
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic
Answer to Problem 23.1P
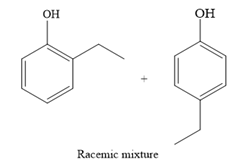
The major product for the given reaction is
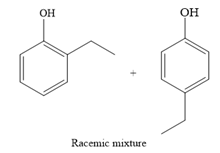
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
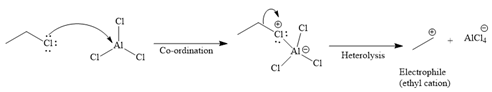
Formation of the electrophile:
Formation of the product (a racemic mixture of ortho and para isomer):
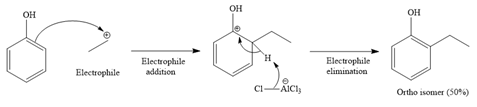
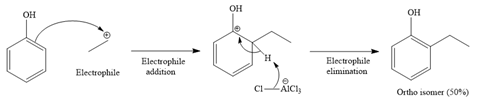
For ortho isomer:
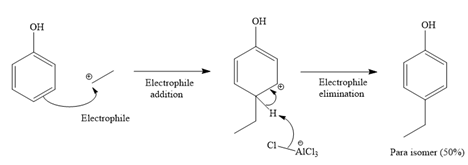
For para isomer:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
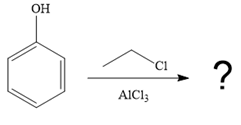
It is noticed that the given substrate, phenol, is treated with ethyl chloride in the presence of
The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, the electron-rich chlorine of the ethyl chloride is coordinated with an electron-deficient aluminum of
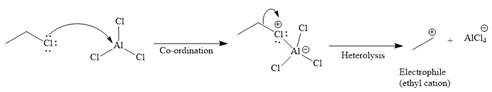
The formed electrophile, ethyl cation (
For ortho isomer:
For para isomer:
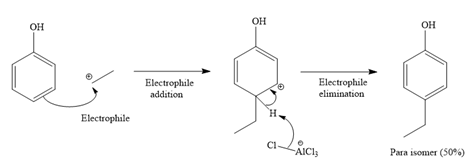
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
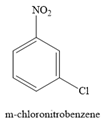
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
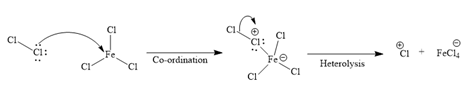
Formation of the electrophile:
Formation of the product:
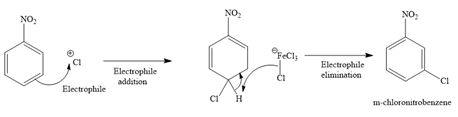
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
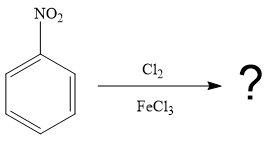
It is noticed that the given substrate is treated with

The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, one of the electron-rich chlorine atoms of

The formed electrophile (

The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
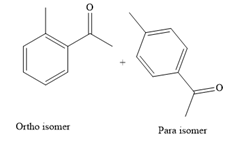
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
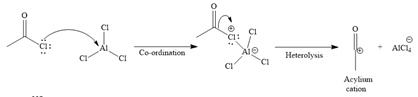
Formation of the electrophile:
Formation of the product (a racemic mixture of ortho and para isomer):
For ortho isomer:
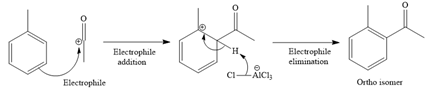
For para isomer:
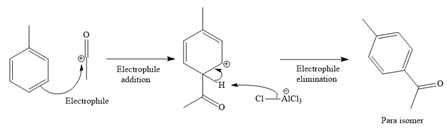
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
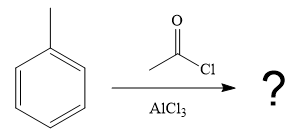
It is noticed that the given substrate, toluene, is treated with an acyl chloride in the presence of

From the Table 23-1, the product is a mixture of o+p isomer more than 95%.
The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, electron-rich chlorine of the ethyl chloride is coordinated with an electron-deficient aluminum of

The formed electrophile, acylium cation, then undergoes electrophilic addition to the benzene ring, followed by electrophilic elimination mechanism, to form the ortho and para isomers shown below:
For ortho isomer:

For para isomer:
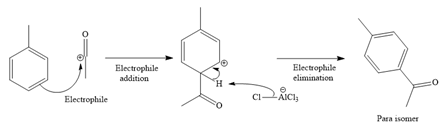
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction is to be predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the case of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, a substituent influences the site of reaction. The electron-donating groups are ortho/para directing groups while electron-withdrawing groups are meta directing groups in the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation are an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The chlorination of the aromatic ring can be carried out by reacting with
Answer to Problem 23.1P
The major product for the given reaction is
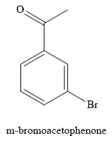
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Formation of the electrophile:
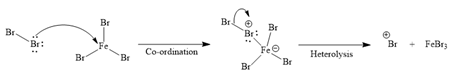
Formation of the product:
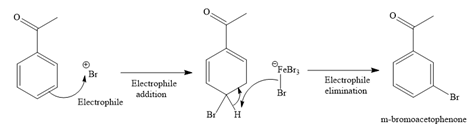
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
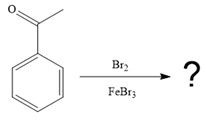
It is noticed that the given substrate is treated with

The mechanism for the given reaction is given below.
Since the given reaction is an example of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the first step is the formation of the electrophile as given below.
Initially, one of the electron-rich bromine atoms of
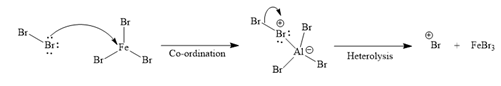
The formed electrophile (
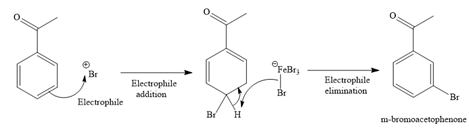
The major product for the given reaction is predicted, and the complete, detailed mechanism for the same reaction is drawn on the basis of the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- ΗΝ, Draw Final Product C cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Edit Enamine H3O+ CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H Edit Iminium Ionarrow_forwardHow many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?arrow_forwardIdentify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forward
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forward
- What is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





