
To label: The somatosensory receptors in Figure 23.1 (a).
Introduction: A cell or a group of cells that is specialized in detecting the changes in the environment and triggers the impulses in the sensory nervous system is referred to as the somatosensory receptors. The somatosensory receptors are categorized into five types, namely the thermoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, pain receptors, proprioceptors, and chemoreceptors.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
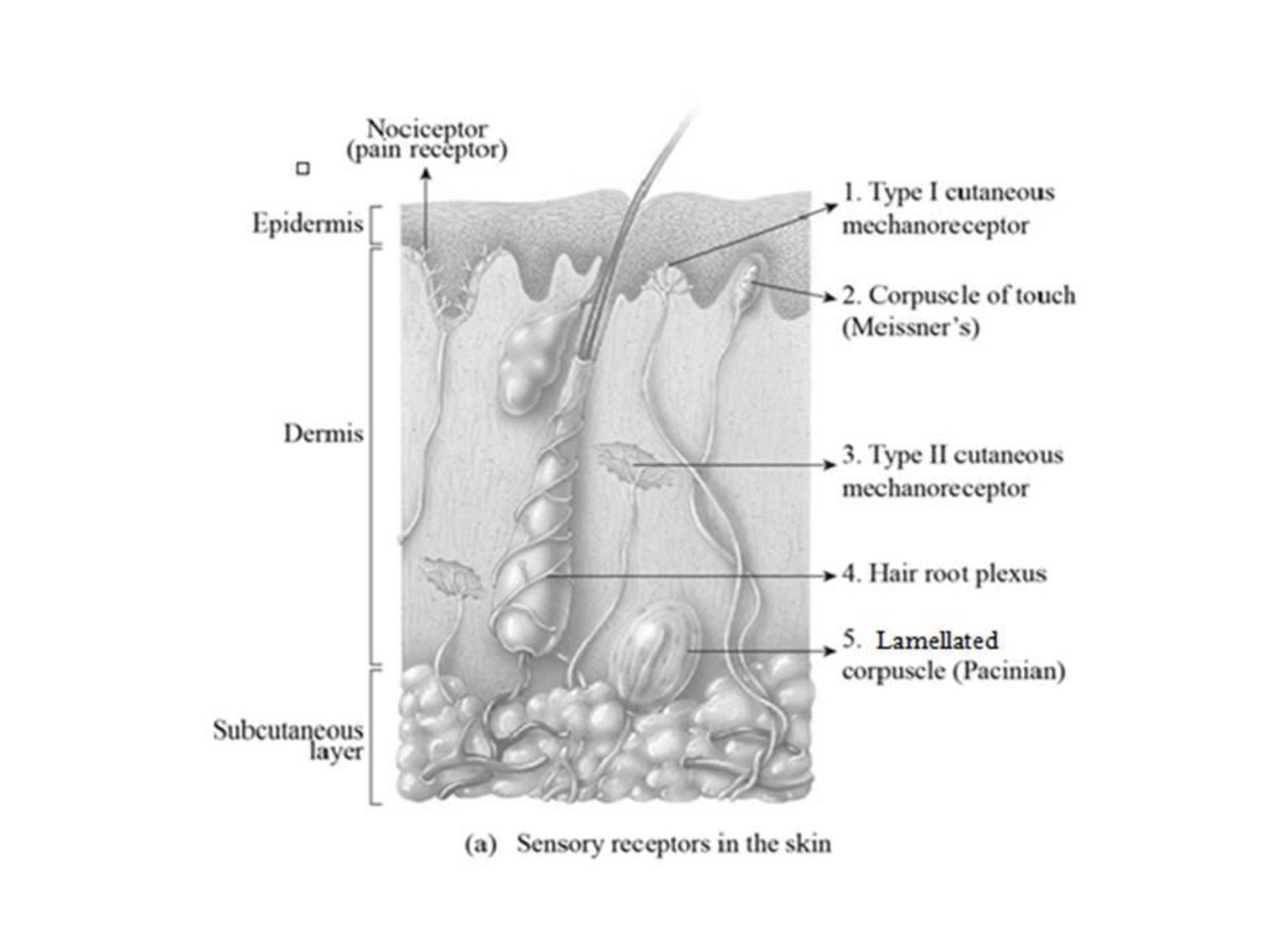
Explanation of Solution
1. Type I cutaneous mechanoreceptor: They are free nerve endings located in the skin and is associated with the Merkel cells in the stratum basale layer of the epidermis. The stimuli of these receptors are touch and pressure.
2. Corpuscle of touch: They are encapsulated nerve endings situated in the dermal papillae of the hairless skin. Touch and pressure are the stimuli of these receptors.
3. Type II cutaneous mechanoreceptor: They are encapsulated nerve endings that are situated on the tendons, ligaments, and dermis. Stretching of the limbs and digits are the stimuli of these receptors.
4. Root hair plexus: They are the free nerve endings that surround the follicles of hair. The stimuli of root hair plexus touch the hair.
5. Lamellated corpuscle: They are encapsulated nerve endings situated in the subcutaneous and submucosal muscles, tissues, joints, and tendons. Touch and pressure are the stimuli of these receptors.
To label: The somatosensory receptors in Figure 23.1 (b).
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
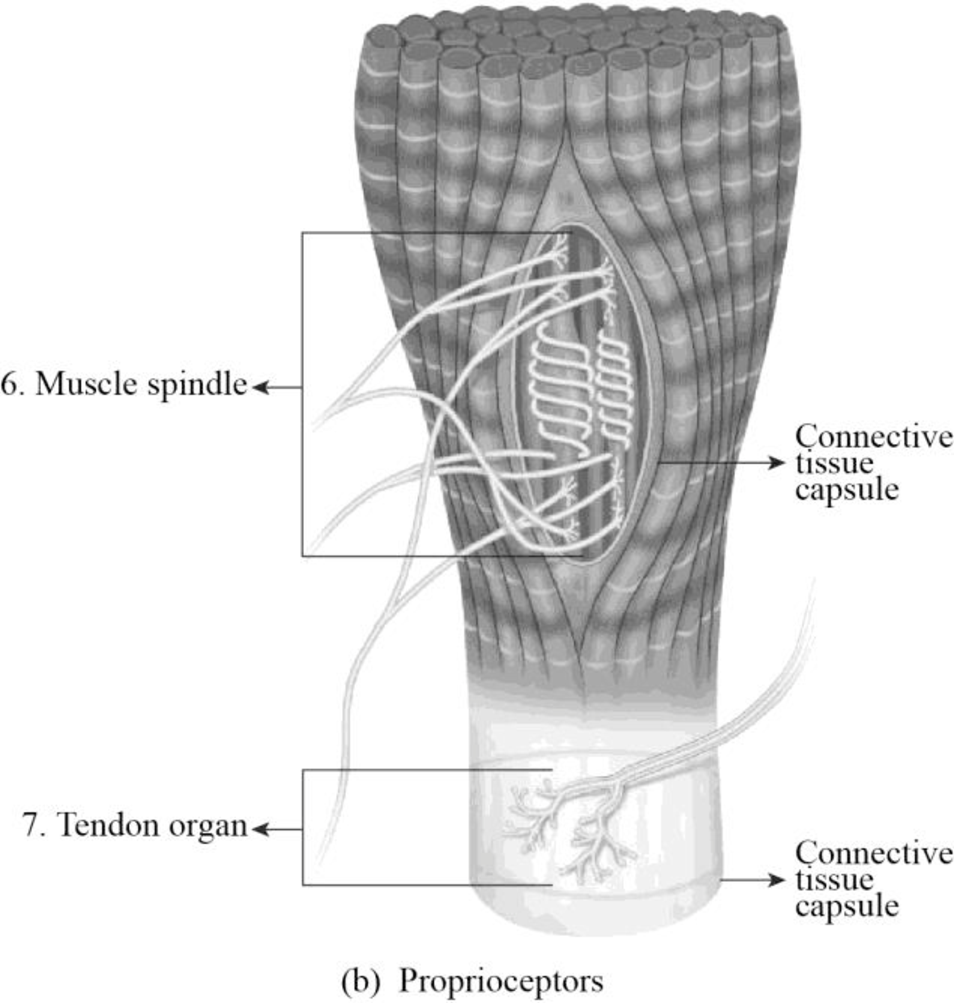
Explanation of Solution
6. Muscle spindle: They are encapsulated nerve endings located within most of the skeletal muscles. These receptors respond to the changes in the length of the muscles.
7. Tendon organ: They are encapsulated nerve endings situated at the junction of the muscles and tendons. These receptors respond to the changes in the movement and position of the joints.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e Loose-Leaf Print Companion
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





