
BIOCHEMISTRY II >CUSTOM<
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781337449014
Author: GARRETT
Publisher: CENGAGE C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 22, Problem 7P
Interpretation Introduction
To calculate:
The number of reducing ends and non-reducing ends in given cases.
Introduction:
Glycogen is composed of glucose linked via alpha (1-4) linkages and branches occurring through alpha (1-6) linkages. In glycogen, the free C-1 end on glucose end of the molecule is called a reducing end and all the other ends are non-reducing ends.
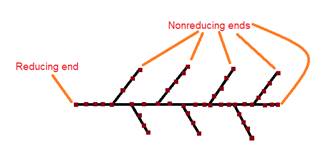
Black line indicate the glycogen chain and red dot indicates the glucose monomers.
Therefore, regardless of the number of residues in the glycogen chain, there is only one reducing end for a glycogen chain. All other ends are non-reducing.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
9. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from
the following reaction sequence, starting with ethyl acetoacetate?
요요.
1. NaOCH2CH3
CH3CH2OH
1. NaOH, H₂O
2. H3O+
3. A
OCH2CH3
2.
ethyl acetoacetate
ii
A
3. H3O+
OH
B
C
D
E
7. Only one of the following ketones cannot be made via an acetoacetic ester
synthesis. Which one is it?
Ph
کہ
A
B
C
D
E
2. Which one is the
major organic
product obtained
from the following
reaction sequence?
HO
A
OH
1. NaOEt, EtOH
1. LiAlH4
EtO
OEt
2. H3O+
2. H3O+
OH
B
OH
OH
C
-OH
HO
-OH
OH
D
E
.CO₂Et
Chapter 22 Solutions
BIOCHEMISTRY II >CUSTOM<
Ch. 22 - Prob. 1PCh. 22 - Prob. 2PCh. 22 - Prob. 3PCh. 22 - Prob. 4PCh. 22 - Prob. 5PCh. 22 - Prob. 6PCh. 22 - Prob. 7PCh. 22 - Prob. 8PCh. 22 - Prob. 9PCh. 22 - Understanding Enzyme Mechanisms Related to...
Ch. 22 - Understanding the Mechanisms of Reactions Related...Ch. 22 - Prob. 12PCh. 22 - Prob. 13PCh. 22 - Prob. 14PCh. 22 - Prob. 15PCh. 22 - Prob. 16PCh. 22 - Prob. 17PCh. 22 - Prob. 18PCh. 22 - Prob. 19PCh. 22 - Prob. 20PCh. 22 - Prob. 21PCh. 22 - Prob. 22PCh. 22 - Using the ActiveModel for aldose reductase,...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- what is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forwardFour distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forward
- Examine the metabolic pathway. The enzymes that catalyze each step are identified as "e" with a numeric subscript. e₁ e3 e4 A B с 1° B' 02 e5 e6 e7 E F Which enzymes catalyze irreversible reactions? ப e ez ☐ ez e4 ☐ ப es 26 5 e7 Which of the enzymes is likely to be the allosteric enzyme that controls the synthesis of G? €2 ез e4 es 26 5 e7arrow_forwardAn allosteric enzyme that follows the concerted model has an allosteric coefficient (T/R) of 300 in the absence of substrate. Suppose that a mutation reversed the ratio. Select the effects this mutation will have on the relationship between the rate of the reaction (V) and substrate concentration, [S]. ㅁㅁㅁ The enzyme would likely follow Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The plot of V versus [S] would be sigmoidal. The enzyme would mostly be in the T form. The plot of V versus [S] would be hyperbolic. The enzyme would be more active.arrow_forwardPenicillin is hydrolyzed and thereby rendered inactive by penicillinase (also known as ẞ-lactamase), an enzyme present in some penicillin-resistant bacteria. The mass of this enzyme in Staphylococcus aureus is 29.6 kDa. The amount of penicillin hydrolyzed in 1 minute in a 10.0 mL. solution containing 1.00 x 10 g of purified penicillinase was measured as a function of the concentration of penicillin. Assume that the concentration of penicillin does not change appreciably during the assay. Plots of V versus [S] and 1/V versus 1/[S] for these data are shown. Vo (* 10 M minute"¹) 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 20 1.0 0.0 о 10 20 30 1/Vo (* 10 M1 minute) 20 103 90 BO 70 50 [S] (* 100 M) 40 50 60 y=762x+1.46 × 10" [Penicillin] (M) Amount hydrolyzed (uM) 1 0.11 3 0.25 5 0.34 10 0.45 30 0.58 50 0.61arrow_forward
- Consider the four graphs shown. In each graph, the solid blue curve represents the unmodified allosteric enzyme and the dashed green curve represents the enzyme in the presence of the effector. Identify which graphs correctly illustrate the effect of a negative modifier (allosteric inhibitor) and a positive modifier (allosteric activator) on the velocity curve of an allosteric enzyme. Place the correct graph in the set of axes for each type of modifier. Negative modifier Reaction velocity - Positive modifier Substrate concentration - Reaction velocity →→→→ Substrate concentration Answer Bankarrow_forwardConsider the reaction: phosphoglucoisomerase Glucose 6-phosphate: glucose 1-phosphate After reactant and product were mixed and allowed to reach at 25 °C, the concentration of each compound at equilibrium was measured: [Glucose 1-phosphate] = 0.01 M [Glucose 6-phosphate] = 0.19 M Calculate Keq and AG°'. Код .0526 Incorrect Answer 7.30 AG°' kJ mol-1 Incorrect Answerarrow_forwardClassify each phrase as describing kinases, phosphatases, neither, or both. Kinases Phosphatases Neither Both Answer Bank transfer phosphoryl groups to acidic amino acids in eukaryotes may use ATP as a phosphoryl group donor remove phosphoryl groups from proteins catalyze reactions that are the reverse of dephosphorylation reactions regulate the activity of other proteins catalyze phosphorylation reactions PKA as an example turn off signaling pathways triggered by kinasesarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction. kp S P kg What effects are produced by an enzyme on the general reaction? AG for the reaction increases. The rate constant for the reverse reaction (kr) increases. The reaction equilibrium is shifted toward the products. The concentration of the reactants is increased. The activation energy for the reaction is lowered. The formation of the transition state is promoted.arrow_forwardThe graph displays the activities of wild-type and several mutated forms of subtilisin on a logarithmic scale. The mutations are identified as: • The first letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid being altered. • The number identifies the position of the residue in the primary structure. ⚫ The second letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid replacing the original one. • Uncat. refers to the estimated rate for the uncatalyzed reaction. Log₁(S-1) Wild type S221A H64A -5 D32A S221A H64A D32A -10 Uncat. How would the activity of a reaction catalyzed by a version of subtilisin with all three residues in the catalytic triad mutated compare to the activity of the uncatalyzed reaction? It would have more activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately three-fold faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. It would have less activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately 1000-fold slower than the…arrow_forwardB Substrate Product AL Product Substrate Reaction progress- Reaction progress- omplete the passage describing the two reactions. In reaction A, the stability of the substrate is (AG) of the reaction is positive, Incorrect Answer greater than the stability of the product. The free-energy change Incorrect Answer so the reaction is considered In reaction B, the stability of the substrate is (AG) of the reaction is less than Incorrect Answer endergonic and Incorrect Answer not spontaneous. Incorrect Answer the stability of the product. The free-energy change negative, so the reaction is considered Incorrect Answer exergonic and spontaneous. Incorrect Answer Incorrect Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning