
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify whether the list of the electron carrier
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
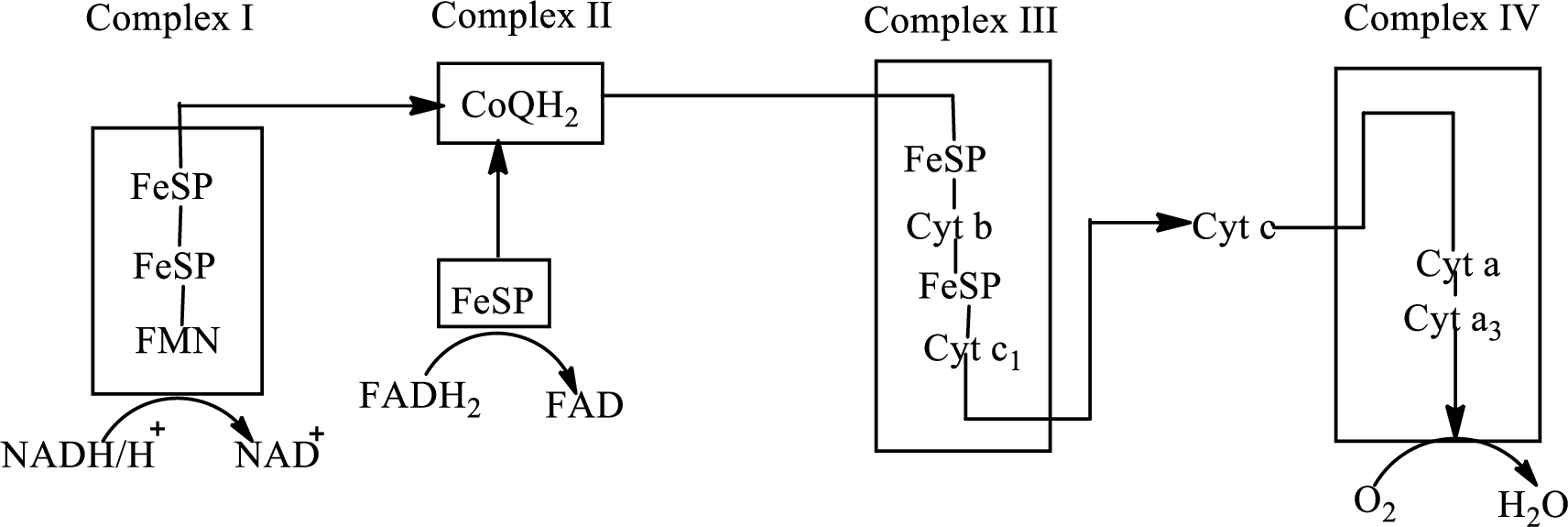
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.85EP
Yes, the given order for electron carriers
Explanation of Solution
In the electron transport chain, electrons are transferred from complex I and II to complex III through
(b)
Interpretation: To identify whether the list of the electron carrier
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
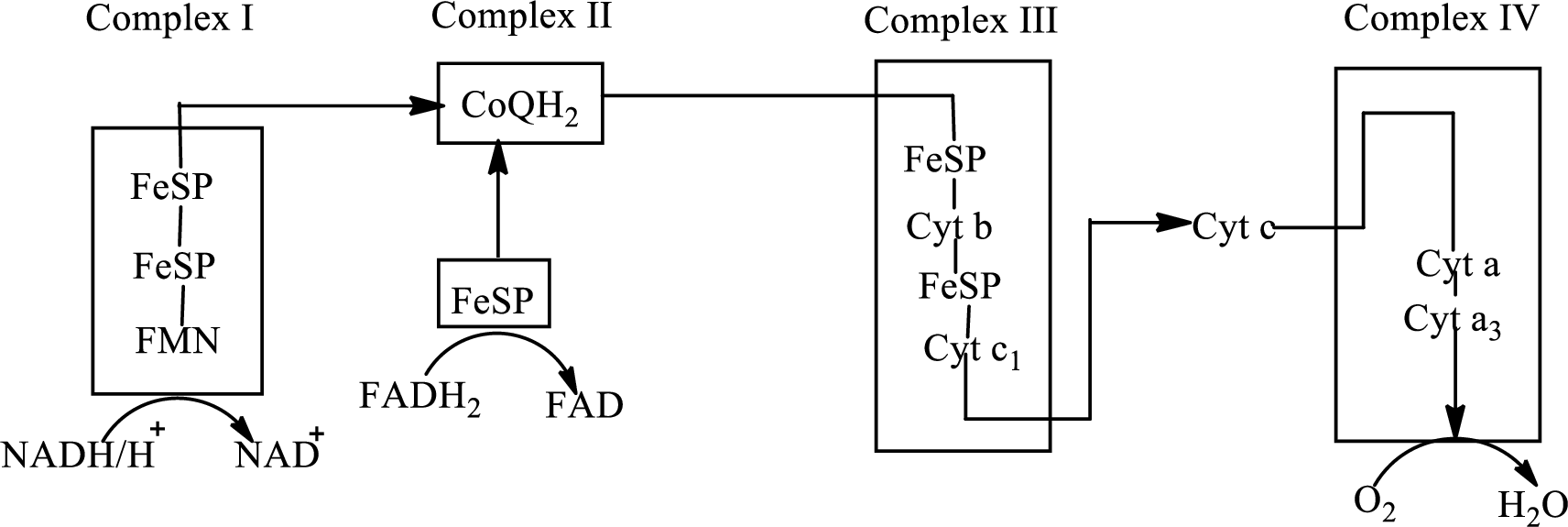
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.85EP
No, the given order for electron carriers
Explanation of Solution
In the electron transport chain, electrons are transferred from complex I and II to complex III through
(c)
Interpretation: To identify whether the list of the electron carrier
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
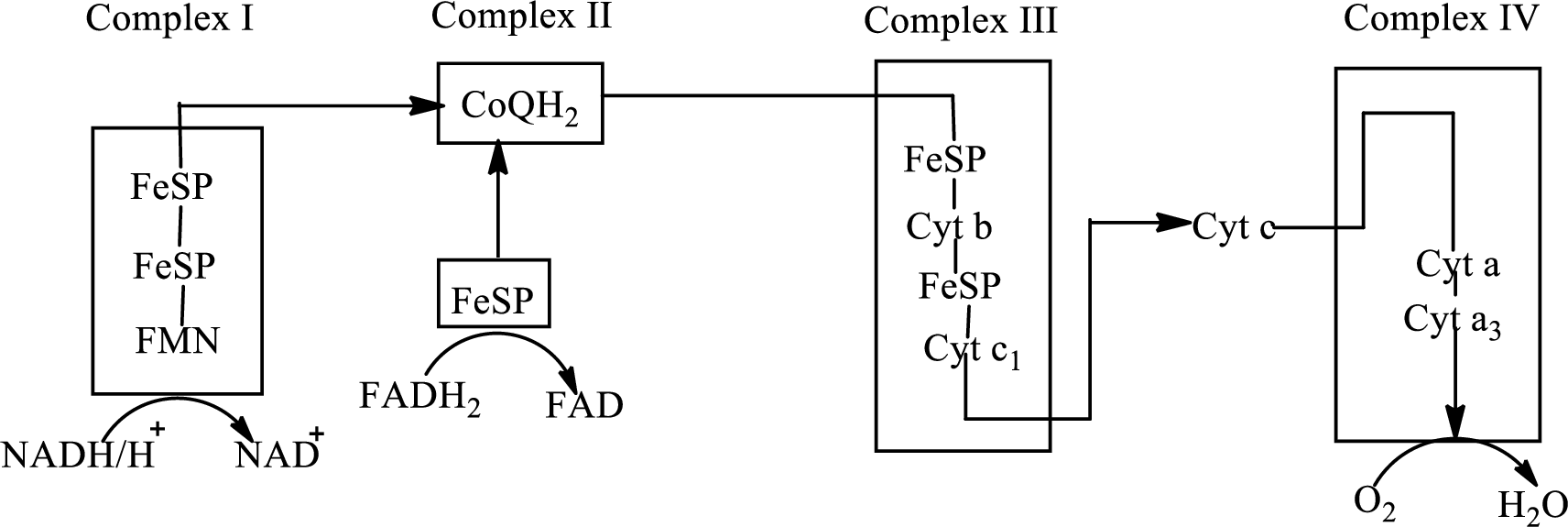
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.85EP
No, the given order for electron carriers
Explanation of Solution
In the complex I initially, NADH is oxidized and releases two electrons that reduce
(d)
Interpretation: To identify whether the list of the electron carrierFADH2, NADH and
Concept introduction: Electron transport chain is a sequence of biochemical reactions in which electrons and hydrogen atoms from the citric acid cycle are transferred to various intermediate carriers and finally reacts with molecular oxygen to form a water molecule.
There are four complexes associated with the electron transport chain that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The four complexes that help in the electron transfer in the electron transport chain are:
Complex I:
Complex II:
Complex III:
Complex IV:
An overview of the electron transport chain is as follows:
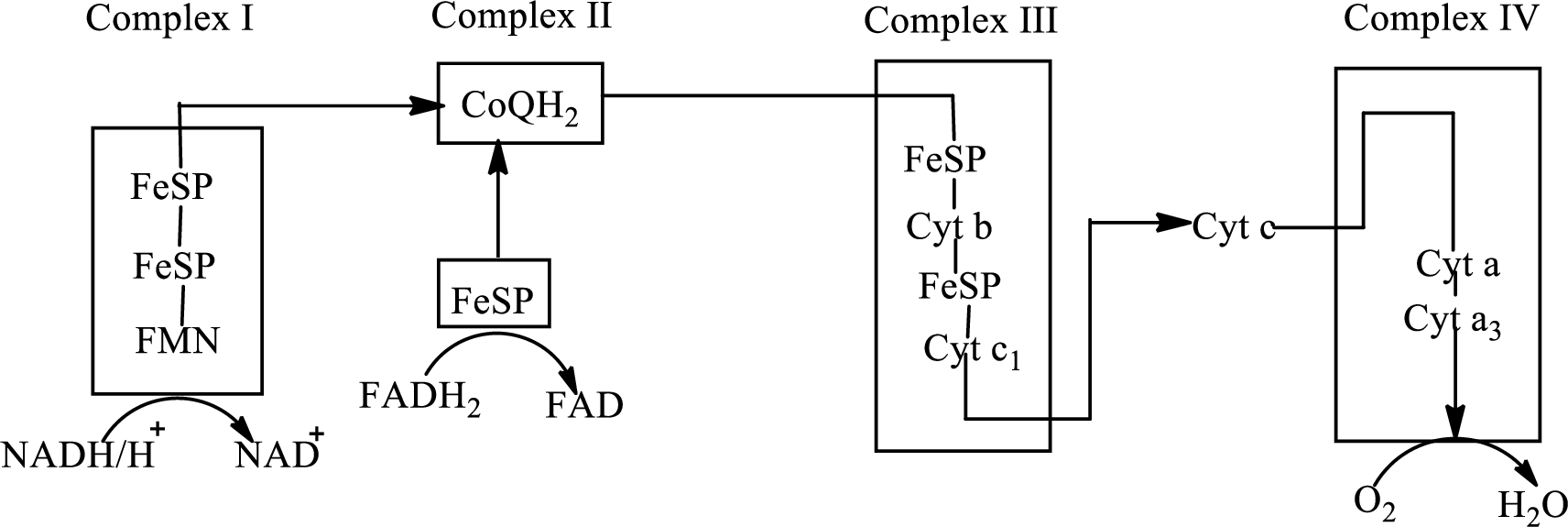
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.85EP
No, the given order for electron carriers
Explanation of Solution
In complex I, electrons are transferred from the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



