
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.2, Problem 1FP
When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC, point B displaces vertically downward through a distance of 0.2 mm. Determine the normal strain in wire CD.
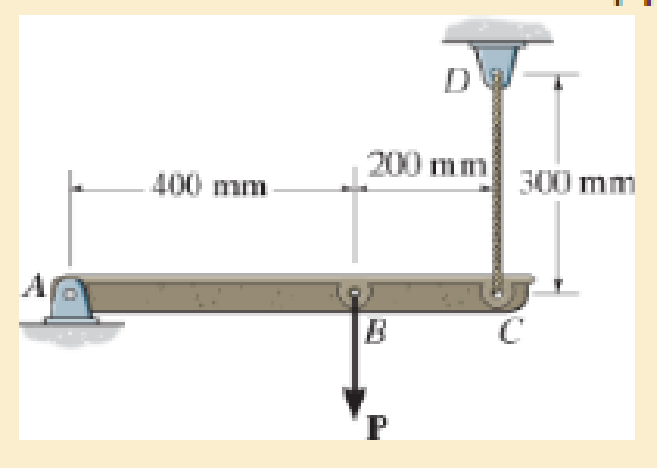
F2–1
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:27
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a
mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and
(y2), respectively.
Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s].
Givens:
y1 = 4.112 m
y2 =
0.387 m
b = 0.942 m
Answers:
( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s
( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s
( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s
( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/s
Problem (14): A pump is being used to lift water from an underground
tank through a pipe of diameter (d) at discharge (Q). The total head
loss until the pump entrance can be calculated as (h₁ = K[V²/2g]), h
where (V) is the flow velocity in the pipe. The elevation difference
between the pump and tank surface is (h).
Given the values of h [cm], d [cm], and K [-], calculate the maximum
discharge Q [Lit/s] beyond which cavitation would take place at the
pump entrance. Assume Turbulent flow conditions.
Givens:
h = 120.31 cm
d = 14.455 cm
K = 8.976
Q
Answers:
(1) 94.917 lit/s
(2) 49.048 lit/s
( 3 ) 80.722 lit/s
68.588 lit/s
4
Problem (13): A pump is being used to lift water from the bottom
tank to the top tank in a galvanized iron pipe at a discharge (Q).
The length and diameter of the pipe section from the bottom tank
to the pump are (L₁) and (d₁), respectively. The length and
diameter of the pipe section from the pump to the top tank are
(L2) and (d2), respectively.
Given the values of Q [L/s], L₁ [m], d₁ [m], L₂ [m], d₂ [m],
calculate total head loss due to friction (i.e., major loss) in the
pipe (hmajor-loss) in [cm].
Givens:
L₁,d₁
Pump
L₂,d2
오
0.533 lit/s
L1 =
6920.729 m
d1 =
1.065 m
L2 =
70.946 m
d2
0.072 m
Answers:
(1)
3.069 cm
(2) 3.914 cm
( 3 ) 2.519 cm
( 4 ) 1.855 cm
TABLE 8.1
Equivalent Roughness for New Pipes
Pipe
Riveted steel
Concrete
Wood stave
Cast iron
Galvanized iron
Equivalent Roughness, &
Feet
Millimeters
0.003-0.03 0.9-9.0
0.001-0.01 0.3-3.0
0.0006-0.003 0.18-0.9
0.00085
0.26
0.0005
0.15
0.045
0.000005
0.0015
0.0 (smooth) 0.0 (smooth)
Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.00015
Drawn…
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 2.2 - When force P is applied to the rigid arm ABC,...Ch. 2.2 - If the force P causes the rigid arm ABC to rotate...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The square plate is deformed into the shape shown...Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2.2 - The square deforms into the position shown by the...Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 2.2 - Prob. 13PCh. 2.2 - Part of a control linkage for an airplane consists...
Ch. 2.2 - Prob. 16PCh. 2.2 - A thin wire, lying along the x axis, is strained...Ch. 2.2 - The corners of the square plate are given the...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its...Ch. 2.2 - The polysulfone block is glued at its top and...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The rectangular plate is deformed into the shape...Ch. 2.2 - The nonuniform loading causes a normal strain in...Ch. 2.2 - The fiber AB has a length L and orientation . If...Ch. 2.2 - If the normal strain is defined in reference to...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Mobile Service Provider A mobile phone service provider has three different subscription packages for its custo...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
When displaying a Java applet, the browser invokes the _____ to interpret the bytecode into the appropriate mac...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Big data Big data describes datasets with huge volumes that are beyond the ability of typical database manageme...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Design a nested loop that displays 10 rows of # characters. There should be 15 # characters in each row.
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
ICA 17-24
The decay of a radioactive isotope can be theoretically modeled with the following equation, where C0...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Do Practice Program 5 from Chapter 5 but add a constructor that allows the user to initialize the name and alco...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (20): Given the value of APm/Lm [kPa/m], and assuming pressure coefficient similitude, calculate the drop in the pressure per unit length of the water main (APP/Lp) in [Pa/m]. Givens: AP M/L m = 590.637 kPa/m meen Answers: ( 1 ) 59.369 Pa/m ( 2 ) 73.83 Pa/m (3) 95.443 Pa/m ( 4 ) 44.444 Pa/m *******arrow_forwardFind the reaction force in y if Ain = 0.169 m^2, Aout = 0.143 m^2, p_in = 0.552 atm, Q = 0.367 m^3/s, α = 31.72 degrees. The pipe is flat on the ground so do not factor in weight of the pipe and fluid.arrow_forward
- Find the reaction force in x if Ain = 0.301 m^2, Aout = 0.177 m^2, p_in = 1.338 atm, Q = 0.669 m^3/s, and α = 37.183 degreesarrow_forwardProblem 5: Three-Force Equilibrium A structural connection at point O is in equilibrium under the action of three forces. • • . Member A applies a force of 9 kN vertically upward along the y-axis. Member B applies an unknown force F at the angle shown. Member C applies an unknown force T along its length at an angle shown. Determine the magnitudes of forces F and T required for equilibrium, assuming 0 = 90° y 9 kN Aarrow_forwardProblem 19: Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression. 4 ft K J I H G B C D E F -3 ft -3 ft 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft- 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lbarrow_forward
- Problem 14: Determine the reactions at the pin A, and the tension in cord. Neglect the thickness of the beam. F1=26kN F2 13 12 80° -2m 3marrow_forwardProblem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forwardProblem 20: Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG. After the truss is sectioned use a single equation of equilibrium for the calculation of each force. State if the members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B D E F 3 m -5 m- -5 m- 5 m 5 m-arrow_forward
- An experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (19): Given the value of Qp [m³/s], and assuming Reynolds number similitude between the water main and experimental tube, calculate the flow rate in the model tube (Qm) in [lit/s]. = 30.015 m^3/sarrow_forwardProblem 11: The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by the six cords connected together as shown. Determine the tension in each cord and the angle 0 for equilibrium. Cord BC is horizontal. E 30° B 60° Aarrow_forwardProblem 10: If the bucket weighs 50 lb, determine the tension developed in each of the wires. B $30° 5 E D 130°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY