
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring, on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid (
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given
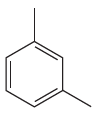
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two methyl groups attached. The alkyl groups are electron inductively donating and activate the ring. The ring can then undergo sulfonation on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, and there is no need to add fuming sulfuric acid.
It is determined that sulfonation of the given compound can be carried out with concentrated sulfuric acid only and no need to add fuming sulfuric acid based on the activation of the aromatic ring.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring, on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid, undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
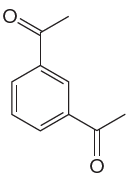
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has two carbonyl groups attached. The carbonyl groups have electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreasing the electron density around the ring and deactivating it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation.
It is determined that sulfonation of the given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of the aromatic ring.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
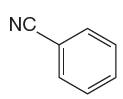
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has a nitrile group attached. The nitrile group has electron withdrawing resonance effect, thus decreasing the electron density around the ring and deactivating it. As the ring is electron poor and deactivated, fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation.
It is determined that sulfonation of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increases the electron density around the ring and activates it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation. The resonance effect is predominant over inductive effect due to actual delocalization of pi electrons.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
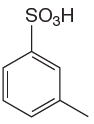
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that sulfonation of a given compound can be carried by addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
Fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound as the aromatic ring is deactivated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
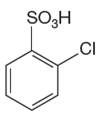
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has
It is determined that the sulfonation of a given compound can be carried out by the addition of sulfuric acid to concentrated sulfuric acid based on deactivation of aromatic ring.
(f)
Interpretation:
Whether fuming sulfuric acid should be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out sulfonation on the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The sulfonation is the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The aromatic ring on reaction with sulfuric acid or with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid undergoes substitution of one of the ring hydrogen by nitro group and forms nitrobenzene; this is called sulfonation. The selection of reagent either sulfuric acid or mixture of sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid is depends on whether the aromatic ring is activated or deactivated. The electron donating groups increase the electron density around the ring and activate it whereas the electron withdrawing groups decrease the electron density around the ring and deactivate it. The activated aromatic ring can undergo sulfonation on reaction with sulfuric acid. The deactivated ring requires the addition of sulfuric acid to sulfuric acid to undergo sulfonation.
Answer to Problem 23.50P
The fuming sulfuric acid should not be added to concentrated sulfuric acid to carry out a sulfonation on given compound as the aromatic ring is activated.
Explanation of Solution
The given aromatic compound is:
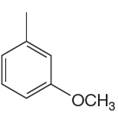
In this aromatic compound, the benzene ring has one methyl and one methoxy group attached. The alkyl groups are electron donating inductively, and methoxy group has electron donating resonance effect, thus increasing the electron density around the ring and activating it. As the ring is electron rich and activated, it can undergo sulfonation on reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid, and there is no need to add sulfuric acid.
It is determined that the sulfonation of a given compound can be carried out with concentrated sulfuric acid only and no need to add fuming sulfuric acid based on the activation of aromatic ring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





