PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781323834831
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 11CQ
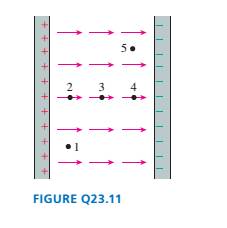
Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the electric field strengths
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2.
1.
Tube Rating
Charts
Name:
Directions: For the given information state if the technique is safe or unsafe and why.
60 Hertz Stator Operation
Effective Focal Spot Size- 0.6 mm
Peak Kilovolts
MA
2
150
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
2501
60
50
40
30
.01 .02 .04.06 .1
.2
.4.6 1
8 10
Maximum Exposure Time In Seconds
Is an exposure of 80 kVp, 0.1 second and 200 mA within the limits of the single
phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above?
Is an exposure of 100 kVp, 0.9 second and 150 mA within the limits of the single
phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above?
Q: You have a CO2 laser resonator (λ = 10.6 μm). It has two curved mirrors with
R₁=10m, R2= 8m, and mirror separation /= 5m. Find:
R2-10 m
tl
Z-O
12
R1-8 m
1. Confocal parameter. b= 21w2/2 =√1 (R1-1)(R2-1)(R1+R2-21)/R1+R2-21)
2. Beam waist at t₁ & t2-
3. Waist radius (wo).
4.
5.
The radius of the laser beam outside the resonator and about 0.5m from R₂-
Divergence angle.
6. Radius of curvature for phase front on the mirrors R₁ & R2-
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 23 Solutions
PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
Ch. 23 - l. You've been assigned the task of determining...Ch. 23 - Reproduce FIGURE Q23.2 on your paper. For each...Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A small segment of wire in FIGURE Q23.4 contains...Ch. 23 - An electron experiences a force of magnitude F...Ch. 23 - FIGURE Q23.6 shows a hollow soda straw that has...Ch. 23 - The irregularly shaped area of charge in FIGURE...Ch. 23 - A circular disk has surface charge density 8...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R has charge Q . The electric...Ch. 23 - The ball in FIGURE Q23.10 is suspended from a...
Ch. 23 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor consists of two square...Ch. 23 - A small object is released at point 3 in the...Ch. 23 - A proton and an electron are released from rest in...Ch. 23 - Three charges are placed at the comers of the...Ch. 23 - l. What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from two charges, q ,...Ch. 23 - An electric dipole is formed from ± 1.0 nC charges...Ch. 23 - An electret is similar to a magnet, but rather...Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 10.0 cm from a very...Ch. 23 - A 10-cm-long thin glass rod uniformly charged to...Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-long thin glass rods uniformly charged...Ch. 23 - A small glass bead charged to + 6.0 nC is in the...Ch. 23 - The electric field 5.0 cm from a very long charged...Ch. 23 - A 12-cm-long thin rod has the nonuniform charge...Ch. 23 - Two charged rings face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - Two 10-cm-diameter charged rings face each other,...Ch. 23 - Two charged disks face each other, 20 cm apart....Ch. 23 - The electric field strength 2.0 cm from the...Ch. 23 - A 20cm20cm cm horizontal metal electrode is...Ch. 23 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter insulating spheres have a 6.0...Ch. 23 - You've hung two very large sheets of plastic...Ch. 23 - A 2.0m X 4.0m flat carpet acquires a uniformly...Ch. 23 - Two circular disks spaced 0.50 mm apart form a...Ch. 23 - A parallel-plate capacitor is formed from two...Ch. 23 - Air "breaks down" when the electric field strength...Ch. 23 - Two parallel plates 1.0 cm apart are equally and...Ch. 23 - a. What is the electric field strength between the...Ch. 23 - Honeybees acquire a charge while flying due to...Ch. 23 - An electron traveling parallel to a uniform...Ch. 23 - The surface charge density on an infinite charged...Ch. 23 - An electron in a vacuum chamber is fired with a...Ch. 23 - A 1.0m -diameter oil droplet (density 900 kg/m3)...Ch. 23 - The permanent electric dipole moment of the water...Ch. 23 - A point charge Q is distance r from a dipole...Ch. 23 - An ammonia molecule (NH3) has a permanent electric...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 23 - Derive Equation 23.11 for the field Edipolein the...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.41 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - FIGURE P23.42 is a cross section of two infinite...Ch. 23 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 23 - A plastic rod with linear charge density ? is bent...Ch. 23 - An infinite plane of charge with surface charge...Ch. 23 - A sphere of radius R and surface charge density ?...Ch. 23 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 23 - An electron is launched at a 45 angle and a speed...Ch. 23 - The two parallel plates in FIGURE P23.53 are 2.0...Ch. 23 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 23 - 56. Your physics assignment is to figure out a way...Ch. 23 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 23 - In Problems 63 through 66 you are given the...Ch. 23 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 66EAPCh. 23 - A rod of length L lies along the y-axis with its...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - a. An infinitely long sheet of charge of width L...Ch. 23 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 23 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 23 - 72. A proton orbits a long charged wire, making ...Ch. 23 - Prob. 73EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- SARET CRKS AUTOWAY 12. A stone is dropped from the top of a cliff. It is seen to hit the ground below after 3.55 s. How high is the cliff? 13. A ball is dropped from rest at the top of a building that is 320 m tall. Assuming no air resistance, what is the speed of the ball just before it strikes the ground? 14. Estimate (a) how long it took King Kong to fall straight down from the top of the Empire State Building (280m high), and (b) his velocity just before "landing". Useful equations For Constant Velocity: V => D X = V₁t + Xo For Constant Acceleration: Vr = V + at X = Xo+Vot + v=V+2a(X-Xo) \prom = V +V V velocity t = time D Distance X = Final Position Xo Initial Position V = Final Velocity Vo Initial Velocity a = acceleration For free fall Yf = Final Position Yo Initial Position g = 9.80 m $2 For free fall: V = V + gt Y=Yo+Vo t + +gt V,² = V₁²+2g (Y-Yo) V+Vo Vprom= 2 6arrow_forwardSolve the problemsarrow_forwardA 11 kg weight is attached to a spring with constant k = 99 N/m and subjected to an external force F(t) =-704 sin(5t). The weight is initially displaced 4 meters above equilibrium and given an upward velocity of 5 m/s. Find its displacement for t> 0. y(t) וןarrow_forward
- 7. A race car accelerates from rest to 55 m s-1 in 5.0 seconds. The acceleration of the car Is m s-² 8. An object's speed increases uniformly from 10.5 km per hour to 99.8 km per hour in 2.41 seconds. Calculate the acceleration in m s-2 and express your answer to three significant figures. 9. The acceleration-time graph of a car is shown below. The initial speed of the car is 5.0 m s-1. # Acceleration (ms) 12 8.0- 4.0- 2.0 4.0 6.0 Time (s) Calculate the velocity of the car at t = 4.0 s. 3arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Problem Seven. A football receiver running straight downfield at 5.60 m/s is 11.5 m in front of the quarterback when a pass is thrown downfield at an angle of 35.0° horizon. above the 8.) If the receiver never changes speed and the ball is caught at the same height from which it was thrown, find the distance between the quarterback and the receiver when the catch is made. (A) 21.3 (B) 17.8 (C) 18.8 (D) 19.9 (E) 67.5arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Please view both photos, and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA thrown brick hits a window, but doesn't break it. Instead it reverses direction and ends down on the ground below the window. Since the brick didn't break the glass, we know: О The force of the brick on the glass > the force of the glass on the brick. О The force of the brick on the glass the force of the glass on the brick. = О The force of the brick on the glass < the force of the glass on the brick. О The brick didn't slow down as it broke the glass.arrow_forwardAlexandra (wearing rubber boots for traction) is attempting to drag her 32.6-kg Golden Retriever across the smooth ice by applying a horizontal force. What force must she apply to move the dog with a constant speed of 0.950 m/s? ☐ 31.0 lb. ☐ 319 kg. ○ Zero. 32.6 kg.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY