
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Combustion reaction is the one in which, the substance is burnt in presence of oxygen. If any hydrocarbon is burnt in presence of oxygen, the products obtained are carbon dioxide and water only.
(a)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction in the problem statement is an combustion reaction and hence, the product obtained will be carbon dioxide and water only. Hence, the raw equation can be written as,
As the total number of atoms present in both reactants and products must be equal, balancing has to be done. To balance the carbon atom in both sides, the product side has to be multiplied by 4 for carbon dioxide and 5 for water. This leads, balancing of both carbon and hydrogen atoms on both sides.
Oxygen count was thirteen in product side. But in the reactant side it is two. Hence, multiplying by 13/2 on reactant side balances the oxygen atom also on both sides. Therefore, the balanced chemical equation for the given reaction can be given as,
To remove the fraction multiply all the compounds by 2. This gives the balanced equation as,
The given incomplete combustion reaction is completed and the balanced chemical equation also written.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation is loss of electron by a species. This also can be said as addition of oxygen. Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by a species.
(b)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
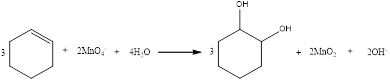
Explanation of Solution
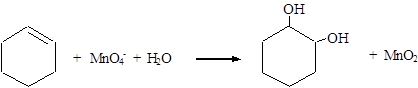
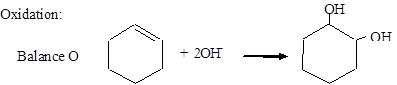
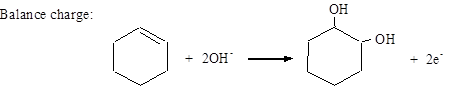
Reduction: MnO4− → MnO2
Balance O: MnO4− + 2H2O → MnO2 + 4OH−
Balance charge: MnO4− + 2H2O + 3e− → MnO2 + 4OH−
Add half-reactions:
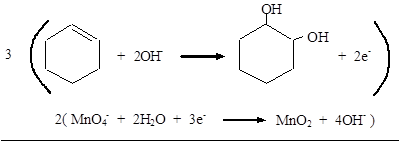
Therefore, the complete equation for the given reaction can be given as,

The balanced equation for the given reaction was written.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Bromination of
(c)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
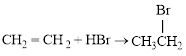
Explanation of Solution
Bromination across the double bond.
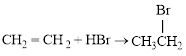
The given bromination reaction was completed and the product was written with balanced equation.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Nitration of
(d)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
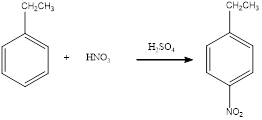
Explanation of Solution
Nitration of ethylbenzene takes place in presence of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. As ethyl is a para directing group, the nitro group is substituted in the para position. By considering this, the complete reaction can be given as,
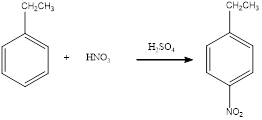
The given nitration reaction product was drawn and the equation was completed.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given reactions, the equation has to be completed and balanced.
Concept Introduction:
Chlorination of aromatic compound happens in presence of catalyst. Usually this does not occur in absence of catalyst. The position of chlorination in the aromatic ring depends upon the group already substituted in the ring.
(e)
Answer to Problem 23.32QP
The balanced equation for the given reaction can be written as,
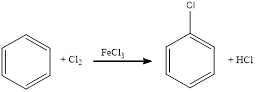
Explanation of Solution
Chlorination of benzene takes place in presence of catalyst with chlorine. By considering this, the complete reaction can be given as,
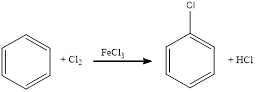
The given chlorination reaction was completed and the product was written with balanced equation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forwardion. A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io : :0: : Cl : - - : :0: ك Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom central O formal charge ☐ top O ☐ right O ☐ bottom O ☐ Cl ☐arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Yes. Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Cl- : 2: :Z: :Z: N—N : 0: C C1: O CO No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". ☑arrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions ΔΗ is (pick one) A This reaction is faster above 103. °C than below. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous only above -9. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) C The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous. AS is (pick one) 18 Ararrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + H CH3CH2OH HCI Drawingarrow_forwardplease explain this in simple termsarrow_forwardK Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward
- (2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forwardDecide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





