
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of diethyl malonate showing acidic hydrogens is to be stated. The reason as to why it is more acidic than ordinary ester is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidic hydrogen is defined as hydrogen that carries positive charge when the acid dissociates. The acidity in esters depends upon the stability of enolate ion. The higher is the stability of enolate ion higher is the acidity.
Answer to Problem 22.1P
The structure of the diethyl malonate showing acidic hydrogens is given below.
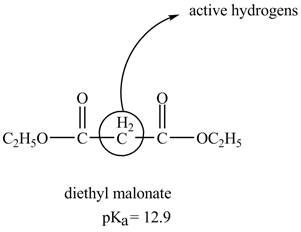
The diethyl malonate is more acidic than ordinary ester because its conjugate base is stabilized by delocalization of negative charge as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In diethyl malonate the methylene group is surrounded by two carbonyl groups as shown below.
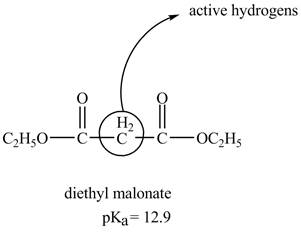
Figure 1
This active hydrogen is abstracted by base and generates a negative charge. The negative charge is delocalized between carbon and oxygen. This delocalization stabilizes the enolate ion. However, the presence of two carbonyl group increases the polar effect and stabilize the enolate ion. The diethyl malonate is more acidic than ordinary ester as its conjugate base is stabilized by delocalization of negative charge.
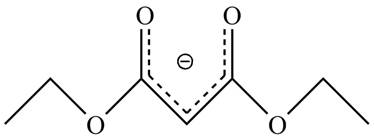
The acidity of the carbonyl compound is directly proportional to the stability of the enolate ion. The conjugate base stabilized by delocalization of diethyl malonate is shown below.
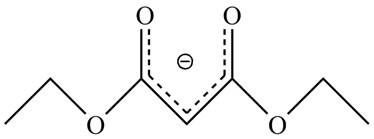
Figure 2
The structure of the diethyl malonate showing acidic hydrogens is given in Figure 2. The diethyl malonate is more acidic than ordinary ester due to delocalization of negative charge in its conjugate base.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of ethyl acetoacetate showing acidic hydrogens is to be stated. The reason as to why it is more acidic than ordinary ester is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Acidic hydrogen is defined as hydrogen carry positive charge when the acid dissociates. The acidity in esters depends upon the stability of enolate ion. The higher is the stability of enolate ion higher is the acidity.
Answer to Problem 22.1P
The structure of ethyl acetoacetate showing acidic hydrogens is given below.
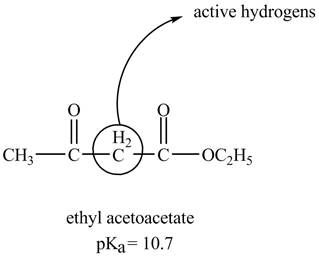
The ethyl acetoacetate is more acidic than ordinary ester because its conjugate base is stabilized by delocalization of negative charge as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In ethyl acetoacetate, the methylene group is surrounded by two carbonyl groups as shown below.
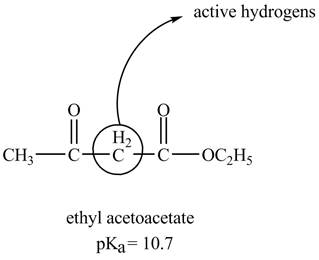
Figure 3
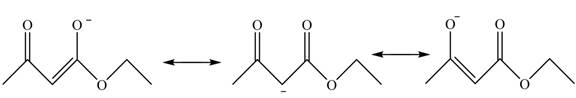
This active hydrogen is abstracted by base and generates a negative charge. The negative charge is delocalized between carbon and oxygen. This delocalization stabilizes the enolate ion. However, the presence of two carbonyl groups increases the polar effect and stabilize the enolate ions. The conjugate base stabilized by delocalization of ethyl acetoacetate is shown below.

Figure 4
The ethyl acetoacetate is more acidic than ordinary ester as its conjugate base is stabilized by delocalization of negative charge.
The structure of ethyl acetoacetate is shown in Figure 3 and the acidic character of ethyl acetoacetate is shown in Figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- help draw the moleculearrow_forwardHow to draw this claisen condensation reaction mechanisms/arrow_forwardWrite all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forward
- How can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forwarddraw out these molecules pleasearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


