
(a)
Interpretation: Which fatty acid would most contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
Concept Used:
Oil consists of large number of unsaturated fatty acids, whereas fats consists of large number of saturated fatty acid.
Also, saturated fatty acid do not have any carbon-carbon double bond, whereas unsaturated fatty acid consists of carbon-carbon double bond.
Unsaturated fatty acids which have more than one carbon-carbon double bond are referred to as polyunsaturated fatty acid.
To determine:
Find out if fatty acid 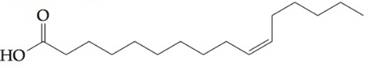 would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
(b)
Interpretation: Which fatty acid would most contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
Concept Used:
Oil consists of large number of unsaturated fatty acids, whereas fats consists of large number of saturated fatty acid.
Also, saturated fatty acid do not have any carbon-carbon double bond, whereas unsaturated fatty acid consists of carbon-carbon double bond.
Unsaturated fatty acids which have more than one carbon-carbon double bond are referred to as polyunsaturated fatty acid.
To determine: Find out if fatty acid 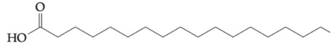 would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
(c)
Interpretation: Which fatty acid would most contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
Concept Used:
Oil consists of large number of unsaturated fatty acids, whereas fats consists of large number of saturated fatty acid.
Also, saturated fatty acid do not have any carbon-carbon double bond, whereas unsaturated fatty acid consists of carbon-carbon double bond.
Unsaturated fatty acids which have more than one carbon-carbon double bond are referred to as polyunsaturated fatty acid
To determine: Find out if fatty acid 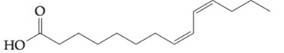 would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
would contribute to a triacylglyceride being oil, rather than a fat, at a room temperature.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Chemistry (7th Edition)
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





