
(a)
Interpretation:
A portion of the polymer made from tetrachloroethylene needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
A polymer is a long chain consists of large number of monomer units. In a polymer, the monomers are linked to each other in a continuous or repetitive manner. These monomer units are linked to each other either through the formation of peptide linkage,glycosidic linkage or by removal of any moiety such as a water molecule.Polyvinyl chloride, Bakelite and polystyrene are some of the examples of the
(a)
Answer to Problem 1QAP
A portion of polymer made from tetrachloroethylene is as follows:
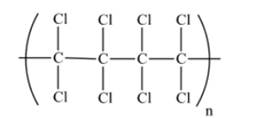
Explanation of Solution
Tetrachloroethylene polymer consists of number of monomer unit of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethylene.
The structure of tetrachloroethylene or monomer unit of the polymer is as follows:
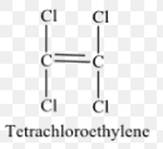
The polymer is formed after breaking of C-C double bonds, the two terminal carbon atoms of 1 tetrachloroethylene unit form bond with 2 terminal carbons of two other tetrachloroethyleneunits. To form a polymer, n numbers of such tetrachloroethyleneunits combined in the same way.
A portion of this polymer is shown as follows:
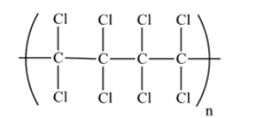
(b)
Interpretation:
The molar mass of the polymer needs to be calculated if it contains
Concept Introduction:
A polymer is a long chain consists of large number of monomer units. In a polymer, the monomers are linked to each other in a continuous or repetitive manner. These monomer units are linked to each other either through the formation of peptide linkage, glycosidic linkage or by removal of any moiety such as a water molecule. Polyvinyl chloride, Bakelite and polystyrene are some of the examples of the polymers.
Tetrachloroethylene polymer consists of number of monomer unit of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethylene.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1QAP
The molar mass of complete polymer is
Explanation of Solution
Molar mass of 1 monomer unit of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethylene is 168 g /mol. This is mass of 1 molecule of the 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethylene.
If the polymer contains
Thus, molar mass of complete polymer is
(c)
Interpretation:
The mass percent of C and Cl in the polymer needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Mass percent of an atom present in the sample can be determined by dividing mass of atom present in the monomer to the overall mass of the monomer unit and multiplying the overall result with 100%.
For example, the mass percent of x g of an atom present in the y g of monomer unit can be determined as:
(c)
Answer to Problem 1QAP
Mass percent of C in polymer is 14.28 %.
Mass percent of Cl in polymer is 83.33 %.
Explanation of Solution
The molar mass of the 1 tetrachloroethylene unit is 168 g/mol.
There are 2 C atoms in a monomer unit of tetrachloroethylene.
Now, molar mass of C atom in a monomer will be:
Putting the values,
Thus, mass percent of C in polymer is 14.28 %.
The number of Cl atoms in the monomer unit of tetrachloroethylene is 4.
Molar mass of Cl in a monomer will be:
Mass percent of Cl can be calculated as follows:
Putting the values,
Thus, mass percent of Cl in the polymer is 83.33 %
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:PRIN.+REACTIONS-OWLV2 ACCESS
- At 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forwardDraw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward11. Use the equation below to answer the following questions: 2 Al(s) + 3 Cd(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 Cd(s) a. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction? b. Which species is a spectator ion in this reaction? Define a spectator ion. c. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





