
MECHANICS OF MATERIAL IN SI UNITS
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781292178202
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 2.1PP
A loading causes the member to deform into the dashed shape. Explain how to determine the normal strains εCD and εAB. The displacement Δ and the lettered dimensions are known.
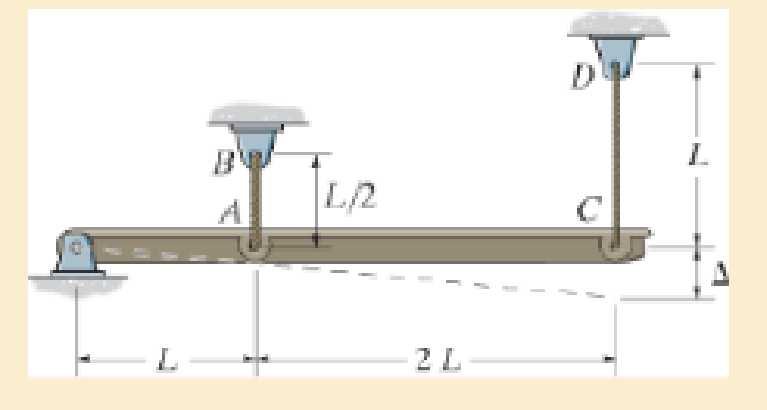
P2–1
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:27
Students have asked these similar questions
so
A
4
I need a detailed drawing with explanation
し
i need drawing in solution
motion is as follows;
1- Dwell 45°.
Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required
2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion.
3- Dwell 90°.
4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion.
5- Dwell 45°.
cam is 50 mm.
Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the
か
---2-125
750 x2.01
98P
Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an
anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm,
BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D.
A 45
B
Space Diagram
o NTS (Not-to-Scale)
C
D
I need a detailed drawing with explanation
so
Solle
4
يكا
Pax Pu + 96**
motion is as follows;
1- Dwell 45°.
Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required
2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion.
3- Dwell 90°.
4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion.
5- Dwell 45°.
cam is 50 mm.
Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the
55
---20125
750 X 2.01
1989
Chapter 2 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIAL IN SI UNITS
Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the member to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the mamber to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the wires to elongate into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - A loading causes the block to deform into the...Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...
Ch. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - The pin-connected rigid rods AB and BC are...Ch. 2.2 - The wire AB is unstretched when = 45. If a load...Ch. 2.2 - If a horizontal load applied to the bar AC causes...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - The material distorts into the dashed position...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...Ch. 2.2 - The nylon cord has an original length L and is...Ch. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners A and B...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the shear strain xy at corners D and C...Ch. 2.2 - Determine the average normal strain that occurs...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The block is deformed into the position shown by...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate undergoes a deformation...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
For the circuit shown, use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and i1.
How much power is delivered to the c...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
The following are instructions written in Vole machine language. Rewrite them in English. a. 0x368A b. 0xBADE c...
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Describe a method that can be used to gather a piece of data such as the users age.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
What is the importance of modeling in engineering? How are the mathematical models for engineering processes pr...
HEAT+MASS TRANSFER:FUND.+APPL.
In an IDE that allows you to visually construct a window, how do you place an item such as a button in the wind...
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Even though a binary file is not a text file, it can contain embedded text. To find out if this is the case, wr...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ashaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNM 20,000 10,000 0 90 270 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 720arrow_forwardchanism shown in figure below, the crank OA rotates at 60 RPM counterclockwise. The velocity diagram is also drawn to scale (take dimensions from space diagram). Knowing that QCD is rigid plate, determine: a. Linear acceleration of slider at B, b. Angular acceleration of the links AC, plate CQD, and BD. D Space Diagram Scale 1:10 A ES a o,p,g b Velocity Diagram Scale 50 mm/(m/s) darrow_forwardA thick closed cylinder, 100 mm inner diameter and 200 mm outer diameter is subjected to an internal pressure of 230 MPa and outer pressure of 70 MPa. Modulus of elasticity, E=200 GPa. and Poisson's ratio is 0.3, determine: i) The maximum hoop stress ii) The maximum shear stress iii) The new dimension of the outer diameter due to these inner and outer pressures.arrow_forward
- A ә レ shaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNm 20,000 10,000 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 270 0 90 か ---20125 750 X 2.01 44 720 sarrow_forwardThe gas tank is made from A-36 steel (σy = 250 MPa) and has an inner diameter of 3.50 m. If the tank is designed to withstand a pressure of 1.2 MPa, determine the required minimum wall thickness to the nearest millimeter using (a) The maximum-shear-stress theory (b) Maximum distortion- energy theory. Apply a factor of safety of 1.5 against yielding.arrow_forwardә レ Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A A B # Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C 10 =--20125 735) 750 x2.01 اهarrow_forward
- 2 レ Tanism in which the link OA mm. O anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s, the lengths of the various links are OA=75mm, OB=150mm, BC=150mm,CD=300mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A A Space Diagram o NT$ (Not-to-Scale) B # C か 750 x2.01 165 79622arrow_forwardAshaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNM 20,000 10,000 0 90 270 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 720arrow_forwardFigure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forward
- motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forwardAn ideal gas, occupying a volume of 0.02 m3 , has a temperature of 25 0C and is at 1.2 bar. The gas is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to a final pressure of 8 bar. Assuming the gas has an adiabatic index of γ = 1.4, calculate (a) the final temperature, (b) the final volume, (c) the work performed during the compression and (d) the heat transferred.arrow_forwardattached is a past paper question in which we werent given the solution. a solution with clear steps and justification would be massively appreciated thankyou.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical Design (Machine Design) Clutches, Brakes and Flywheels Intro (S20 ME470 Class 15); Author: Professor Ted Diehl;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eMvbePrsT34;License: Standard Youtube License