
Concept explainers
Review. Rail guns have been suggested for launching projectiles into space without chemical rockets. A tabletop model rail gun (Fig. P22.76) consists of two long, parallel, horizontal rails ℓ = 3.50 cm apart, bridged by a bar of mass m = 3.00 g that is free to slide without friction. The rails and bar have low electric resistance, and the current is limited to a constant I = 24.0 A by a power supply that is far to the left of the figure, so it has no magnetic effect on the bar. Figure P22.76 shows the bar at rest at the midpoint of the rails at the moment the current is established. We wish to find the speed with which the bar leaves the rails after being released from the midpoint of the rails. (a) Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance of 1.75 cm from a single long wire carrying a current of 2.40 A. (b) For purposes of evaluating the magnetic field, model the rails as infinitely long. Using the result of part (a), find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the midpoint of the bar. (c) Argue that this value of the field will be the same at all positions of the bar to the right of the midpoint of the rails. At other points along the bar, the field is in the same direction as at the midpoint, but is larger in magnitude. Assume the average effective magnetic field along the bar is five times larger than the field at the midpoint. With this assumption, find (d) the magnitude and (e) the direction of the force on the bar. (f) Is the bar properly modeled as a particle under constant acceleration? (g) Find the velocity of the bar after it has traveled a distance d = 130 cm to the end of the rails.
Figure P22.76
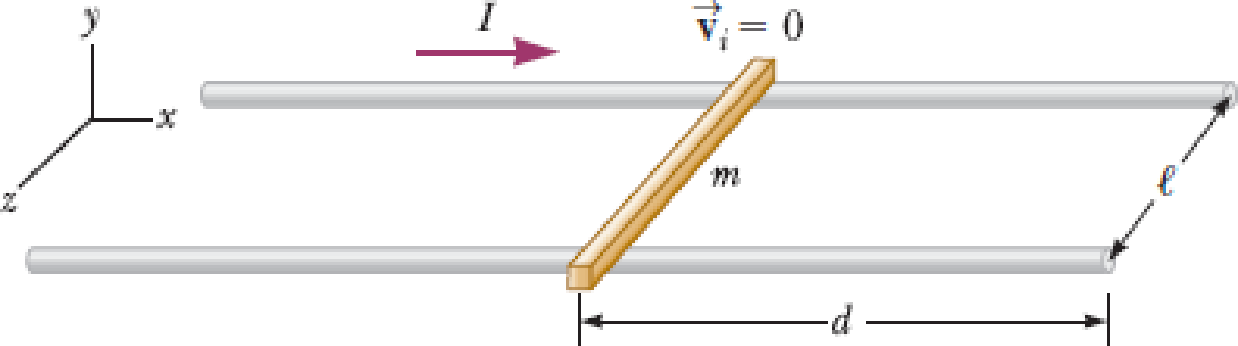
(a)
The magnitude of the magnetic field.
Answer to Problem 76P
The magnitude of the magnetic field is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the magnetic field for a conductor,
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The magnitude of the magnetic field is
(b)
The magnitude and the direction of the magnetic field from the mid- point of the bar.
Answer to Problem 76P
The magnitude of the field at the mid-point of the bar is
Explanation of Solution
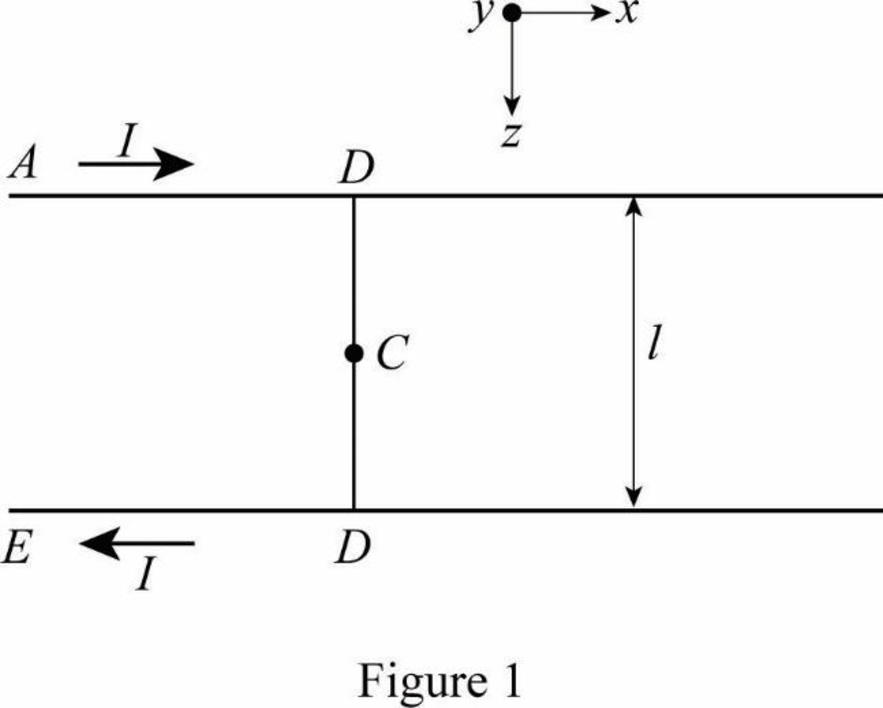
From the figure1 the current is diverted through the bar, here only half of each rails carriers currents, so the field produce by each rail are half of the infinitely long wire produces.
Conclusion:
Write the expression for the magnetic field produced by the conductor
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the magnetic field produced by the conductor
Here,
Substitute
The total magnetic field at the point
Therefore, the magnitude of the field at the mid-point of the bar is
(c)
The reason for the value of the magnetic field will be same at all position of the bar to the right of the midpoint of the rails.
Answer to Problem 76P
The rail is long so the location of the bar does not depend upon the length of the rail to the right side.
Explanation of Solution
Here, it is assumed as the rail is infinitely long so, the length of the rail to the right of the bar does not depend upon the location of the bar.
Therefore the magnetic field will be same at all position of the bar to the right of the midpoint of the rails.
Conclusion:
The rail is long so the location of the bar does not depend upon the length of the rail to the right side.
(d)
The magnitude of the force on the bar.
Answer to Problem 76P
The magnitude of the force on the bar is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the magnetic field in a wire,
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The magnitude of the force on the bar is
(e)
The direction of the force on the bar.
Answer to Problem 76P
The direction of the force on the bar is in positive
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the magnetic field in a wire,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The force vector on the bar is
(f)
Whether the bar is properly modeled as a particle under constant acceleration.
Answer to Problem 76P
Yes, the bar will move with constant acceleration of magnitude
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the acceleration of bar,
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the bar will move with constant acceleration of magnitude
(g)
The velocity of the bar.
Answer to Problem 76P
The velocity of the bar is
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for velocity of the bar,
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The velocity of the bar is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, Hybrid (with Enhanced WebAssign Printed Access Card)
- RT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





