
(a)
The tension
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.45P
The tension
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The force (F) in point C is 1.98 kN.
The horizontal (AC) length between point A and C is 4.8 m.
The horizontal (CB) length between point C and B is 3 m.
The height (A) at point A is 3.4 m.
The height (B) at point B is 3.6 m.
Calculation:
Calculate vertical distance
Substitute 3.4 m for A and 2 m for d.
Calculate vertical distance
Substitute 3.6 m for B and 2 m for d.
Show the free body diagram of two cables as in Figure (1).
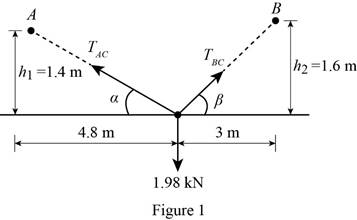
Calculate the angle
Substitute 1.4 m for
Calculate the angle
Substitute 1.6 m for
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Show the force triangle as in Figure (2).
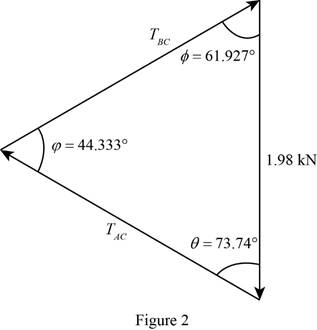
Refer Figure (2),
Write the below expression by applying law of sine.
Calculate the tension
Eliminate the
Substitute 1.98 kN for F,
Thus, the tension
(b)
The tension
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.45P
The tension
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The force (F) in point C is 1.98 kN.
The horizontal (AC) length between point A and C is 4.8 m.
The horizontal (CB) length between point C and B is 3 m.
The height (A) at point A is 3.4 m.
The height (B) at point B is 3.6 m.
Calculation:
Calculate the tension
Eliminate the
Substitute 1.98 kN for F,
Thus, the tension
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Auto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward-400" 150" in Datum 80" 90" -280"arrow_forwardUsing hand drawing both of themarrow_forward
- A 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forwardCalculate the speed of the driven member with the following conditions: Diameter of the motor pulley: 4 in Diameter of the driven pulley: 12 in Speed of the motor pulley: 1800 rpmarrow_forward4. In the figure, shaft A made of AISI 1010 hot-rolled steel, is welded to a fixed support and is subjected to loading by equal and opposite Forces F via shaft B. Stress concentration factors K₁ (1.7) and Kts (1.6) are induced by the 3mm fillet. Notch sensitivities are q₁=0.9 and qts=1. The length of shaft A from the fixed support to the connection at shaft B is 1m. The load F cycles from 0.5 to 2kN and a static load P is 100N. For shaft A, find the factor of safety (for infinite life) using the modified Goodman fatigue failure criterion. 3 mm fillet Shaft A 20 mm 25 mm Shaft B 25 mmarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





