
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To list the steps, by number in the citric acid cycle that involves oxidation.
Concept introduction: Citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and
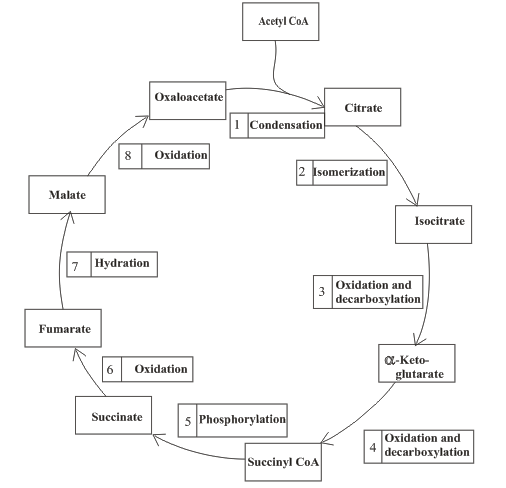
Oxidation step involves the oxidation of the reactant in that step of the citric acid cycle to produce the product.
(b)
Interpretation: To list the steps, by number in the citric acid cycle that involves isomerisation.
Concept introduction: Citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and

Isomerization step involves the isomerization of the reactant in that step of the citric acid cycle to produce the product.
(c)
Interpretation: To list the steps, by number in the citric acid cycle that involves hydration.
Concept introduction: Citric acid cycle is the third stage of the biochemical energy production process. The cycle includes the reactions in which the acetyl part of acetyl CoA is oxidized and leads to the formation of carbon dioxide and

Hydration step involves the hydration of the reactant in that step of the citric acid cycle to produce the product.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
General, Organic, And Biological Chemistry, Hybrid (with Owlv2 Quick Prep For General Chemistry Printed Access Card)
- Please help me solve this reaction.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,




