
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780131495081
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: Addison-Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 34P
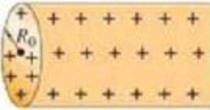
(II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of radius R0 and length ℓ (R0 ≪ ℓ) possesses a uniform volume charge density ρE (C/m3), Fig. 22–34. Determine the electric field at points (a) outside the cylinder (R > R0) and (b) inside the cylinder (R < R0). Do only for points far from the ends and for which R ≪ ℓ.
FIGURE 22–34 Problem 34.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 22 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 22.1 - Which of the following would cause a change in the...Ch. 22.2 - A point charge Q is at the center of a spherical...Ch. 22.2 - Three 2.95 C charges are in a small box. What is...Ch. 22.3 - A charge Q is placed on a hollow metal ball. We...Ch. 22.3 - CHAPTER-OPENING QUESTIONGuess now! A nonconducting...Ch. 22.3 - Which of the following statements about Gausss law...Ch. 22 - If the electric flux through a closed surface is...Ch. 22 - Is the electric field E in Gausss law....Ch. 22 - A point charge is surrounded by a spherical...Ch. 22 - What can you say about the flux through a closed...
Ch. 22 - The electric field E is zero at all points on a...Ch. 22 - Define gravitational flux in analogy to electric...Ch. 22 - Would Gausss law be helpful in determining the...Ch. 22 - A spherical basketball (a nonconductor) is given a...Ch. 22 - In Example 226, it may seem that the electric...Ch. 22 - Suppose the line of charge in Example 226 extended...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is surrounded by a spherical...Ch. 22 - A solid conductor carries a net positive charge Q....Ch. 22 - A point charge q is placed at the center of the...Ch. 22 - A small charged ball is inserted into a balloon....Ch. 22 - (I) A uniform electric field of magnitude 5.8 102...Ch. 22 - (I) The Earth possesses an electric field of...Ch. 22 - (II) A cube of side l is placed in a uniform field...Ch. 22 - (II) A uniform field E is parallel to the axis of...Ch. 22 - (I) The total electric flux from a cubical box...Ch. 22 - (I) Figure 2226 shows five closed surfaces that...Ch. 22 - (II) In Fig. 2227, two objects, O1 and O2, have...Ch. 22 - (II) A ring of charge with uniform charge density...Ch. 22 - (II) In a certain region of space, the electric...Ch. 22 - (II) A point charge Q is placed at the center of a...Ch. 22 - (II) A 15.0-cm-long uniformly charged plastic rod...Ch. 22 - (I) Draw the electric field lines around a...Ch. 22 - (I) The field just outside a 3.50-cm-radius metal...Ch. 22 - (I) Starting from the result of Example 223, show...Ch. 22 - (I) A long thin wire, hundreds of meters long,...Ch. 22 - (I) A metal globe has l.50 mC of charge put on it...Ch. 22 - (II) A nonconducting sphere is made of two layers....Ch. 22 - (II) A solid metal sphere of radius 3.00 m carries...Ch. 22 - (II) A 15.0-cm-diameter nonconducting sphere...Ch. 22 - (II) A flat square sheet of thin aluminum foil,...Ch. 22 - (II) A spherical cavity of radius 4.50 cm is at...Ch. 22 - (II) A point charge Q rests at the center of an...Ch. 22 - (II) A solid metal cube has a spherical cavity at...Ch. 22 - (II) Two large, flat metal plates are separated by...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the two conducting plates in Problem...Ch. 22 - (II) The electric field between two square metal...Ch. 22 - (II) Two thin concentric spherical shells of radii...Ch. 22 - (II) A spherical rubber balloon carries a total...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the nonconducting sphere of Example...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose in Fig. 2232, Problem 29, there is...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose the thick spherical shell of Problem...Ch. 22 - (II) Suppose that at the center of the cavity...Ch. 22 - (II) A long cylindrical shell of radius R0 and...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A thin cylindrical shell of radius R1 is...Ch. 22 - (II) A thin cylindrical shell of radius R1 = 6.5...Ch. 22 - (II) (a) If an electron (m = 9.1 1031 kg) escaped...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A nonconducting sphere of radius r0 is...Ch. 22 - (II) A very long solid nonconducting cylinder of...Ch. 22 - (II) A flat ring (inner radius R0, outer radius...Ch. 22 - (II) An uncharged solid conducting sphere of...Ch. 22 - (III) A very large (i.e., assume infinite) flat...Ch. 22 - (III) Suppose the density of charge between r1 and...Ch. 22 - (III) Suppose two thin flat plates measure 1.0 m ...Ch. 22 - (III) A flat slab of nonconducting material (Fig....Ch. 22 - (III) A flat slab of nonconducting material has...Ch. 22 - (III) An extremely long, solid nonconducting...Ch. 22 - (III) Charge is distributed within a solid sphere...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is on the axis of a short...Ch. 22 - Prob. 51GPCh. 22 - The Earth is surrounded by an electric field,...Ch. 22 - A cube of side has one corner at the origin of...Ch. 22 - A solid nonconducting sphere of radius r0 has a...Ch. 22 - A point charge of 9.20 nC is located at the origin...Ch. 22 - A point charge produces an electric flux of +235 N...Ch. 22 - A point charge Q is placed a distance r0/2 above...Ch. 22 - Three large but thin charged sheets are parallel...Ch. 22 - Neutral hydrogen can be modeled as a positive...Ch. 22 - A very large thin plane has uniform surface charge...Ch. 22 - A sphere of radius r0 carries a volume charge...Ch. 22 - Dry air will break down and generate a spark if...Ch. 22 - Three very large sheets are separated by equal...Ch. 22 - In a cubical volume, 0.70 m on a side, the...Ch. 22 - A conducting spherical shell (Fig. 2249) has inner...Ch. 22 - A hemisphere of radius R is placed in a...Ch. 22 - (III) An electric field is given by...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
28. Consider the reaction
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of e...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
WRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS In a short essay (100-150 words), identify the factor or factors in Figure 53...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Which coastal area experiences the smallest tidal range? ____________
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Use the key to classify each of the following described tissue types into one of the four major tissue categori...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Why are BSL-4 suits pressurized? Why not just wear tough regular suits?
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?arrow_forwardSolve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY