
MCAT-Style Passage Problems
Lightbulb Failure
You’ve probably observed that the most common time for an incandescent lightbulb to fail is the moment when it is turned on. Let’s look at the properties of the bulb’s filament to see why this happens.
The current in the tungsten filament of a lightbulb heats the filament until it glows. The filament is so hot that some of the atoms on its surface fly off and end up sticking on a cooler part of the bulb. Thus the filament gets progressively thinner as the bulb ages. There will certainly be one spot on the filament that is a bit thinner than elsewhere. This thin segment will have a higher resistance than the surrounding filament. More power will be dissipated at this spot, so it won’t only be a thin spot, it also will be a hot spot.
Now, let’s look at the resistance of the filament. The graph in Figure P22.70 shows data for the current in a lightbulb as a function of the potential difference across it. The graph is not linear, so the filament is not an ohmic material with a constant resistance. However, we can define the resistance at any particular potential difference ∆V to be R = ∆V/I. This ratio, and hence the resistance, increases with ∆V and thus with temperature.
Figure P22. 70
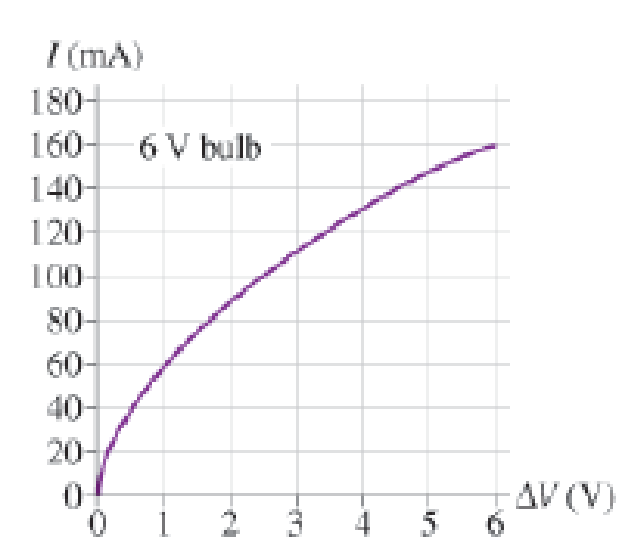
When the bulb is turned on, the filament is cold and its resistance is much lower than during normal, high-temperature operation. The low resistance causes a surge of higher-than-normal current lasting a fraction of a second until the filament heats up. Because power dissipation is I2R, the power dissipated during this first fraction of a second is much larger than the bulb’s rated power. This current surge concentrates the power dissipation at the high-resistance thin spot, perhaps melting it and breaking the filament.
There are devices to put in a light socket that control the current through a lightbulb, thereby increasing its lifetime. Which of the following strategies would increase the lifetime of a bulb without making it dimmer?
A. Reducing the average current through the bulb
B. Limiting the maximum current through the bulb
C. Increasing the average current through the bulb
D. Limiting the minimum current through the bulb
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Books a la Carte Edition (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- 3.37(a) Five free electrons exist in a three-dimensional infinite potential well with all three widths equal to \( a = 12 \, \text{Å} \). Determine the Fermi energy level at \( T = 0 \, \text{K} \). (b) Repeat part (a) for 13 electrons. Book: Semiconductor Physics and Devices 4th ed, NeamanChapter-3Please expert answer only. don't give gpt-generated answers, & please clear the concept of quantum states for determining nx, ny, nz to determine E, as I don't have much idea about that topic.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. a Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) 1) Determine the angle of refraction of the ray of light in the water. Barrow_forward
- Hi can u please solvearrow_forward6. Bending a lens in OpticStudio or OSLO. In either package, create a BK7 singlet lens of 10 mm semi-diameter and with 10 mm thickness. Set the wavelength to the (default) 0.55 microns and a single on-axis field point at infinite object distance. Set the image distance to 200 mm. Make the first surface the stop insure that the lens is fully filled (that is, that the entrance beam has a radius of 10 mm). Use the lens-maker's equation to calculate initial glass curvatures assuming you want a symmetric, bi-convex lens with an effective focal length of 200 mm. Get this working and examine the RMS spot size using the "Text" tab of the Spot Diagram analysis tab (OpticStudio) or the Spd command of the text widnow (OSLO). You should find the lens is far from diffraction limited, with a spot size of more than 100 microns. Now let's optimize this lens. In OpticStudio, create a default merit function optimizing on spot size.Then insert one extra line at the top of the merit function. Assign the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer .arrow_forward
- Use the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the next question. Two mirrors meet an angle, a, of 105°. A ray of light is incident upon mirror A at an angle, i, of 42°. The ray of light reflects off mirror B and then enters water, as shown below: A Incident ray at A Note: This diagram is not to scale. Air (n = 1.00) Water (n = 1.34) Barrow_forwardGood explanation it sure experts solve it.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Asaparrow_forwardA satellite has a mass of 100kg and is located at 2.00 x 10^6 m above the surface of the earth. a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this loction? b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





