
Why does the melting point of hydrocarbons increase as the number of carbon atoms per molecule increases?
(a) An increase in the number of carbon atoms per molecules also means an increase in the density of the hydrocarbon.
(b) Because of greater induced dipole-induced dipole molecular attractions.
(c) Larger hydrocarbon chains tend to be branched.
(d) Because the molecular mass also increases.
The correct option for the statement “Why does the melting point of hydrocarbons increase as the number of carbon atoms per molecule increases?”
Answer to Problem 1RAT
The correct option for the statement “Why does the melting point of hydrocarbons increase as the number of carbon atoms per molecule increases?” is option (b)
Explanation of Solution
Hydrocarbon-hydrocarbons are the organic compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. Carbon has unique property multiple bonding (alkane-single bonding,alkene-double bonding and alkyne-triple bonding) as well as long chain formation.
Induced dipole-induced dipole molecular attraction-this attraction is also known as London forces or dispersion forces.
To understand the origin of these forces, suppose carbon A and carbon B atoms are there and each are symmetrically distributed with electronic charge as we can see in the below diagram-

However, due to motion of electrons, suppose A becomes unsymmetrical (charge cloud is more in one side than the other. During this a very short period, unsymmetrical centres of positive charge and negative charge do not coincide. Thus, instantaneous distribution of electrons creates instantaneous dipole, this electron distribution distorts the adjacent atom B known as induced dipole, thus A and B attract each other.
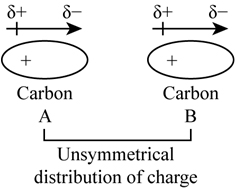
Thus, as the carbon atoms increases resulting in the great chances of distortion and producing great molecular attraction in the molecule. Therefore, the strength of Van der Waals forces increases with molecular size which increases the closer packing of the atoms and hence increase in melting point.
Due to Van der Waals force of attraction, Density of hydrocarbon also increases with increase in the number of carbon atom, which increases the melting point of hydrocarbon.
As the number of carbon atoms increases, mass of the molecule also increases resulting in the great Van der Waals forcesof attraction.
Branching of the molecule decreases the melting point as it decreases the attraction between the carbo atoms.
Conclusion:
Therefore,the correct option for the statement “Why does the melting point of hydrocarbons increase as the number of carbon atoms per molecule increases?” is option (b)
Chapter 22 Solutions
Conceptual Physical Science Explorations
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- 3arrow_forwardSet ба ||Axl 49.32 6b 71 Ay 22 Magnitude of A Angle of A 24.04 Angle of -A 22 54 155.96 ° (pos Ax) 204.04 ° (neg Ax) 335.96 ° (pos Ax) ° (neg Ax) 115.77 ° (pos Ax) 295.77 ° (pos Ax) -39 81 208.78 ° (neg Ax) 28.78 ° (neg Ax)arrow_forward3AA . not sure what i am getting wrongarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





