
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure and chemical shifts of all the protons of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
Double bond equivalent(DBE) can be calculated as follows:
Where,
- C is the number of Carbon.
- N is the number of nitrogen.
- H is the number of hydrogen.
- X is the number of halogen.
The DBE for the
DBE zero implies the absence of any double bond or a ring.
Total there are 2 types of hydrogen. 9 hydrogen are singlet indicate the presence of methyl group on carbon with no hydrogen adjacent to it for splitting, 2 hydrogen singlet indicate the presence of
The signals and chemical shift values are indicated as follows:
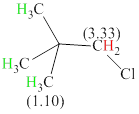
The compound is
The chemical shifts of green hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of red hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure and chemical shifts of all the protons of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
Double bond equivalent(DBE) can be calculated as follows:
Where,
- C is the number of Carbon.
- N is the number of nitrogen.
- H is the number of hydrogen.
- X is the number of halogen.
The DBE for the compound
DBE 1 implies the presence of any double bond or a ring. The presence of 2 oxygen implies either the compound is alcohol or carbonyl compound or both.
There are 3 types of hydrogen in total. 6 hydrogen are singlet indicate the presence of methyl group on a carbon with no hydrogen adjacent to it for splitting, 1 hydrogen singlet indicate the presence of
The signals and chemical shift values are indicated as follows:
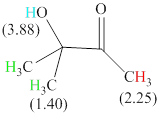
The compound is
The chemical shifts of green hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of red hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure and chemical shifts of all the protons of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
Double bond equivalent(DBE) can be calculated as follows:
Where,
- C is the number of Carbon.
- N is the number of nitrogen.
- H is the number of hydrogen.
- X is the number of halogen.
The DBE for the compound
DBE 1 implies the presence of one double bond or a ring. The presence of 2 oxygen implies either the compound is alcohol or carbonyl compound or both.
There are 4 types of hydrogen in total. 6 hydrogen are singlet indicate the presence of methyl group on a carbon with no hydrogen adjacent to it for splitting, 1 hydrogen singlet indicate the presence of
The signals and chemical shift values are indicated as follows:
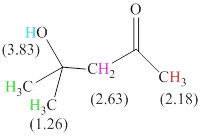
The chemical shifts of green hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of red hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of pink hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure and chemical shifts of all the protons of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
Double bond equivalent(DBE) can be calculated as follows:
Where,
- C is the number of Carbon.
- N is the number of nitrogen.
- H is the number of hydrogen.
- X is the number of halogen.
The DBE for the compound
DBE 1implies the presence of one double bond or a ring. The presence of 1 oxygen implies either the compound is alcohol or carbonyl compound.
Total there are 4 types of hydrogen. 1 hydrogen as multiplet indicates the presence of
The signals and chemical shift values are indicated as follows:
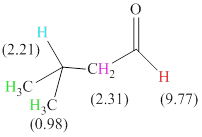
The chemical shifts of green hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of blue hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of pink hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure and chemical shifts of all the protons of
Concept introduction:
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is applied for the identification of the structure of molecules. The energy in the radiofrequency region is suitable for NMR. Nuclear magnetic resonance results from the spin of the nucleus of an atom. The value of I is obtained using the atomic number and the mass number of an atom. The non-zero magnetic moment of an isotopic nucleus is detectable by the NMR technique.
Any nucleus with both an even atomic number and the mass number has 0 nuclear spins. There are a total of
However, energy levels become non-degenerate in the presence of a magnetic field.
Deuterated chloroform
The total signal intensity of each set of proton is given by the height of each set of steps. The integration value defines the relative number of each kind of proton in the molecule.
In NMR spectrum, the intensity of signals is plotted against the magnetic field or frequency. Nuclei that are non-equivalent show only one peak in the NMR spectrum. However, protons absorb at different frequencies that are non-equivalent.
An increase in the electron density that surrounds the nucleus shields it from the applied field. This results in a net decrease in the field experienced by the nucleus. The value of the observed chemical shift of the signal therefore decreases, and, on a typical NMR spectrum, the signal moves to the right, which is called an upfield shift because, at a constant frequency, a slightly higher applied magnetic field is required for resonance to occur. De-shielding is the effect of a decline in the electron density around a nucleus which leads to shifting in the peaks of a chemical shift towards left in the NMR spectrum that results in an increase in delta values, hence downshift.
Explanation of Solution
Double bond equivalent(DBE) can be calculated as follows:
Where,
- C is the number of Carbon.
- N is the number of nitrogen.
- H is the number of hydrogen.
- X is the number of halogen.
The DBE for the compound
DBE 1 implies the presence of one double bond or a ring. The presence of 1 oxygen implies either the compound is alcohol or carbonyl compound.
Total there are 6 types of hydrogen and 3 hydrogen atoms are vinyl hydrogens per their chemical shift values.
The signals and chemical shift values are indicated as follows:
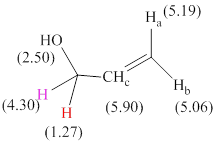
The chemical shifts of red hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of pink hydrogen atoms can be estimated as follows:
The chemical shifts of
The chemical shifts of
The chemical shifts of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES IN ORGANIC CHEMIS
- How many chiral centers are there in the following molecule? HO 0 1 ○ 2 ♡ 4 'N'arrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

