 | $25,500 | |
| Indirect labor | $6.00 | $78,000 | $90,000 | $102,000 | |
| Power | $1.50 | $19,500 | $22,500 | $25,500 | |
| Repairs and maintenance | $3.00 | $39,000 | $45,000 | $51,000 | |
| Total variable overhead costs | $12.00 | $156,000 | $180,000 | $204,000 | |
| Fixed overhead costs | |||||
| Depreciation – Building | $24,000 | $24,000 | $24,000 | $24,000 | |
| Depreciation – Machinery | $72,000 | $72,000 | $72,000 | $72,000 | |
| Taxes and insurance | $18,000 | $18,000 | $18,000 | $18,000 | |
| Supervision | $66,000 | $66,000 | $66,000 | $66,000 | |
| Total fixed overhead costs | $180,000 | $180,000 | $180,000 | $180,000 | |
| Total Overhead Costs | $336,000 | $360,000 | $384,000 | ||
| Predetermined overhead rate per standard direct labor hour | $16.00 | ||||
3.
Computation of direct materials cost variance, including its price and quantity variances
4.
Computation of direct labor cost variance, including its rate and efficiency variances
5.
| SUNCOAST COMPANY Overhead Variance Report For the Month Ended December 31. |
||||
| Overhead Volume Variance | ||||
| Expected production level | 75% of capacity 15,000 units | |||
| Production level achieved | 85% of capacity 17,000 units | |||
| Budgeted fixed overhead (22,500 hrs. X $16.00) | $360,000 | |||
| Fixed overhead applied (25,500 hrs. X $16.00) | $408,000 | |||
| Volume Variance | $48,000 F | |||
| Overhead Controllable Variance | Flexible Budget | Actual Results |
Variances | |
| Variable overhead costs | ||||
| Indirect materials | $22,500 | $21,600 | $900 F | |
| Indirect labor | $90,000 | $82,260 | $7,740 F | |
| Power | $22,500 | $23,100 | $600 U | |
| Repairs and maintenance | $45,000 | $46,800 | $1,800 U | |
| Total variable overhead costs | $180,000 | $173,760 | $6,240 F | |
| Fixed overhead costs | ||||
| Depreciation – Building | $24,000 | $24,000 | 0 | |
| Depreciation – Machinery | $72,000 | $75,000 | $3,000 U | |
| Taxes and insurance | $18,000 | $16,500 | $1,500 F | |
| Supervision | $66,000 | $66,000 | 0 | |
| Total fixed overhead costs | $180,000 | $181,500 | $1,500 U | |
| Total Overhead costs | $360,000 | $355,260 | $4,740 U | |
Conclusion:
The direct material pro=ice variance is $6,900 Unfavorable
The direct material quantity variance is $9,000 Unfavorable
The direct material cost variance is $15,900 Unfavorable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Fundamental Accounting Principles
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





