
Concept explainers
A solid sphere of radius 40.0 cm has a total positive charge of 26.0 μC uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field (a) 0 cm, (b) 10.0 cm, (c) 40.0 cm, and (d) 60.0 cm from the center of the sphere.
(a)
The electric field at
Answer to Problem 33P
The electric field at
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The radius of solid sphere is
The diagram for the given condition is shown below.
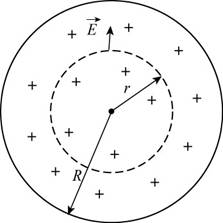
Figure (1)
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is,
Here,
The area of the sphere is,
The Gauss law is,
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field at
(b)
The electric field at
Answer to Problem 33P
The electric field at
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The radius of solid sphere is
Recall the equation (1).
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field at
(c)
The electric field at
Answer to Problem 33P
The electric field at
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The radius of solid sphere is
Recall the equation (1).
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field at
(d)
The electric field at
Answer to Problem 33P
The electric field at
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The radius of solid sphere is
The distance
Then,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Multi-term
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Chemistry: Atoms First
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Part C Find the height yi from which the rock was launched. Express your answer in meters to three significant figures. Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 4.1 for projectile motion problems. A rock thrown with speed 12.0 m/s and launch angle 30.0 ∘ (above the horizontal) travels a horizontal distance of d = 19.0 m before hitting the ground. From what height was the rock thrown? Use the value g = 9.800 m/s2 for the free-fall acceleration. PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGY 4.1 Projectile motion problems MODEL: Is it reasonable to ignore air resistance? If so, use the projectile motion model. VISUALIZE: Establish a coordinate system with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical. Define symbols and identify what the problem is trying to find. For a launch at angle θ, the initial velocity components are vix=v0cosθ and viy=v0sinθ. SOLVE: The acceleration is known: ax=0 and ay=−g. Thus, the problem becomes one of…arrow_forwardPhys 25arrow_forwardPhys 22arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





